Paradoxes challenge your understanding by presenting seemingly contradictory statements that reveal deeper truths. They highlight complexities in logic, language, and reality that provoke critical thinking and insight. Explore the rest of the article to uncover intriguing examples and the significance of paradoxes in philosophy and science.
Table of Comparison
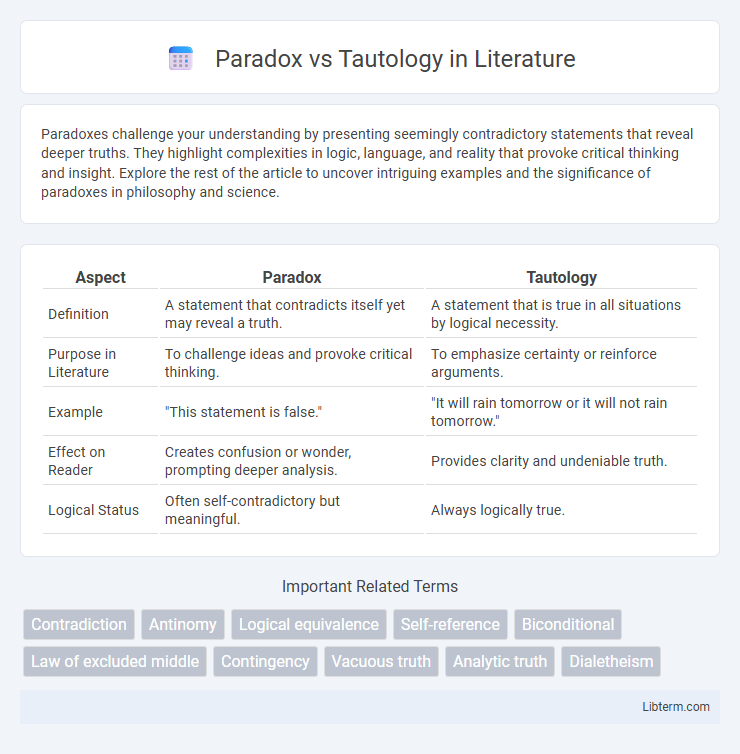
| Aspect | Paradox | Tautology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A statement that contradicts itself yet may reveal a truth. | A statement that is true in all situations by logical necessity. |
| Purpose in Literature | To challenge ideas and provoke critical thinking. | To emphasize certainty or reinforce arguments. |
| Example | "This statement is false." | "It will rain tomorrow or it will not rain tomorrow." |
| Effect on Reader | Creates confusion or wonder, prompting deeper analysis. | Provides clarity and undeniable truth. |
| Logical Status | Often self-contradictory but meaningful. | Always logically true. |
Introduction to Paradox and Tautology
Paradoxes are statements or propositions that contradict themselves or lead to a conclusion that defies intuition, often revealing complexities in logic or language. Tautologies are logical statements that are true in every possible interpretation, serving as fundamental truths in formal logic. Understanding the distinction between paradoxes and tautologies is essential for grasping logical consistency and the foundations of mathematical reasoning.
Defining Paradox: Meaning and Examples
A paradox is a statement or proposition that appears self-contradictory or logically unacceptable but may reveal an underlying truth upon closer examination. Common examples include the "liar paradox," where a statement declares itself false, challenging binary logic, and Zeno's paradoxes, which question concepts of motion and infinity. Paradoxes highlight the complexity of language and reasoning, often prompting reconsideration of established assumptions in philosophy and mathematics.
Understanding Tautology: Definition and Illustrations
A tautology in logic is a statement that is true in every possible interpretation, making it universally valid regardless of the truth values of its components. Examples include "It will either rain or not rain" and the formula (P !P), which always evaluates to true. Understanding tautologies is crucial in fields like mathematics, computer science, and philosophy for constructing sound arguments and verifying logical consistency.
Key Differences Between Paradox and Tautology
A paradox is a statement that contradicts itself or defies intuition, often revealing deeper truths through apparent logical inconsistency, while a tautology is a statement that is always true by virtue of its logical form. Paradoxes challenge the boundaries of logic by presenting situations that cannot be resolved within standard frameworks, whereas tautologies provide tautological certainty, affirming truth regardless of any conditions. The key difference lies in paradoxes producing puzzling or conflicting conclusions, while tautologies offer undeniable, redundant truths.
Logical Roles of Paradoxes and Tautologies
Paradoxes reveal contradictions that challenge established logical frameworks by presenting statements that cannot consistently be true or false, thereby driving critical examination and refinement of logical theories. Tautologies, by contrast, are logically valid statements that hold true in every possible interpretation, serving as foundational truths within formal logic and enabling reliable inference. Understanding their distinct logical roles aids in differentiating between problematic contradictions and universally valid principles essential for logical analysis.
Paradoxes in Philosophy and Logic
Paradoxes in philosophy and logic reveal contradictions that challenge conventional reasoning, often exposing limitations within existing conceptual frameworks. Famous examples such as the Liar Paradox and Russell's Paradox highlight how self-reference and set theory complications question fundamental assumptions in truth and set membership. These paradoxes provoke critical analysis and drive advancements in formal logic, semantics, and metaphysics by unsettling presumed logical coherence.
Tautologies in Formal Logic and Reasoning
Tautologies in formal logic are statements that are true in every possible interpretation, providing a foundation for logical reasoning and proof validation. They serve as logical truths regardless of the truth values of their components, underpinning deductive systems and automated theorem proving. Recognizing tautologies helps in simplifying complex logical expressions and ensures the consistency of logical frameworks.
Impact on Critical Thinking and Argumentation
Paradoxes challenge critical thinking by presenting situations that defy intuition or conventional logic, prompting deeper analysis and questioning of assumptions. Tautologies, being statements true by definition, reinforce logical consistency but offer limited insight or argumentative advancement. Understanding the distinction enhances argumentation skills by enabling recognition of complex contradictions versus self-evident truths.
Common Misconceptions About Paradox and Tautology
Common misconceptions about paradoxes include the belief that they are simply logical errors or contradictions, whereas paradoxes often reveal deeper, valid complexities in reasoning. Tautologies are frequently misunderstood as uninformative or trivial statements, but they are essential in logic for establishing truths that hold under all conditions. Confusing paradoxes with tautologies leads to overlooking the distinct roles each plays in logic, reasoning, and philosophical analysis.
Conclusion: The Significance of Paradox and Tautology in Thought
Paradoxes challenge conventional logic by presenting statements that defy straightforward truth evaluation, fostering deeper critical analysis and innovation in philosophical inquiry. Tautologies, being universally true statements in logic, provide foundational certainty and clarity essential for formal reasoning and the validation of arguments. Understanding the interplay between paradox and tautology enhances cognitive flexibility, promoting rigorous thought and the advancement of knowledge across disciplines.
Paradox Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com