Syncope, commonly known as fainting, occurs when the brain temporarily receives insufficient blood flow, leading to a brief loss of consciousness. Causes can range from dehydration and sudden drops in blood pressure to underlying heart conditions that require medical attention. Discover more about the symptoms, causes, and treatments to protect your well-being in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
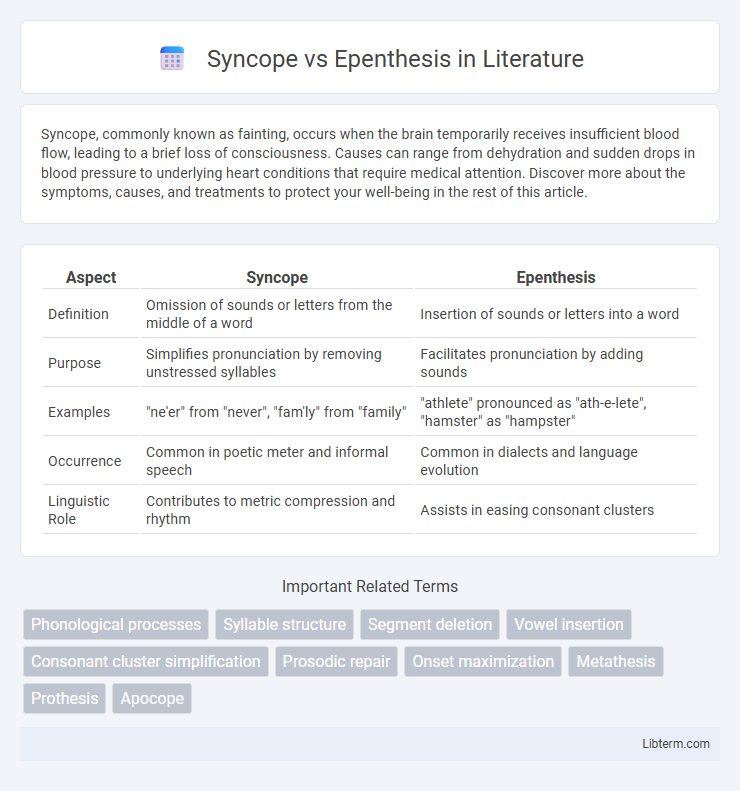
| Aspect | Syncope | Epenthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Omission of sounds or letters from the middle of a word | Insertion of sounds or letters into a word |
| Purpose | Simplifies pronunciation by removing unstressed syllables | Facilitates pronunciation by adding sounds |
| Examples | "ne'er" from "never", "fam'ly" from "family" | "athlete" pronounced as "ath-e-lete", "hamster" as "hampster" |
| Occurrence | Common in poetic meter and informal speech | Common in dialects and language evolution |
| Linguistic Role | Contributes to metric compression and rhythm | Assists in easing consonant clusters |
Understanding Syncope and Epenthesis
Syncope involves the omission of sounds, typically vowels, within a word to streamline pronunciation, such as the reduction of "family" to "fam'ly." Epenthesis refers to the insertion of an extra sound, often a vowel or consonant, within a word to facilitate smoother articulation, exemplified by pronouncing "athlete" as "ath-e-lete." Understanding syncope and epenthesis is essential in phonology for analyzing language evolution, dialectal variations, and speech patterns.
Definitions: What is Syncope?
Syncope is a phonological process involving the omission of one or more sounds, typically vowels, from the interior of a word, resulting in a shorter form while preserving the original meaning. This phenomenon commonly occurs in rapid or casual speech, affecting words such as "family" (pronounced as "fam'ly") or "chocolate" (pronounced as "choc'late"). Understanding syncope helps linguists analyze historical language changes and modern speech patterns.
Definitions: What is Epenthesis?
Epenthesis is the phonological process involving the insertion of one or more sounds into a word, often to simplify pronunciation or alter syllable structure. This contrasts with syncope, which refers to the deletion of sounds, typically unstressed vowels, within a word. Epenthesis commonly occurs in language evolution and speech patterns, enhancing ease of articulation and maintaining rhythmic balance.
Linguistic Mechanisms Behind Syncope
Syncope involves the loss of one or more sounds from the interior of a word, typically vowels, to streamline pronunciation and enhance speech efficiency. This phonological process is driven by mechanisms such as syllable reduction and prosodic constraints, aiming to maintain rhythmic balance and ease articulatory effort. In contrast, epenthesis inserts additional sounds, often consonants or vowels, to break up complex clusters or improve phonotactic conformity.
Linguistic Mechanisms Behind Epenthesis
Epenthesis is a phonological process that involves the insertion of an extra sound, typically a vowel or consonant, within a word to ease pronunciation or prevent difficult consonant clusters. This mechanism contrasts with syncope, which deletes sounds from within a word, often vowels, to simplify speech. Epenthesis plays a key role in language evolution and dialect formation by facilitating smoother transitions between sounds according to the phonotactic constraints of a language.
Syncope vs Epenthesis: Key Differences
Syncope involves the omission of sounds or letters from the interior of a word, often to simplify pronunciation, such as "family" pronounced as "fam'ly." Epenthesis refers to the insertion of one or more sounds within a word to break up difficult consonant clusters, like the pronunciation "athalete" for "athlete." The primary difference lies in syncope removing sounds while epenthesis adds sounds to alter word structure and ease articulation.
Examples of Syncope in Language
Syncope occurs when sounds, especially unstressed vowels or consonants, are omitted from the middle of words, such as the dropping of the unstressed vowel in "family" pronounced as "fam'ly." In contrast, epenthesis involves the insertion of sounds within a word, like the addition of a vowel in "athlete" pronounced as "ath-e-lete." Examples of syncope appear in various languages, including English words like "chocolate" (often pronounced "choc'late") and in Latin with "calidus" becoming "caldus.
Examples of Epenthesis in Language
Epenthesis involves the insertion of an extra sound within a word, such as the commonly cited example in English where "hamster" is pronounced as "hampster." In Japanese, epenthetic vowels are often inserted to break up consonant clusters, exemplified by the loanword "baseball," pronounced as "besuboru." Similarly, in Spanish, epenthesis occurs in the pronunciation of "Israel" as "Is-ra-el," adding a slight vowel sound to ease articulation.
Implications for Phonological Theory
Syncope and epenthesis reveal crucial insights into phonological theory by highlighting contrasting processes of segment deletion and insertion that impact syllable structure and stress patterns. These phenomena challenge straightforward linear models and support non-linear representations such as feature geometry and autosegmental phonology, emphasizing the interplay between underlying forms and surface outputs. Understanding their distribution and conditioning factors enhances theories on phonotactic constraints and the cognitive mechanisms governing speech processing and production.
Syncope and Epenthesis in Language Evolution
Syncope and epenthesis are crucial phonological processes influencing language evolution by altering word structures over time. Syncope involves the loss of medial sounds, often vowels, streamlining pronunciation and contributing to language economy, such as the transition from Latin "familia" to Old French "famille." Epenthesis inserts additional sounds to ease articulation or prevent disallowed consonant clusters, shaping phonotactic constraints and resulting in forms like Old English "athlete" becoming "ath-e-lete" in some dialects, reflecting dynamic linguistic adaptation.
Syncope Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com