Utopia represents an ideal society where harmony, equality, and prosperity prevail, inspiring generations to imagine a better world. Exploring the principles and visions behind utopian concepts can reveal valuable insights into human values and aspirations. Discover how these timeless ideas might influence Your perspective on society by reading the rest of the article.
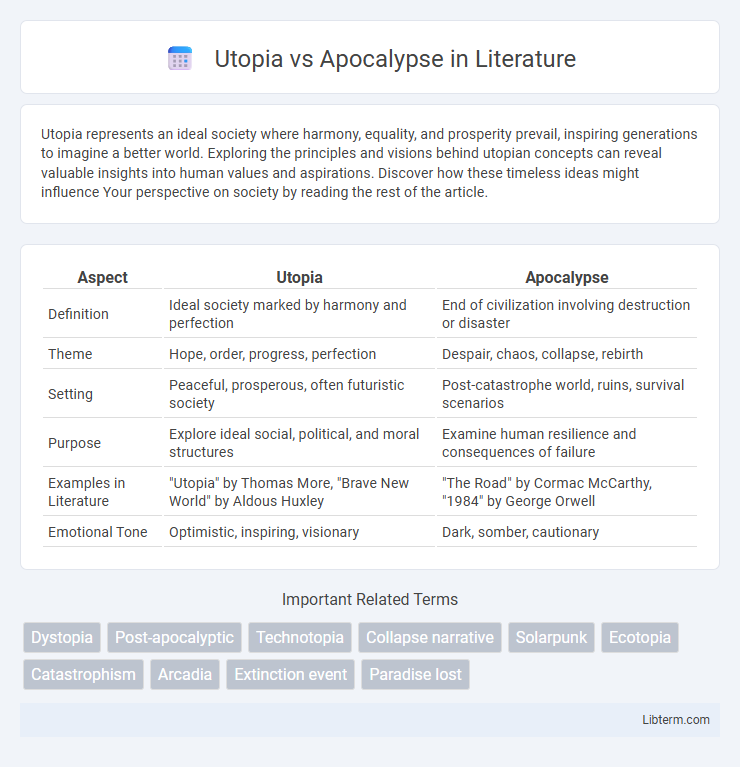
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Utopia | Apocalypse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ideal society marked by harmony and perfection | End of civilization involving destruction or disaster |
| Theme | Hope, order, progress, perfection | Despair, chaos, collapse, rebirth |
| Setting | Peaceful, prosperous, often futuristic society | Post-catastrophe world, ruins, survival scenarios |
| Purpose | Explore ideal social, political, and moral structures | Examine human resilience and consequences of failure |
| Examples in Literature | "Utopia" by Thomas More, "Brave New World" by Aldous Huxley | "The Road" by Cormac McCarthy, "1984" by George Orwell |
| Emotional Tone | Optimistic, inspiring, visionary | Dark, somber, cautionary |
Defining Utopia: Ideal Societies Explored
Utopia represents an ideal society characterized by perfect social, political, and economic systems that promote harmony, equality, and prosperity for all inhabitants. Key features often include equitable resource distribution, universal access to education and healthcare, and sustainable environmental practices that ensure long-term well-being. Philosophers and writers like Thomas More and Plato have explored these concepts, envisioning societies where justice and happiness prevail without conflict or suffering.
Understanding Apocalypse: Visions of Collapse
Apocalypse embodies visions of societal collapse characterized by widespread destruction, chaos, and the breakdown of social order. These narratives often explore themes of environmental disaster, nuclear war, pandemics, or technological failure, reflecting collective anxieties about humanity's future. Understanding apocalypse through literature and media reveals cultural fears and prompts critical reflection on current global challenges and resilience strategies.
Historical Perspectives on Utopia and Apocalypse
Historical perspectives on utopia and apocalypse often reflect societies' responses to cultural, political, and existential challenges. Utopian visions have historically embodied ideals of perfect social order, seen in works like Thomas More's "Utopia" (1516) that imagined equitable communities transcending contemporary flaws. Conversely, apocalyptic narratives, rooted in religious and philosophical traditions such as the Book of Revelation, symbolize cataclysmic endings and transformations, shaping collective fears and hopes about the future throughout history.
Utopian Dreams in Literature and Culture
Utopian dreams in literature and culture often envision idealized societies marked by harmony, equality, and advanced technology, reflecting humanity's aspiration for a perfect world. Classic works such as Thomas More's *Utopia* and Ursula K. Le Guin's *The Dispossessed* explore socio-political reforms and ethical ideals through imaginative narratives that inspire real-world discussions on justice and governance. These visionary texts fuel cultural dialogues about progress, human rights, and the possibility of achieving collective well-being beyond dystopian fears.
Apocalyptic Narratives: Warnings and Lessons
Apocalyptic narratives serve as critical warnings about the consequences of environmental neglect, technological overreach, and social decay, often illustrating the collapse of civilization due to unchecked human behaviors. These stories highlight the importance of sustainability, ethical governance, and community resilience to prevent catastrophic outcomes. By exploring possible futures dominated by chaos and destruction, apocalyptic tales encourage proactive reflection and policy changes to mitigate existential risks.
Social Implications: Hope vs. Fear
Utopian visions inspire collective hope by promoting social harmony, equality, and sustainable progress, encouraging communities to envision a better future. Apocalyptic scenarios evoke fear-driven responses, triggering social fragmentation and defensive behaviors as societies anticipate collapse and chaos. The contrast between hope and fear fundamentally shapes public attitudes toward governance, innovation, and social cohesion.
Technological Advances: Pathway to Utopia or Apocalypse?
Technological advances shape the trajectory toward either utopia or apocalypse, with innovations in AI, biotechnology, and renewable energy offering unprecedented potential for societal improvement or catastrophic risks. Efficient automation and smart infrastructure can elevate quality of life, reduce poverty, and combat climate change, forming a pathway to utopia. Conversely, unchecked AI development, cyber warfare, and environmental degradation pose apocalyptic dangers that threaten global stability and human survival.
Environmental Change: Green Utopia or Ecological Doom
Green Utopia envisions a future where sustainable technologies and renewable energy restore ecological balance, promoting biodiversity and clean air. In contrast, Ecological Doom depicts catastrophic environmental degradation caused by unchecked pollution, deforestation, and climate change. The contrasting scenarios emphasize the critical impact of human actions on planetary health and the urgency of environmental stewardship.
Political Systems and Their Roles in Shaping Futures
Utopian political systems often emphasize equality, cooperation, and democratic governance to create ideal societies where citizens actively participate in decision-making processes. In contrast, apocalyptic political frameworks tend to arise in response to chaos, favoring authoritarian control or militarized rule to maintain order amid societal collapse. The role of these political systems in shaping futures lies in their ability to either foster sustainable development and social harmony or enforce survival through strict hierarchy and power consolidation.
Conclusion: Navigating Between Utopia and Apocalypse
Navigating between utopia and apocalypse requires balancing idealistic aspirations with pragmatic risk management to foster sustainable progress. Emphasizing technologies like renewable energy and artificial intelligence while addressing social inequalities mitigates potential dystopian outcomes. Strategic policymaking and global cooperation remain essential to transform visionary futures into achievable realities.
Utopia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com