A compelling plot drives the narrative forward by introducing conflict, developing characters, and building suspense that keeps readers engaged. Well-structured plots balance rising action, climax, and resolution to create a satisfying storytelling experience. Discover how mastering plot techniques can transform your writing in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
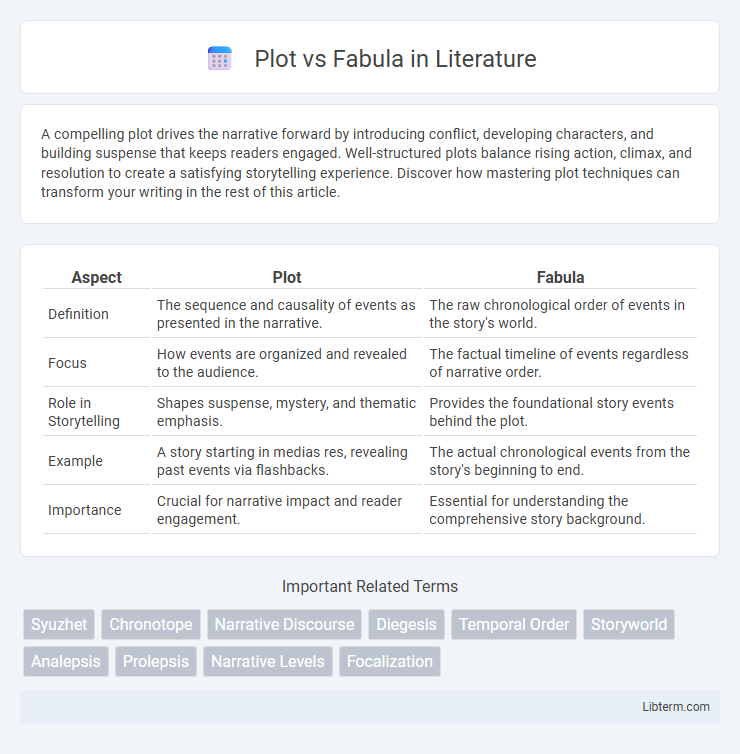
| Aspect | Plot | Fabula |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The sequence and causality of events as presented in the narrative. | The raw chronological order of events in the story's world. |
| Focus | How events are organized and revealed to the audience. | The factual timeline of events regardless of narrative order. |
| Role in Storytelling | Shapes suspense, mystery, and thematic emphasis. | Provides the foundational story events behind the plot. |
| Example | A story starting in medias res, revealing past events via flashbacks. | The actual chronological events from the story's beginning to end. |
| Importance | Crucial for narrative impact and reader engagement. | Essential for understanding the comprehensive story background. |
Understanding Plot and Fabula
Understanding plot and fabula is essential for analyzing narrative structure in literature and film. Fabula refers to the chronological sequence of events as they occur in the story world, while plot represents the way these events are presented to the audience, often involving manipulation of time and perspective. The distinction between plot and fabula enables deeper insight into storytelling techniques, narrative coherence, and authorial choices.
Origins of Plot and Fabula Concepts
The origins of plot and fabula concepts trace back to classical literary theory, notably Aristotle's Poetics, where fabula represents the chronological sequence of events, and plot is the structured presentation of those events in a narrative. Fabula encompasses the raw story events as they naturally occur, while plot involves the artistic arrangement and causality imposed by the storyteller to enhance thematic depth and emotional engagement. These concepts form the foundation for analyzing narrative structures across literature, theater, and film, distinguishing between story content and narrative technique.
Key Differences Between Plot and Fabula
Plot represents the structured sequence of events as they are presented in a narrative, often manipulated for dramatic effect, while fabula refers to the raw chronological order of events within the story world. The key difference lies in their temporal organization: fabula is the natural timeline, and plot is the rearranged timeline crafted to enhance storytelling. Understanding this distinction is crucial for analyzing narrative techniques in literature, film, and other media.
The Role of Chronology in Fabula
The role of chronology in fabula is to present events in their natural, sequential order, reflecting the actual timeline of occurrences within the story's universe. Fabula represents the raw, chronological narrative that underpins the plot, ensuring a coherent temporal structure that the audience can follow. This temporal sequence contrasts with the plot, which often rearranges events for thematic emphasis or dramatic effect, highlighting how fabula maintains fidelity to the story's original time frame.
Narrative Structure and Plot Organization
Plot refers to the structured sequence of events as presented in a narrative, emphasizing causal relationships and the deliberate arrangement of scenes to create suspense and thematic coherence. Fabula represents the raw chronological order of events in the story's universe, independent of how the narrative is constructed or disclosed to the audience. Effective narrative structure manipulates plot organization by reordering fabula elements to enhance engagement, such as using flashbacks, foreshadowing, or non-linear storytelling techniques.
Examples of Plot vs Fabula in Literature
In literature, the fabula represents the chronological sequence of events in a story, while the plot reorganizes these events for dramatic effect. For example, in "Pulp Fiction" by Quentin Tarantino, the fabula is a straightforward timeline of the characters' experiences, but the plot presents these events in a non-linear order, creating suspense and thematic depth. Similarly, in "Wuthering Heights" by Emily Bronte, the fabula follows the actual timeline of the Earnshaw and Linton families, whereas the plot uses multiple narrators and flashbacks to gradually reveal the story's emotional layers.
Why Distinguishing Plot from Fabula Matters
Distinguishing plot from fabula matters because it reveals how narratives are structured and understood by audiences, enhancing the analysis of storytelling techniques. Fabula refers to the raw chronological sequence of events in a story, while the plot is the specific arrangement of these events as presented to create suspense, surprise, or thematic emphasis. Understanding this difference allows critics and creators to explore how manipulation of narrative time shapes emotional impact and meaning in literature, film, and other storytelling media.
Fabula and Plot in Film Narratives
Fabula refers to the chronological sequence of events in a story, representing the raw narrative material in film narratives. Plot organizes these events in a deliberate, often non-linear manner to create suspense, reveal information, or develop character depth, making the narrative more engaging. Understanding the distinction between fabula and plot enhances analysis of film storytelling techniques and narrative structure.
Analyzing Stories Through Plot and Fabula
Plot refers to the structured sequence of events as presented in a narrative, while fabula is the chronological order of those events in the story world. Analyzing stories through plot and fabula helps to distinguish narrative techniques such as flashbacks, foreshadowing, and non-linear storytelling. Understanding the interplay between plot and fabula reveals how meaning and suspense are constructed in literature and film.
Tips for Writers: Balancing Plot and Fabula
Writers can enhance story engagement by carefully balancing plot and fabula, ensuring the narrative's chronological events (fabula) align with the structured presentation (plot) to maintain clarity and suspense. Employing techniques like non-linear storytelling or flashbacks requires meticulous planning to avoid confusing readers while enriching the narrative depth. Prioritize character development and thematic consistency within the plot structure to create a seamless interplay that resonates with audiences.
Plot Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com