Structuralism explores how elements of human culture, language, and thought interrelate within overarching systems and structures. By analyzing these underlying frameworks, it reveals patterns and meanings that shape society and individual experience. Discover how your understanding of communication and culture can deepen by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
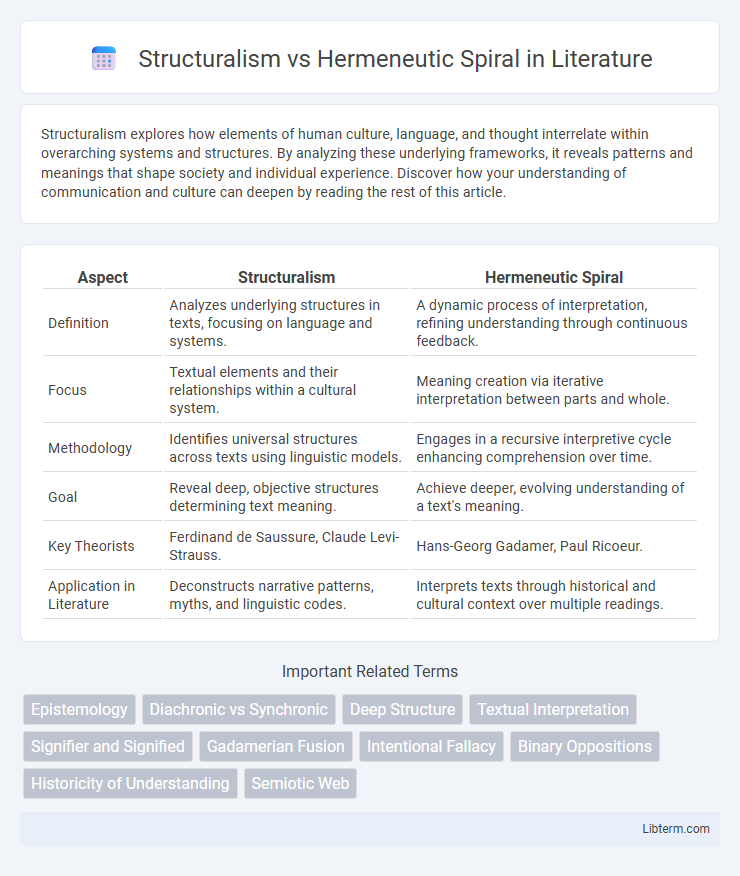
| Aspect | Structuralism | Hermeneutic Spiral |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes underlying structures in texts, focusing on language and systems. | A dynamic process of interpretation, refining understanding through continuous feedback. |
| Focus | Textual elements and their relationships within a cultural system. | Meaning creation via iterative interpretation between parts and whole. |
| Methodology | Identifies universal structures across texts using linguistic models. | Engages in a recursive interpretive cycle enhancing comprehension over time. |
| Goal | Reveal deep, objective structures determining text meaning. | Achieve deeper, evolving understanding of a text's meaning. |
| Key Theorists | Ferdinand de Saussure, Claude Levi-Strauss. | Hans-Georg Gadamer, Paul Ricoeur. |
| Application in Literature | Deconstructs narrative patterns, myths, and linguistic codes. | Interprets texts through historical and cultural context over multiple readings. |
Introduction to Structuralism and Hermeneutic Spiral
Structuralism analyzes culture and language through underlying structures and systems, emphasizing patterns and relationships that shape meaning. The Hermeneutic Spiral involves iterative interpretation where understanding deepens through continuous dialogue between the parts and the whole of a text or phenomenon. Both approaches seek to uncover meaning, with Structuralism focusing on abstract frameworks and the Hermeneutic Spiral on evolving comprehension via interpretive cycles.
Historical Origins and Key Proponents
Structuralism, emerging in early 20th-century Europe, notably through Ferdinand de Saussure's linguistic theories, emphasizes underlying systems and structures shaping human culture and language. The Hermeneutic Spiral traces its roots to ancient philosophical traditions, with key proponents like Hans-Georg Gadamer and Martin Heidegger focusing on the iterative process of interpretation and understanding. While Structuralism prioritizes systematic analysis of underlying frameworks, the Hermeneutic Spiral highlights evolving meaning through continuous dialogue between the interpreter and the text.
Core Principles of Structuralism
Structuralism centers on analyzing underlying structures that shape culture, language, and society, emphasizing binary oppositions and deep systems of meaning. It seeks objective patterns within human experiences, relying on frameworks like Saussure's linguistics to decode symbols and signs. The Hermeneutic Spiral contrasts by focusing on evolving interpretation, highlighting continuous understanding shaped through context and dialogue rather than fixed structures.
The Hermeneutic Spiral Explained
The Hermeneutic Spiral is a dynamic process of understanding where interpretation evolves through iterative engagement with the text and context, moving from parts to whole and back again. Unlike structuralism, which emphasizes fixed structures and underlying systems in language or culture, the Hermeneutic Spiral highlights the fluid interplay between preconceptions and new insights, fostering deeper comprehension. This method acknowledges that meaning is not static but continuously reshaped as interpretation progresses.
Methodological Differences
Structuralism employs a systematic approach analyzing underlying structures within cultural phenomena, focusing on identifying and decoding patterns, binaries, and relationships. The Hermeneutic Spiral emphasizes iterative interpretation, where understanding deepens through continuous dialogue between the parts and the whole, reflecting evolving context and meaning. Structuralism seeks objective frameworks, whereas the Hermeneutic Spiral prioritizes subjective, dynamic comprehension through reflexive engagement.
Language, Meaning, and Interpretation
Structuralism analyzes language as a system of interrelated signs, emphasizing underlying structures that govern meaning through binary oppositions and rules. The Hermeneutic Spiral focuses on iterative interpretation, where understanding language evolves by moving between parts and the whole, constantly refining meaning through contextual engagement. Both approaches address how language shapes meaning but diverge in method: Structuralism seeks fixed patterns, while the Hermeneutic Spiral embraces dynamic, co-constructive interpretation.
Applications in Literary Analysis
Structuralism in literary analysis systematically examines underlying structures such as language systems, narrative patterns, and cultural codes, revealing universal meanings across texts. The Hermeneutic Spiral focuses on iterative interpretation, emphasizing the dynamic interplay between the reader's understanding and the text's evolving meaning through continuous refinement. Structuralism provides a framework for uncovering hidden relations within texts, while the Hermeneutic Spiral enhances depth by engaging the reader in an ongoing contextual dialogue.
Criticisms and Limitations
Structuralism faces criticism for its rigid focus on underlying systems, often neglecting individual context and subjective meaning, which limits its applicability in dynamic social and cultural analysis. The Hermeneutic Spiral, while emphasizing iterative interpretation and understanding, is criticized for its potential circularity and the difficulty in achieving definitive conclusions, leading to challenges in establishing objective knowledge. Both approaches face limitations in balancing systematic analysis with the nuances of human experience and interpretive flexibility.
Intersections and Points of Convergence
Structuralism and the Hermeneutic Spiral intersect in their shared emphasis on understanding underlying frameworks that shape meaning within texts and human experiences. Both approaches prioritize the interpretation of deeper structures--structuralism through identifying universal patterns and binaries, and the Hermeneutic Spiral through iterative interpretation that refines understanding between parts and the whole. Points of convergence include the recognition that meaning is not fixed but emerges through dynamic processes of analysis and reinterpretation, bridging objective frameworks and subjective comprehension.
Implications for Contemporary Theory
Structuralism emphasizes the underlying systems and structures that shape human culture, language, and cognition, influencing contemporary theories in linguistics, anthropology, and literary criticism by promoting the analysis of universal patterns. The Hermeneutic Spiral highlights the iterative process of interpretation where understanding deepens through the continuous interaction between the parts and the whole, impacting modern hermeneutics, phenomenology, and social theory by stressing context and subjective meaning. Together, these approaches inform contemporary theory by balancing systematic frameworks with dynamic interpretive processes, fostering comprehensive analyses of texts, social phenomena, and human experience.
Structuralism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com