Personification is a literary device that gives human characteristics to non-human objects, animals, or ideas, making descriptions more vivid and relatable. This technique enhances storytelling by allowing readers to connect emotionally with the narrative through imaginative imagery. Explore the rest of the article to discover how personification can enrich your writing and captivate your audience.
Table of Comparison
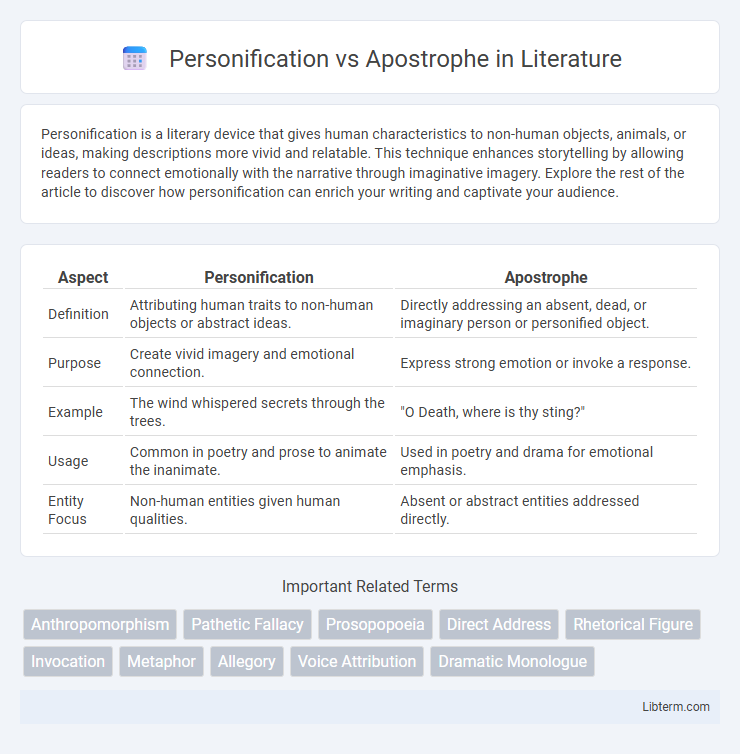
| Aspect | Personification | Apostrophe |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Attributing human traits to non-human objects or abstract ideas. | Directly addressing an absent, dead, or imaginary person or personified object. |
| Purpose | Create vivid imagery and emotional connection. | Express strong emotion or invoke a response. |
| Example | The wind whispered secrets through the trees. | "O Death, where is thy sting?" |
| Usage | Common in poetry and prose to animate the inanimate. | Used in poetry and drama for emotional emphasis. |
| Entity Focus | Non-human entities given human qualities. | Absent or abstract entities addressed directly. |
Introduction to Figurative Language
Personification and apostrophe are key devices in figurative language that enhance expression by attributing human qualities and direct address to non-human entities. Personification gives life-like traits to objects or ideas, making descriptions vivid and relatable, whereas apostrophe involves speaking directly to an absent or abstract entity as if it were present. Both techniques enrich literary texts by deepening emotional resonance and creating imaginative connections for readers.
Defining Personification
Personification is a literary device that attributes human qualities, emotions, or actions to non-human entities such as animals, objects, or ideas, enhancing vivid imagery and emotional connection in writing. It differs from apostrophe, which involves directly addressing an absent, imaginary, or non-human entity as if it were present and capable of response. Understanding personification helps in identifying how writers imbue lifeless elements with human traits to evoke empathy and deepen meaning.
Understanding Apostrophe in Literature
Apostrophe in literature involves directly addressing an absent person, an abstract idea, or a non-human entity as if it were present and capable of response. Unlike personification, which attributes human traits to non-human things, apostrophe engages the audience by creating a dramatic or emotional dialogue with the addressed figure. This rhetorical device enhances the expressive depth of poetry and prose by giving voice to concepts like death, time, or love.
Key Differences Between Personification and Apostrophe
Personification attributes human characteristics to non-human entities, enhancing imagery by making objects or ideas relatable and vivid in literature. Apostrophe involves directly addressing an absent, dead, or imaginary person, or a personified abstraction, creating a dramatic or emotional effect. The key difference lies in personification's descriptive role versus apostrophe's function as a direct vocal or written address.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Personification originated in ancient Greek and Roman literature as a technique to give human traits to abstract concepts, enhancing storytelling and moral lessons. Apostrophe evolved during the classical and Renaissance periods as a rhetorical device where speakers directly address absent or imaginary entities, intensifying emotional expression in poetry and drama. Both techniques reflect shifts in literary style and cultural contexts, shaping the development of figurative language through centuries.
Common Examples of Personification
Personification attributes human traits to animals, objects, or ideas, commonly seen in examples like "the wind whispered through the trees" or "time marches on." This literary device animates inanimate elements to create vivid imagery and emotional connections. Apostrophe differs by directly addressing an absent or abstract entity, such as speaking to "O Death" or "Twilight," which is not present.
Popular Uses of Apostrophe in Poetry
Apostrophe in poetry often involves addressing an absent person, abstract idea, or inanimate object directly, creating an emotional connection and intensifying the poem's impact. This device frequently appears in classical and Romantic poetry, where poets speak to concepts like death, love, or nature as if they were present interlocutors. Unlike personification, which attributes human traits to non-human entities, apostrophe is characterized by the direct invocation or dramatic emphasis on the addressed subject, enhancing the poem's expressive depth.
Impact on Reader Engagement
Personification enhances reader engagement by attributing human traits to non-human entities, creating relatable and vivid imagery that stimulates emotional response. Apostrophe directly addresses an absent or abstract entity, establishing an intimate and evocative connection that draws readers deeper into the narrative. Both techniques intensify involvement, but apostrophe's direct appeal often generates a more immediate and personal engagement.
When to Use Each Figure of Speech
Personification is used when attributing human qualities to inanimate objects or abstract concepts to evoke vivid imagery and emotional connection. Apostrophe is employed when directly addressing an absent person, abstract idea, or inanimate object as if it were present, creating a dramatic or emotional effect. Use personification to animate non-human elements in descriptive writing, while apostrophe is ideal for lyrical or persuasive contexts involving direct address.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Literary Device
Selecting between personification and apostrophe hinges on the desired impact: personification animates abstract concepts or inanimate objects by attributing human traits, enhancing imagery and emotional resonance. Apostrophe directly addresses an absent or nonhuman entity, creating intimacy or urgency that draws the reader into a personal dialogue. Understanding the specific narrative or poetic purpose ensures the effective use of these literary devices to enrich textual meaning and reader engagement.
Personification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com