An elegy is a melancholic poem or song expressing sorrow for the loss of someone or something, often reflecting on themes of mourning and remembrance. Rooted in ancient literary traditions, elegies combine personal emotion with universal reflections on mortality and grief. Discover how understanding elegies can deepen your appreciation of poetic expressions of loss in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
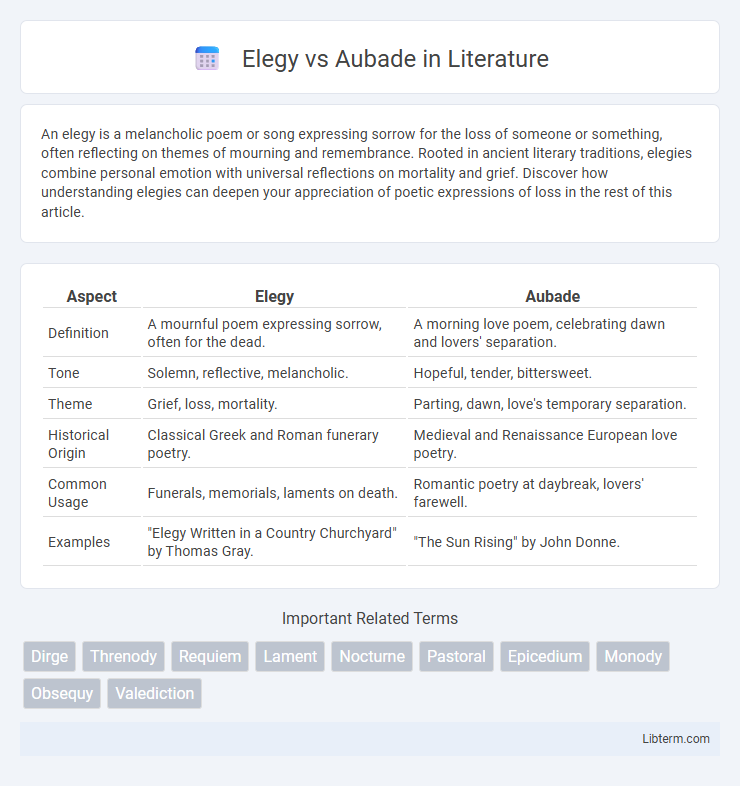
| Aspect | Elegy | Aubade |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A mournful poem expressing sorrow, often for the dead. | A morning love poem, celebrating dawn and lovers' separation. |
| Tone | Solemn, reflective, melancholic. | Hopeful, tender, bittersweet. |
| Theme | Grief, loss, mortality. | Parting, dawn, love's temporary separation. |
| Historical Origin | Classical Greek and Roman funerary poetry. | Medieval and Renaissance European love poetry. |
| Common Usage | Funerals, memorials, laments on death. | Romantic poetry at daybreak, lovers' farewell. |
| Examples | "Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard" by Thomas Gray. | "The Sun Rising" by John Donne. |
Introduction to Elegy and Aubade
An elegy is a mournful poem or song expressing sorrow for the deceased, often reflecting on loss and mortality. An aubade is a morning love song or poem celebrating lovers parting at dawn, symbolizing both intimacy and separation. Both genres explore deep emotional states but differ fundamentally in tone and thematic focus.
Defining Elegy: Themes and Purpose
Elegy is a poetic form centered on mourning and reflection, often addressing themes of loss, grief, and mortality. Its primary purpose is to honor the deceased and express sorrow, capturing the emotional depth of bereavement through contemplative language. Elegies typically navigate the tension between sorrow and acceptance, providing solace by memorializing loved ones and exploring the transient nature of life.
Defining Aubade: Themes and Purpose
An aubade is a dawn poem or song that traditionally explores themes of parting lovers resigned to separation at daybreak, often conveying a bittersweet or melancholic tone. Its purpose centers on capturing the emotional tension between intimacy and the inevitability of morning, highlighting themes of love, awakening, and transience. Unlike elegies, which mourn loss and death, aubades emphasize the dawn's arrival and the complex emotions it brings to lovers.
Historical Origins of the Elegy
The Elegy originated in ancient Greece as a form of lyrical poetry composed in elegiac couplets, traditionally used to express mourning and lamentation for the dead. Unlike the Aubade, which emerged in the medieval courtly love tradition as a morning song bidding farewell to a lover, the Elegy's roots lie in funerary customs and public commemorations. Over time, its themes expanded from strict mourning to include broader reflections on loss, mortality, and sorrow.
Historical Origins of the Aubade
The aubade originated in medieval Europe as a morning love song traditionally sung at dawn to lovers parting after a night together. It traces its roots to the troubadour and trouvere traditions of the 12th and 13th centuries, often contrasting with the elegy, which originated from ancient Greek poetry as a mournful or lamenting verse on death and loss. The aubade's historical function was to celebrate or lament the break of day and separation, emphasizing themes of love and longing within a structured lyrical form.
Structural Differences Between Elegy and Aubade
Elegies typically follow a mournful, reflective structure, often beginning with an expression of grief, progressing through lamentation, and concluding with consolation or acceptance. Aubades are structured around the progression of dawn, opening with themes of separation at night, moving through the arrival of morning light, and ending with expressions of hope or renewal. The tonal shift in elegies is somber and contemplative, while aubades emphasize transition and awakening, creating distinct narrative arcs within their poetic frameworks.
Emotional Tone: Mourning vs. Morning
Elegies convey a somber and reflective emotional tone centered on mourning, loss, and grief, often exploring themes of death and sadness. Aubades evoke a more hopeful and tender emotional tone associated with morning, renewal, and love, celebrating the transition from night to day. The contrast in emotional tone between elegy and aubade highlights the former's focus on sorrow and remembrance, while the latter emphasizes awakening and new beginnings.
Notable Examples in Literature
Notable examples of elegies include John Milton's "Lycidas," which mourns the death of a fellow poet, and W.H. Auden's "Funeral Blues," reflecting profound grief and loss. In contrast, famous aubades such as John Donne's "The Sun Rising" and Philip Larkin's "Aubade" explore themes of morning, separation, and existential reflections with a focus on dawn. These distinct poetic forms showcase different emotional landscapes, with elegies centered on mourning and aubades on the symbolism of daybreak.
Cultural Significance and Evolution
Elegies and aubades hold distinct cultural significance rooted in their thematic focus; elegies traditionally mourn loss and death, reflecting societies' processing of grief and remembrance, while aubades celebrate dawn and parting lovers, embodying themes of renewal and transient love. Over centuries, elegies evolved from classical laments to more personal and varied expressions of sorrow, influencing cultural rituals around mourning, whereas aubades transitioned from medieval courtly love poetry to broader interpretations of separation and new beginnings in modern literature. Both forms illustrate the evolving human relationship with time, emotion, and social customs through their respective poetic structures and symbolic meanings.
Choosing Between Elegy and Aubade in Creative Writing
Choosing between elegy and aubade in creative writing hinges on the poem's emotional tone and temporal focus; elegies center on mourning loss and reflecting on death, while aubades celebrate dawn and separation at daybreak. Writers seeking to explore themes of grief, remembrance, and mortality gravitate toward elegies, employing somber, contemplative language and imagery. In contrast, aubades suit narratives of love, longing, and renewal, capturing the intimate moment between night and morning with light, hopeful diction.
Elegy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com