Self-awareness plays a crucial role in personal growth by helping you understand your emotions, strengths, and weaknesses. Developing a strong sense of self enables better decision-making and enhances relationships with others. Discover more insights on how self-awareness can transform your life in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
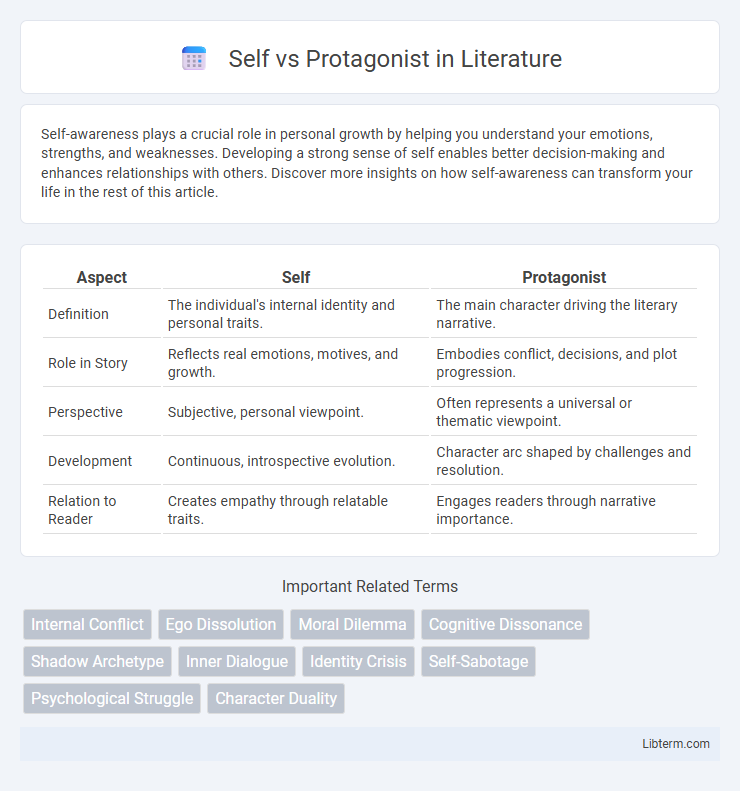
| Aspect | Self | Protagonist |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The individual's internal identity and personal traits. | The main character driving the literary narrative. |
| Role in Story | Reflects real emotions, motives, and growth. | Embodies conflict, decisions, and plot progression. |
| Perspective | Subjective, personal viewpoint. | Often represents a universal or thematic viewpoint. |
| Development | Continuous, introspective evolution. | Character arc shaped by challenges and resolution. |
| Relation to Reader | Creates empathy through relatable traits. | Engages readers through narrative importance. |
Understanding the Concept: Self vs Protagonist
The concept of Self vs Protagonist explores the distinction between an individual's true identity and their role within a narrative framework. Understanding this dynamic reveals how internal motivations, beliefs, and personal growth shape the protagonist's actions and decisions in a story. Examining the Self versus the Protagonist highlights the tension between authentic self-expression and the demands of the plot or external conflicts.
Defining "Self" in Narrative Context
The "Self" in a narrative context represents the internal identity and subjective experience of a character, encompassing their thoughts, emotions, and personal growth throughout the story. Unlike the protagonist, who serves as the primary driver of plot and external action, the self reveals psychological depth and internal conflicts that shape motivations and decisions. Understanding the self allows for a richer interpretation of character development and narrative meaning beyond mere plot progression.
Who is the Protagonist? Key Characteristics
The protagonist is the central character driving the narrative's conflict and resolution, often embodying the story's primary goals and challenges. Key characteristics include a clear motivation, relatability, and growth arc that elicit audience empathy and engagement. Unlike the self, which represents personal identity and internal reflection, the protagonist functions as the external actor whose decisions and actions shape the plot.
The Relationship Between Self and Protagonist
The relationship between self and protagonist is a dynamic interplay where the protagonist often embodies facets of the self, serving as a mirror to personal identity and inner conflict. This connection fosters empathy and introspection, allowing readers to explore their own emotions and motivations through the protagonist's journey. Understanding this relationship enhances narrative engagement by linking character development with the reader's self-perception.
Psychological Perspectives: Navigating Identity
The psychological exploration of self versus protagonist centers on how individuals construct and perceive their identities through internal dialogue and narrative frameworks. Cognitive theories emphasize the role of self-schema in shaping the protagonist's choices and motivations, highlighting the dynamic interplay between personal experience and storytelling. Understanding this relationship offers valuable insights into identity formation, self-awareness, and the psychological processes that influence decision-making within narrative contexts.
Self-Projection in Storytelling
Self-projection in storytelling occurs when creators infuse their personal experiences, emotions, or identity into the protagonist, blurring the line between self and character. This technique enhances authenticity and emotional depth, allowing audiences to connect more intimately with the narrative. Analyzing self-projection reveals how authors navigate identity and empathy through the protagonist's journey.
When the Self Becomes the Protagonist
When the Self becomes the Protagonist, the narrative shifts from external conflict to internal exploration, emphasizing personal growth and self-awareness. This transformation highlights the psychological complexity of characters, where their motivations and emotions drive the story. Such introspective storytelling invites readers to engage deeply with themes of identity, consciousness, and human experience.
External Conflicts: Protagonist Beyond the Self
External conflicts highlight the protagonist's struggle against forces beyond personal identity, such as societal expectations, antagonists, or natural obstacles. These conflicts drive the narrative by challenging the protagonist to confront external pressures while growing beyond internal limitations. The interaction between external challenges and the protagonist's goals intensifies character development and plot progression.
Literary Examples of Self vs Protagonist
The conflict between self and protagonist is evident in Shakespeare's "Hamlet," where Hamlet grapples with internal doubts and moral dilemmas that challenge his identity and actions. In Charlotte Perkins Gilman's "The Yellow Wallpaper," the protagonist's battle with her own mental illness highlights the struggle between self-perception and societal expectations. Similarly, in Franz Kafka's "The Metamorphosis," Gregor Samsa's transformation intensifies the divide between his self-identity and his roles as a son and worker, illustrating existential conflict within the protagonist.
Crafting Authentic Protagonists: Blending Self and Fiction
Crafting authentic protagonists involves blending elements of the author's self with fictional traits to create multidimensional characters that resonate with readers. By integrating personal experiences, emotions, and values, writers anchor their protagonists in reality while enhancing narrative depth through imaginative qualities. This fusion fosters empathy and relatability, transforming fictional narratives into immersive explorations of human identity.
Self Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com