Poetic language weaves emotions into vivid images, transforming ordinary moments into profound experiences. It captures the essence of human feelings through metaphor, rhythm, and sound, evoking deep connections in readers. Explore the rest of this article to discover how poetry enriches your inner world and enhances communication.
Table of Comparison
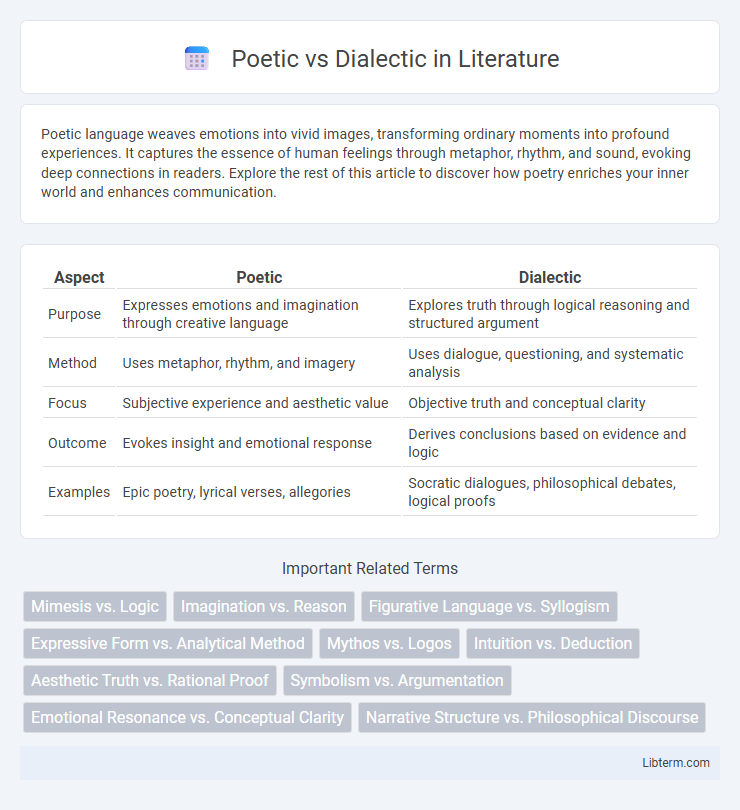
| Aspect | Poetic | Dialectic |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Expresses emotions and imagination through creative language | Explores truth through logical reasoning and structured argument |
| Method | Uses metaphor, rhythm, and imagery | Uses dialogue, questioning, and systematic analysis |
| Focus | Subjective experience and aesthetic value | Objective truth and conceptual clarity |
| Outcome | Evokes insight and emotional response | Derives conclusions based on evidence and logic |
| Examples | Epic poetry, lyrical verses, allegories | Socratic dialogues, philosophical debates, logical proofs |
Understanding Poetic and Dialectic Thought
Poetic thought emphasizes imagery, metaphor, and emotional resonance to convey meaning through creative expression, often capturing complex truths in symbolic or evocative forms. Dialectic thought relies on structured reasoning, logical argumentation, and critical analysis to explore contradictions and synthesize ideas, aiming for clarity and intellectual rigor. Understanding the contrast between poetic and dialectic modes highlights how different cognitive approaches process knowledge--poetic engaging intuition and feeling, dialectic emphasizing systematic inquiry and rational discourse.
Historical Roots of Poetic and Dialectic Traditions
The poetic tradition traces its historical roots to ancient oral cultures, where storytelling and myth-making shaped cultural identity and preserved collective memory through rhythm and metaphor. Dialectic, originating in classical Greek philosophy, particularly with Socratic dialogues, emphasizes structured argumentation and critical examination to reach truth and knowledge. Both traditions have profoundly influenced Western thought, with poetics fostering imaginative expression and dialectics advancing analytical reasoning.
Key Characteristics of Poetic Expression
Poetic expression emphasizes emotional resonance, vivid imagery, and rhythmic structures that evoke sensory experiences and provoke introspective reflection. It often employs metaphor, symbolism, and lyrical language to capture abstract concepts and transcend ordinary discourse. Unlike dialectic, which aims for logical argumentation and systematic inquiry, poetry prioritizes aesthetic beauty and the subtle nuances of human feeling.
Defining Features of Dialectic Reasoning
Dialectic reasoning is characterized by structured dialogue aimed at uncovering truth through logical argumentation and the systematic examination of opposing ideas. It involves a methodical approach to resolving contradictions by synthesizing diverse viewpoints into a coherent conclusion. This reasoning emphasizes critical thinking, rigorous questioning, and the dynamic interplay of thesis, antithesis, and synthesis.
Poetic Language vs Dialectic Argument
Poetic language employs metaphor, imagery, and emotional resonance to evoke intuition and subjective experience, prioritizing aesthetic and imaginative comprehension. Dialectic argument relies on structured reasoning, logical analysis, and objective discourse to reach conclusions through systematic debate and evidence evaluation. While poetic language engages the senses and emotions, dialectic argument emphasizes clarity, consistency, and rational persuasion.
Roles in Shaping Philosophy and Literature
Poetic language shapes philosophy and literature by evoking emotion, imagination, and symbolic meaning, encouraging creative and reflective thinking through metaphor and narrative. Dialectic plays a critical role by structuring philosophical inquiry with logical argumentation, debate, and systematic reasoning to clarify concepts and uncover truth. The interplay between Poetic and Dialectic methods enriches intellectual traditions, balancing expressive creativity with analytical rigor in the development of ideas.
Emotional Resonance in Poetic Form
Poetic form harnesses emotional resonance through vivid imagery, rhythm, and metaphor, enabling readers to connect deeply with the text on a personal and sensory level. The use of symbolic language and varied poetic devices evokes complex feelings and subconscious understanding that dialectic discourse, centered on logical argumentation, often cannot achieve. This emotional impact in poetry fosters empathy and introspection, enriching the reader's experience beyond mere intellectual engagement.
Logical Structure in Dialectic Processes
Dialectic processes emphasize a rigorous logical structure involving thesis, antithesis, and synthesis to arrive at coherent conclusions through reasoned argumentation. Unlike poetic expressions that rely on metaphor and emotive language, dialectic prioritizes clarity, systematic progression, and critical examination of opposing ideas. This logical framework enables the resolution of contradictions and facilitates deeper understanding within philosophical and analytical discourse.
When Poetic and Dialectic Intersect
Poetic and dialectic intersect when language transcends mere argumentation to evoke deeper emotional and intellectual responses, blending imaginative expression with logical reasoning. This fusion enhances philosophical discourse by incorporating metaphor, narrative, and rhythm alongside analytical rigor, creating a more holistic understanding of complex ideas. The intersection fosters a dynamic interplay where poetic creativity illuminates dialectic clarity, enriching both communication and comprehension.
Choosing Between Poetic and Dialectic Approaches
Choosing between poetic and dialectic approaches depends on the objective and desired impact of communication. Poetic methods evoke emotion and imagination, using metaphor and rhythm to connect with audiences on a sensory level. Dialectic approaches prioritize logical reasoning and structured dialogue, fostering clarity and critical thinking for problem-solving or academic discussions.
Poetic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com