A minstrel was a medieval European entertainer known for singing, playing instruments, and reciting poetry, often performing at courts and public gatherings. Their role combined storytelling and music to preserve history and culture through oral tradition. Discover more about minstrels' fascinating impact on art and society in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
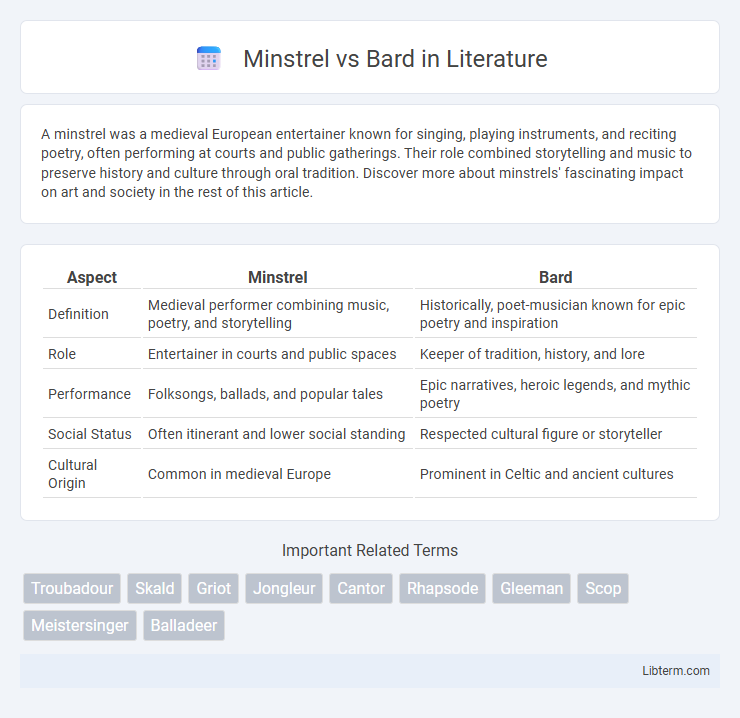
| Aspect | Minstrel | Bard |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Medieval performer combining music, poetry, and storytelling | Historically, poet-musician known for epic poetry and inspiration |
| Role | Entertainer in courts and public spaces | Keeper of tradition, history, and lore |
| Performance | Folksongs, ballads, and popular tales | Epic narratives, heroic legends, and mythic poetry |
| Social Status | Often itinerant and lower social standing | Respected cultural figure or storyteller |
| Cultural Origin | Common in medieval Europe | Prominent in Celtic and ancient cultures |
Introduction to Minstrels and Bards
Minstrels and bards played essential roles in medieval storytelling and music, with minstrels often serving as traveling entertainers who performed songs, poetry, and tales to diverse audiences. Bards, closely linked to Celtic traditions, specialized in preserving oral history and cultural heritage, often composing epic poetry and chronicles for noble patrons. Both minstrels and bards contributed significantly to cultural transmission, blending music and narrative in distinctive social contexts.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Minstrels originated in medieval Europe as traveling musicians and storytellers who entertained courts and common folk with news and ballads, often emphasizing vocal performance and simple instrumentation like lutes or harps. Bards, primarily associated with Celtic cultures, held a more formalized role as poets, historians, and genealogists, preserving oral traditions and cultural heritage through complex poetry and song. Over time, minstrels evolved into more versatile entertainers with varied repertoires, while bards maintained a revered status linked to cultural identity and spiritual significance.
Roles and Functions in Society
Minstrels primarily served as entertainers in medieval society, performing musical storytelling and preserving oral traditions for both nobility and common folk. Bards held a more esteemed cultural role, acting as historians, genealogists, and keepers of heroic lore, often integral to maintaining the social identity of clans and tribes. While minstrels focused on widespread public amusement, bards functioned as vital custodians of cultural heritage and social cohesion.
Musical Styles and Instruments
Minstrels traditionally performed narrative ballads and historical songs using instruments like the lute, rebec, and hurdy-gurdy, emphasizing storytelling through melodic and rhythmic structures. Bards specialized in poetic and epic compositions, often accompanying themselves on the harp or lyre, which suited their role in preserving cultural lore and oral traditions. The musical styles of minstrels tended toward accessible, popular entertainment, while bards focused on ceremonial and courtly music with complex lyrical content.
Storytelling Traditions Compared
Minstrels and bards both served as oral historians, preserving cultural tales through song and narrative, yet minstrels often specialized in performance art across courts and public spaces, while bards were primarily custodians of genealogies and heroic legends within Celtic societies. Minstrels adapted their storytelling to entertain diverse audiences with versatile repertoires including ballads and romances, whereas bards maintained a structured role in ritualistic and ceremonial contexts, upholding the clan's historical memory. The distinctive storytelling traditions reveal a contrast between minstrels' entertainment-driven performances and bards' function as hereditary lore keepers.
Patronage and Social Status
Minstrels typically relied on noble patronage, performing in royal courts or wealthy households, which granted them a moderate social status linked to their service role. Bards, often regarded as cultural custodians and storytellers, held a higher social standing in Celtic societies due to their sacred role in preserving history and lore through oral tradition. While minstrels were entertainers dependent on patron generosity, bards wielded influence and respect as esteemed members of their community's intellectual elite.
Cultural Impact and Legacy
Minstrels and bards both played crucial roles in preserving and transmitting cultural heritage through oral traditions and music, with minstrels typically serving as traveling entertainers in medieval Europe, spreading stories, news, and songs across regions. Bards held a more revered status in Celtic cultures, often acting as historians, genealogists, and poets who reinforced social values and royal legitimacy through their compositions. Their legacies persist today in the influence on modern storytelling, folk music, and the continuing appreciation of oral narrative traditions.
Representations in Literature and Media
Minstrels and bards are often depicted in literature and media with distinct roles: minstrels typically appear as traveling entertainers performing songs and stories for courts and common folk, while bards are portrayed as revered poets and historians preserving cultural heritage. In medieval and fantasy settings, minstrels are shown as versatile performers skilled in various instruments, whereas bards are characterized by their deep connection to myth and lore, often possessing magical or prophetic abilities. These representations highlight the minstrel's focus on entertainment and social commentary contrasted with the bard's role as a keeper of tradition and epic storytelling.
Key Similarities and Differences
Minstrels and bards both functioned as traditional storytellers and musicians, preserving history and cultural tales through song and poetry across medieval Europe. Minstrels often traveled extensively, performing secular entertainment such as ballads and humorous songs in courts or public spaces, while bards held a more specialized role as revered poets and historians, particularly in Celtic cultures, responsible for maintaining genealogies and oral traditions. The distinction lies in their social status and scope; bards were typically regarded as elite cultural custodians, whereas minstrels were versatile entertainers with a broader, more popular audience.
Modern Interpretations and Revival
Modern interpretations of Minstrels and Bards highlight their distinct cultural roles, with Minstrels often portrayed as itinerant musicians engaging popular audiences, while Bards are celebrated for their poetic storytelling and preservation of history. The revival of both forms has seen contemporary artists blending traditional melodies with modern genres, emphasizing heritage through festivals, academic research, and digital platforms. This resurgence fosters appreciation for medieval and Celtic musical traditions, ensuring their relevance in today's cultural landscape.
Minstrel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com