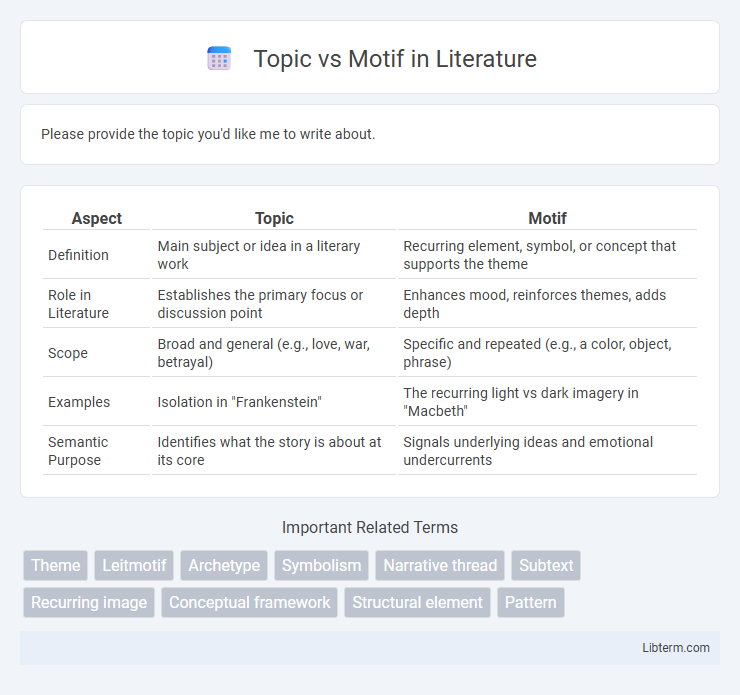
Please provide the topic you'd like me to write about.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Topic | Motif |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Main subject or idea in a literary work | Recurring element, symbol, or concept that supports the theme |
| Role in Literature | Establishes the primary focus or discussion point | Enhances mood, reinforces themes, adds depth |
| Scope | Broad and general (e.g., love, war, betrayal) | Specific and repeated (e.g., a color, object, phrase) |
| Examples | Isolation in "Frankenstein" | The recurring light vs dark imagery in "Macbeth" |
| Semantic Purpose | Identifies what the story is about at its core | Signals underlying ideas and emotional undercurrents |
Understanding the Basics: What is a Topic?
A topic is the central subject or idea explored in a literary work, representing the general area of discussion such as love, war, or identity. It serves as the foundation for the narrative, providing a broad framework within which themes and motifs develop. Understanding the topic helps readers grasp what the story is about at a fundamental level, distinguishing it from more specific elements like motifs that reinforce the underlying message.
Defining Motif: Meaning and Importance
A motif is a recurring element, symbol, or idea within a literary or artistic work that reinforces the central theme and adds depth to the narrative. It functions as a symbolic device that helps to unify the story and evoke emotional responses, making it a critical tool for writers and creators. Understanding motifs is essential for interpreting complex texts, as they highlight underlying messages and enrich the audience's experience.
Key Differences Between Topic and Motif
Topic refers to the general subject or main idea of a literary work, such as love, war, or betrayal, while motif is a recurring element, symbol, or pattern that reinforces the theme or mood. Topics are broad and can be expressed in a single word or phrase, whereas motifs are specific images, phrases, or situations that recur throughout the narrative. Understanding the key difference helps in literary analysis by distinguishing between the overarching themes (topics) and their repeated symbolic representation (motifs).
How Topics Drive the Narrative
Topics serve as the central ideas that guide the development of a narrative, providing a broad framework that shapes character motivations, plot progression, and thematic exploration. By establishing underlying subjects such as love, power, or betrayal, topics influence the direction and emotional depth of the story, anchoring the audience's expectations and engagement. Unlike motifs, which are recurring symbols or themes that reinforce meaning, topics function as the driving forces behind the narrative's structure and purpose.
The Role of Motifs in Storytelling
Motifs play a crucial role in storytelling by reinforcing themes and enhancing the emotional resonance of a narrative through recurring symbols, images, or ideas. Unlike the broader topic, motifs provide a specific, tangible element that deepens the audience's understanding of the story's underlying message. Effective use of motifs, such as the green light in "The Great Gatsby," adds layers of meaning and creates continuity across the plot.
Examples of Topics in Literature
Topics in literature refer to broad subjects like love, betrayal, or courage found across many works, such as love in Shakespeare's "Romeo and Juliet" and courage in Harper Lee's "To Kill a Mockingbird." Motifs are recurring elements, like the green light in F. Scott Fitzgerald's "The Great Gatsby," symbolizing hope and the American Dream. Understanding the distinction helps in analyzing themes and narrative techniques in literary texts.
Notable Motifs Across Famous Works
Notable motifs such as the green light in "The Great Gatsby" symbolize unattainable dreams, while the journey in "The Odyssey" represents the hero's quest for self-discovery. Recurring motifs like the use of shadows in "Macbeth" emphasize themes of guilt and moral ambiguity. These motifs enhance the narrative by providing deeper symbolic meaning beyond the central topics of the works.
Topic vs Motif: Common Misconceptions
Common misconceptions confuse topic with motif by treating them as interchangeable when they serve distinct roles in literature. A topic is the subject or main idea of a work, such as love or betrayal, while a motif is a recurring element that reinforces themes, like a repeated symbol or phrase. Understanding this differentiation clarifies how motifs support thematic development beyond mere subject matter.
Integrating Topics and Motifs for Depth
Integrating topics and motifs enriches literary works by weaving overarching themes with recurring symbolic elements that resonate throughout the narrative. Topics identify the central subject matter, while motifs emphasize particular ideas or emotions through repetition, creating layers of meaning and emotional depth. This fusion enables writers to construct nuanced stories that engage readers by connecting abstract concepts with tangible, reiterated imagery.
Tips for Identifying Topic and Motif in Texts
Topics often represent the broad subject matter of a text, such as love, war, or freedom, while motifs are recurring elements like symbols, phrases, or images that reinforce the theme. To identify a topic, look for the main ideas or issues the text addresses repeatedly, whereas spotting motifs involves noticing repeated patterns, objects, or language that enhance emotional or thematic depth. Analyzing character actions, setting details, and recurring symbols provides clear clues for distinguishing between a text's overall topic and its specific motifs.
Topic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com