Polyphony is a musical texture featuring multiple independent melodic lines performed simultaneously, creating rich harmonies and intricate soundscapes. This technique, prominent in Renaissance and Baroque music, enhances the depth and complexity of compositions by intertwining voices or instruments. Explore the rest of this article to discover how polyphony shapes your listening experience and its impact on various musical genres.
Table of Comparison
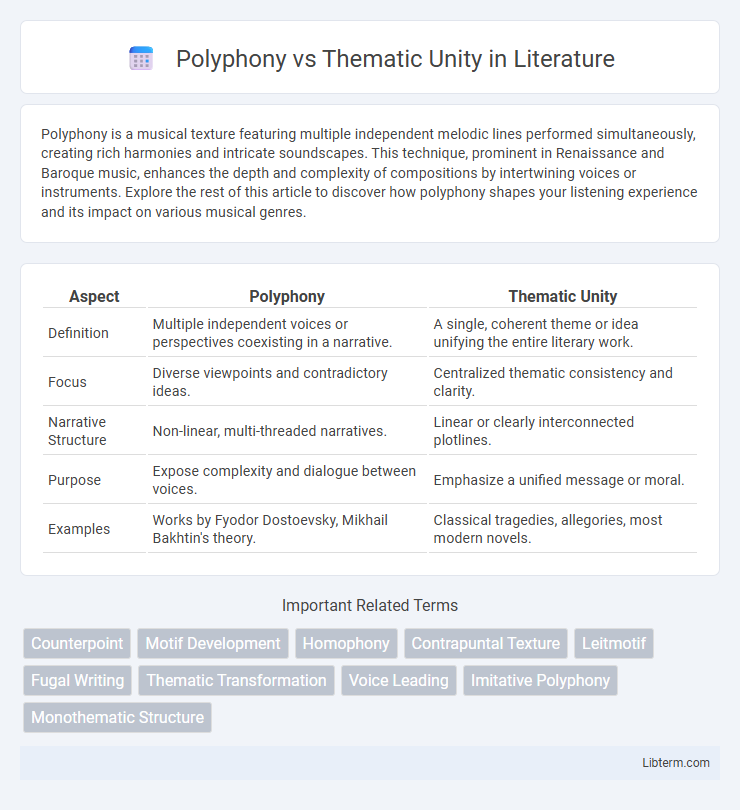
| Aspect | Polyphony | Thematic Unity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple independent voices or perspectives coexisting in a narrative. | A single, coherent theme or idea unifying the entire literary work. |
| Focus | Diverse viewpoints and contradictory ideas. | Centralized thematic consistency and clarity. |
| Narrative Structure | Non-linear, multi-threaded narratives. | Linear or clearly interconnected plotlines. |
| Purpose | Expose complexity and dialogue between voices. | Emphasize a unified message or moral. |
| Examples | Works by Fyodor Dostoevsky, Mikhail Bakhtin's theory. | Classical tragedies, allegories, most modern novels. |
Introduction to Polyphony and Thematic Unity
Polyphony involves multiple independent melodic lines occurring simultaneously, creating complex textures essential in Baroque and Renaissance music. Thematic unity refers to the consistent development and recurrence of a central musical theme throughout a composition, providing coherence and structural integrity. Understanding polyphony highlights how composers interweave distinct melodies, while thematic unity emphasizes the intentional reinforcement of a single idea or motif across a piece.
Defining Polyphony in Music
Polyphony in music refers to the simultaneous combination of two or more independent melodic lines, each maintaining its own distinct contour and rhythm, creating a rich and complex texture. This contrasts with thematic unity, where a single melody or theme is developed and varied throughout a composition to provide coherence and structural integrity. Polyphonic music often features counterpoint techniques, exemplified by Baroque composers like Johann Sebastian Bach, emphasizing interweaving melodies rather than thematic repetition.
Understanding Thematic Unity
Thematic unity refers to the coherent development and integration of a central theme throughout a musical composition, ensuring all elements contribute to a singular expressive idea. Unlike polyphony, which layers multiple independent melodies simultaneously, thematic unity emphasizes the consistent transformation and reinforcement of one primary theme. This approach creates a focused narrative arc and emotional cohesion within the piece.
Historical Evolution of Polyphony
Polyphony evolved during the Medieval period as an innovative musical texture featuring multiple independent melodic lines, contrasting with the earlier emphasis on monophonic thematic unity. The development of polyphony is traced through landmark periods such as the Ars Nova in the 14th century, which introduced greater rhythmic complexity and independence between voices, shaping Western music theory and practice. This evolution marked a shift from singular thematic cohesion toward intricate interweaving melodies that enriched harmonic and structural depth in compositions.
The Role of Thematic Unity in Composition
Thematic unity in composition establishes coherence by developing a central musical idea or motif that recurs throughout a piece, creating a sense of connection and purpose. It guides the listener's experience by providing recognizable patterns and variations, enhancing emotional impact and structural clarity. This approach contrasts with polyphony, which emphasizes multiple independent melodies, as thematic unity prioritizes a singular thematic thread to unify the musical narrative.
Polyphony vs Thematic Unity: Core Differences
Polyphony and thematic unity represent distinct compositional approaches in music, where polyphony involves multiple independent melodic lines performed simultaneously, creating complex interweaving textures. Thematic unity centers on the repetition and development of a single, cohesive theme or motif throughout a piece, reinforcing structural coherence and memorability. While polyphony emphasizes contrapuntal interplay and textural richness, thematic unity prioritizes thematic consistency and narrative clarity within the composition.
Notable Examples of Polyphonic Works
Polyphony, characterized by multiple independent melodic lines, is exemplified in Johann Sebastian Bach's fugues and Giovanni Palestrina's masses, showcasing intricate interweaving of voices that maintain their distinctiveness. These works contrast with thematic unity, where a single theme or motif drives the composition's coherence, as seen in Beethoven's symphonies. Polyphonic compositions highlight complexity and texture, enriching the musical tapestry through contrapuntal techniques.
Famous Pieces Showcasing Thematic Unity
Beethoven's Symphony No. 5 exemplifies thematic unity through its iconic four-note motif that recurs and transforms across all movements, creating a cohesive narrative. Mozart's Symphony No. 40 in G minor demonstrates clear thematic unity by developing its main themes consistently, ensuring a tightly woven musical structure. Brahms' Symphony No. 1 also showcases thematic unity by employing recurring melodic ideas that bind the symphony's sections into a unified whole.
Impact on Listener Experience and Interpretation
Polyphony enhances listener experience by intertwining multiple independent melodic lines, creating rich textures that invite active interpretation and emotional engagement. Thematic unity provides cohesion through recurring motifs, guiding listeners toward a clear narrative or emotional journey. Balancing polyphony and thematic unity shapes both complex auditory landscapes and accessible interpretive frameworks, influencing how audiences perceive and connect with the music.
Choosing Between Polyphony and Thematic Unity in Modern Composition
Choosing between polyphony and thematic unity in modern composition depends on the desired textural complexity and narrative coherence. Polyphony enhances musical depth by interweaving independent melodic lines, fostering intricate interactions that evoke varied emotional responses. Thematic unity emphasizes consistency and development of a central motif, ensuring listener recognition and structural clarity throughout the piece.
Polyphony Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com