Narrative storytelling creates immersive experiences by weaving characters, settings, and events into a coherent and engaging plot. This technique helps convey complex ideas and emotions, making your message more relatable and memorable. Explore the rest of this article to discover how narrative can transform your communication skills.
Table of Comparison
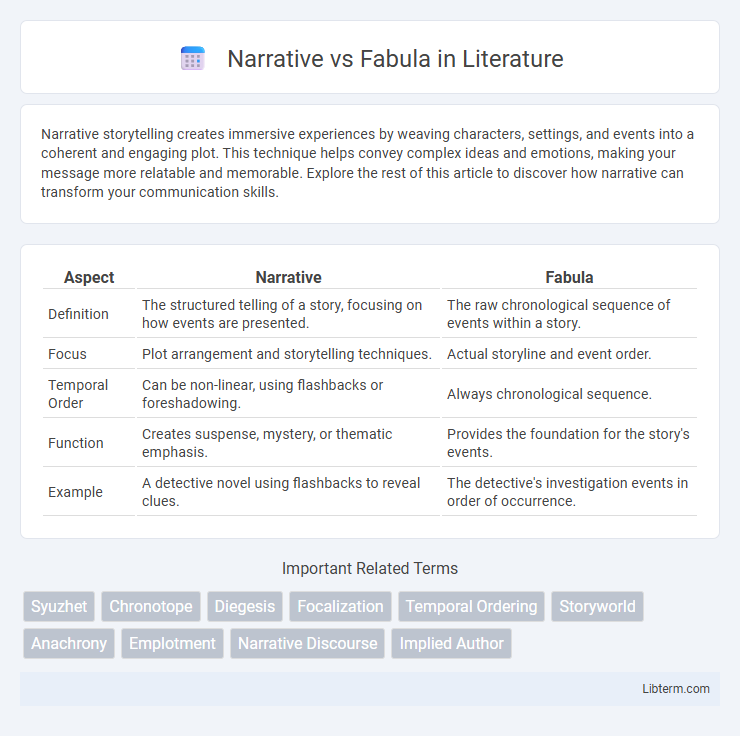
| Aspect | Narrative | Fabula |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The structured telling of a story, focusing on how events are presented. | The raw chronological sequence of events within a story. |
| Focus | Plot arrangement and storytelling techniques. | Actual storyline and event order. |
| Temporal Order | Can be non-linear, using flashbacks or foreshadowing. | Always chronological sequence. |
| Function | Creates suspense, mystery, or thematic emphasis. | Provides the foundation for the story's events. |
| Example | A detective novel using flashbacks to reveal clues. | The detective's investigation events in order of occurrence. |
Introduction to Narrative and Fabula
Narrative refers to the structured sequence of events as presented in a story, encompassing the order, perspective, and style chosen by the storyteller. Fabula represents the raw chronological events of a story, independent of how or when they are revealed to the audience. Understanding the distinction between narrative and fabula is essential for analyzing storytelling techniques, plot development, and the manipulation of time in literature and film.
Defining Narrative: Structure and Purpose
Narrative refers to the structured presentation of events arranged to convey a particular story, emphasizing the way the plot unfolds rather than just the chronological sequence of events (fabula). It organizes events into a coherent framework with elements like exposition, rising action, climax, and resolution to guide the audience's understanding and emotional engagement. The purpose of narrative structure is to shape the audience's perception and interpretation, creating meaning through selective arrangement and emphasis of story components.
What is Fabula? Origins and Meaning
Fabula refers to the raw chronological sequence of events in a story, representing the foundational timeline as it would naturally occur. Originating from Russian Formalism, particularly the work of scholars like Viktor Shklovsky and Vladimir Propp, fabula contrasts with the narrative (sjuzhet), which is the structured presentation of these events. The term emphasizes the story's underlying causality and temporal order, distinct from how the narrative rearranges or highlights elements for thematic or emotional impact.
Narrative vs Fabula: Key Differences
Narrative and fabula differ primarily in structure and presentation; fabula refers to the chronological sequence of events in a story, while narrative encompasses the order and manner the story is told, including any reordering or emphasis. The distinction highlights how narrative can manipulate time and perspective to create suspense or thematic depth, whereas fabula remains the underlying timeline of events. Understanding the key difference between narrative and fabula aids in analyzing storytelling techniques and the impact of non-linear narratives in literature and film.
Historical Development of the Concepts
Narrative and fabula concepts have evolved through structuralist and narratological theories, prominently shaped by Russian Formalists like Viktor Shklovsky and Boris Tomashevsky in the early 20th century, who distinguished fabula as raw chronological events and narrative as the artistic arrangement of these events. Gerard Genette expanded this framework in the 1970s, introducing terms like order, duration, and frequency to analyze narrative discourse more precisely. The development underscores the shift from simply recounting events (fabula) to exploring the complexity of their presentation (narrative), influencing contemporary literary and film studies.
Narrative Techniques Derived from Fabula
Fabula refers to the chronological sequence of events in a story, while narrative encompasses the structured presentation of these events through various techniques. Narrative techniques derived from fabula include flashbacks, foreshadowing, and non-linear storytelling, which manipulate the original timeline to enhance engagement and thematic depth. These methods enable storytellers to control pacing, build suspense, and provide deeper insight into characters and plot development.
The Role of Chronology in Fabula and Narrative
Fabula represents the chronological sequence of events as they occur in a story's universe, serving as the foundation for narrative coherence and temporal understanding. Narrative manipulates this chronological order through techniques like flashbacks, foreshadowing, or non-linear storytelling to create suspense, thematic depth, and emotional impact. The role of chronology in fabula ensures logical event progression, whereas narrative reconfigures this timeline to enhance audience engagement and interpretive complexity.
Examples in Literature and Film
Narrative structures in literature and film often distinguish between fabula, the raw chronological sequence of events, and syuzhet, the way those events are organized and presented to the audience. For example, in the film "Pulp Fiction" by Quentin Tarantino, the fabula includes all events in their actual chronological order, while the narrative rearranges scenes to create suspense and thematic depth. Similarly, in literature, Vladimir Propp's analysis of folktales separates the fabula--the linear plot--from the narrative techniques that manipulate reader perception and engagement.
Impact on Storytelling and Reader Perception
Narrative and fabula shape storytelling by controlling the sequence and presentation of events, with fabula representing the raw chronological story and narrative organizing these events for impact and engagement. This distinction influences reader perception by guiding emotional responses and thematic understanding through narrative techniques like flashbacks or foreshadowing. Effective manipulation of narrative structure enhances suspense, character development, and thematic depth, transforming a simple fabula into a compelling storytelling experience.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Narrative and Fabula
Choosing between narrative and fabula depends on your storytelling goals and audience engagement. Narrative emphasizes the sequence and structure of events as presented, enhancing emotional impact and thematic depth. Fabula focuses on the raw chronological order of events, providing clarity and a straightforward understanding of the story's timeline.
Narrative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com