Motifs are recurring elements or themes that enhance the meaning of a story, artwork, or design by reinforcing key concepts and emotions. Recognizing motifs can deepen your understanding of the underlying messages and artistic intentions. Explore the rest of this article to discover how motifs shape narratives and creativity.
Table of Comparison
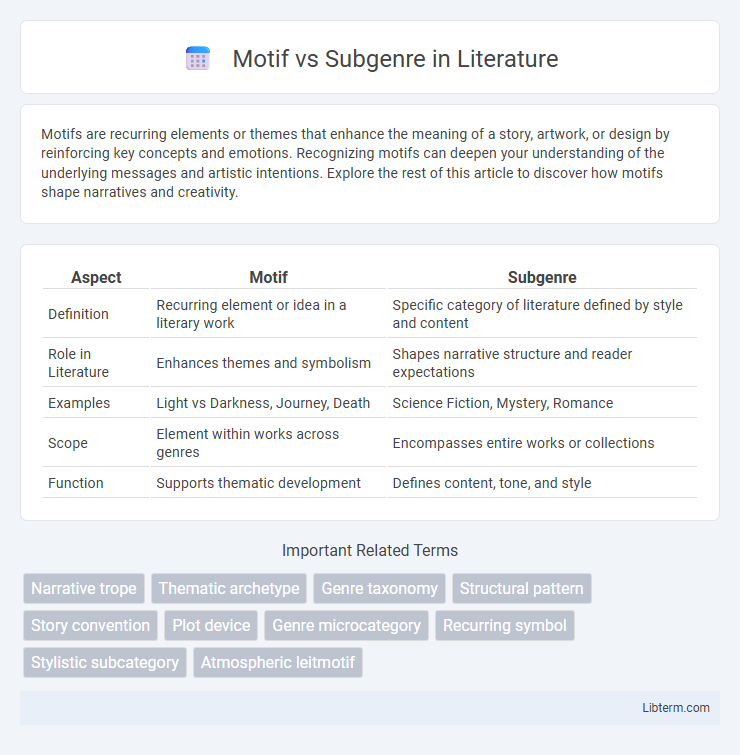
| Aspect | Motif | Subgenre |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recurring element or idea in a literary work | Specific category of literature defined by style and content |
| Role in Literature | Enhances themes and symbolism | Shapes narrative structure and reader expectations |
| Examples | Light vs Darkness, Journey, Death | Science Fiction, Mystery, Romance |
| Scope | Element within works across genres | Encompasses entire works or collections |
| Function | Supports thematic development | Defines content, tone, and style |
Introduction to Motif and Subgenre
Motif refers to a recurring element, symbol, or theme within a literary work that helps convey deeper meaning or reinforce the narrative's central ideas. Subgenre classifies a distinct category within a broader genre, characterized by specific conventions, settings, or styles, such as psychological thriller in the crime genre. Understanding motifs provides insight into thematic patterns, while identifying subgenres aids in categorizing and analyzing literature according to shared structural traits.
Defining Literary Motifs
Literary motifs are recurring elements, such as symbols, themes, or images, that reinforce the underlying message or mood within a narrative. Unlike subgenres, which categorize works based on shared thematic or stylistic characteristics, motifs function at a micro-level to enhance the depth and cohesion of the story. Examples of motifs include darkness symbolizing evil or water representing purification, which subtly guide readers' interpretations.
What is a Subgenre?
A subgenre is a specialized category within a broader genre, defined by distinct thematic elements, settings, or styles that differentiate it from the main genre. It allows for more precise classification of works, helping audiences find specific types of content, such as cyberpunk within science fiction or dark fantasy within fantasy. Subgenres combine unique narrative conventions and artistic techniques to create a niche experience while remaining linked to the overarching genre framework.
Key Differences Between Motif and Subgenre
Motifs are recurring thematic elements or symbols that convey deeper meanings within a narrative, while subgenres categorize stories based on specific thematic or stylistic features within a broader genre. Motifs function as building blocks that enhance the story's themes, whereas subgenres define the overall tone, setting, and conventions of a group of works. Understanding motifs involves analyzing repeated patterns or symbols, whereas recognizing subgenres requires identifying distinct narrative frameworks such as cyberpunk or romantic comedy.
Common Examples of Motifs in Literature
Motifs in literature are recurring elements, such as symbols, themes, or ideas, that reinforce the narrative's deeper meanings, differing from subgenres which categorize works by style or content. Common examples of motifs include darkness symbolizing evil, water representing purification or rebirth, and journeys reflecting personal growth or transformation. These motifs enhance readers' understanding by weaving consistent thematic threads throughout diverse literary works, enriching the overall storytelling experience.
Popular Subgenres Across Media
Popular subgenres across media include cyberpunk, romance, and horror, each defined by specific themes and settings appealing to distinct audiences. Motifs such as dark technology, forbidden love, or supernatural elements recur within these subgenres, enhancing narrative depth and emotional resonance. Understanding the difference between motifs and subgenres helps creators and consumers identify both the broader category and the recurring symbolic elements in storytelling.
How Motifs Influence Subgenres
Motifs serve as recurring thematic elements that shape and define subgenres by providing distinctive narrative or stylistic markers, such as the use of darkness and decay motifs in Gothic literature that establish its eerie atmosphere. These motifs influence subgenres by reinforcing specific emotional tones and cultural motifs, for example, the hero's journey motif prevalent in fantasy subgenres that drives character development and plot progression. The interplay between motifs and subgenres creates a framework that guides audience expectations and deepens genre categorization.
Recognizing Motifs Within Subgenres
Motifs are recurring thematic elements or symbols prevalent within specific subgenres, serving as recognizable markers that enhance narrative depth and audience engagement. Identifying motifs such as the "haunted house" in gothic horror or "mentor figure" in coming-of-age stories provides critical insights into the subgenre's underlying themes and conventions. Understanding these motifs enables a clearer distinction between closely related subgenres by highlighting unique emotional tones and story mechanics.
The Role of Motif and Subgenre in Storytelling
Motifs serve as recurring elements that reinforce themes and evoke emotions throughout a narrative, while subgenres categorize stories by specific stylistic and thematic conventions, guiding audience expectations. The use of motifs deepens character development and thematic resonance, whereas subgenres provide a framework that shapes plot structure and setting. Together, motifs and subgenres enhance storytelling by creating layers of meaning and aligning narrative elements with audience preferences.
Conclusion: Motif vs Subgenre in Creative Writing
Motifs are recurring elements that reinforce themes and deepen narrative meaning, while subgenres categorize stories by specific conventions and styles within a broader genre. Understanding the distinction enhances creative writing by allowing authors to weave motifs that enrich the narrative while adhering to subgenre expectations to meet audience preferences. Mastery of both concepts leads to more nuanced storytelling and targeted reader engagement.
Motif Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com