A metaphor transforms ordinary language into vivid imagery by directly comparing two unrelated things, enriching your communication with depth and creativity. This powerful literary device enhances understanding and evokes emotions, making abstract concepts more tangible and memorable. Explore the rest of the article to discover how metaphors can elevate your writing and speech.
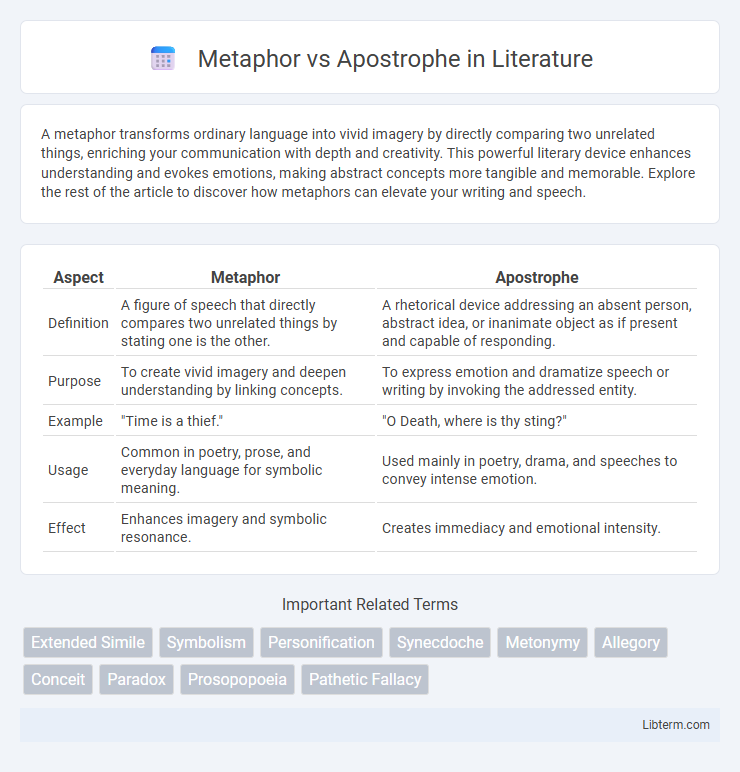
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Metaphor | Apostrophe |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A figure of speech that directly compares two unrelated things by stating one is the other. | A rhetorical device addressing an absent person, abstract idea, or inanimate object as if present and capable of responding. |
| Purpose | To create vivid imagery and deepen understanding by linking concepts. | To express emotion and dramatize speech or writing by invoking the addressed entity. |
| Example | "Time is a thief." | "O Death, where is thy sting?" |
| Usage | Common in poetry, prose, and everyday language for symbolic meaning. | Used mainly in poetry, drama, and speeches to convey intense emotion. |
| Effect | Enhances imagery and symbolic resonance. | Creates immediacy and emotional intensity. |
Defining Metaphor: A Core Figurative Device
Metaphor is a fundamental figurative device that directly compares two unrelated concepts to highlight shared characteristics, enriching meaning and enhancing imagery. It operates by stating one thing is another, such as "Time is a thief," to evoke vivid associations and deepen understanding. Apostrophe, by contrast, involves addressing an absent or abstract entity, distinguishing it from metaphor's comparative nature.
Understanding Apostrophe in Literature
Apostrophe in literature is a rhetorical device where the speaker directly addresses an absent person, abstract idea, or inanimate object, creating an emotional or dramatic effect. Unlike metaphors, which draw implicit comparisons between two unrelated things, apostrophes break the narrative flow to engage with entities beyond the immediate scene, often evoking deeper reflection or heightened emotion. This technique is prevalent in poetry and plays, enhancing the expressiveness and intensity of the text.
Key Differences Between Metaphor and Apostrophe
Metaphor is a figure of speech that directly compares two unrelated objects or concepts by stating one is the other, enhancing imagery and understanding in literature. Apostrophe, on the other hand, involves addressing an absent, imaginary, or inanimate entity as if it were present and capable of responding, often used to express intense emotion or create dramatic emphasis. While metaphor creates symbolism through comparison, apostrophe establishes a direct, emotional appeal to a non-human or absent subject.
The Purpose of Metaphor in Creative Writing
Metaphors enhance creative writing by creating vivid imagery and connecting abstract concepts with concrete experiences, allowing readers to grasp complex emotions or ideas intuitively. They serve to deepen understanding, evoke sensory responses, and add layers of meaning, enriching the reader's engagement with the text. Unlike apostrophes, which address absent or imaginary entities directly, metaphors function by comparison, embedding symbolic significance within the narrative.
Apostrophe: Direct Address for Dramatic Effect
Apostrophe is a literary device where the speaker directly addresses an absent person, abstract idea, or inanimate object, creating a heightened sense of drama and emotional intensity. Unlike metaphor, which compares two unrelated things for symbolic meaning, apostrophe breaks the narrative flow by engaging an external entity, often evoking a vivid emotional response from the audience. This direct address serves to emphasize the speaker's feelings and can reveal inner conflicts or highlight particular themes in poetry and prose.
Semantic Analysis: How Metaphor Conveys Meaning
Metaphors convey meaning by mapping characteristics from a source domain onto a target concept, enabling deeper cognitive connections and abstract understanding through semantic resonance. Semantic analysis reveals how metaphors compress complex ideas into familiar imagery, enriching interpretation by activating associative networks in the mind. Unlike apostrophes, which directly address absent or imaginary entities, metaphors function through implicit relational structures that shape conceptual frameworks and influence perception.
Apostrophe’s Emotional Impact on Readers
Apostrophe directly addresses an absent or abstract entity, creating an intense emotional connection by invoking feelings of longing, urgency, or reverence. This literary device transforms abstract ideas or inanimate objects into active participants, heightening the reader's sense of intimacy and engagement. Unlike metaphor, which relies on comparison, apostrophe's direct invocation elicits a powerful emotional response that deepens narrative resonance.
Examples of Metaphor vs Apostrophe in Classic Literature
Metaphor and apostrophe serve distinct rhetorical purposes in classic literature, with metaphors creating vivid imagery by directly comparing unrelated concepts, such as Shakespeare's description of life as "a walking shadow" in *Macbeth*. Apostrophe involves addressing an absent or abstract entity directly, exemplified by John Donne's invocation of Death in "Death, be not proud." These devices enrich literary texts by engaging readers' imagination and emotion through symbolic and direct addresses.
When to Use Metaphor Versus Apostrophe
Metaphors are used when illustrating abstract ideas or emotions through symbolic comparisons, enhancing vivid imagery and deeper understanding. Apostrophes are employed when addressing an absent person, personified object, or abstract concept directly, creating emotional intensity or emphasizing significance. Choose metaphor to convey complex meanings subtly, while apostrophe suits moments requiring direct engagement or dramatic effect.
Tips for Incorporating Metaphor and Apostrophe Effectively
Incorporate metaphor by choosing vivid, relatable comparisons that resonate with the audience's experiences and deepen understanding of abstract concepts. Use apostrophe to create emotional intensity by directly addressing absent or abstract entities, which can personalize themes and evoke empathy. Balance clarity and creativity by ensuring metaphors illuminate meaning clearly, while apostrophes punctuate emotional moments without confusing the reader.
Metaphor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com