Parody imitates the style of a particular genre, work, or author with deliberate exaggeration for comedic effect. It serves as a tool to critique, entertain, or highlight the original content's quirks while respecting its essence. Discover how parody shapes humor and cultural commentary throughout the rest of this article.
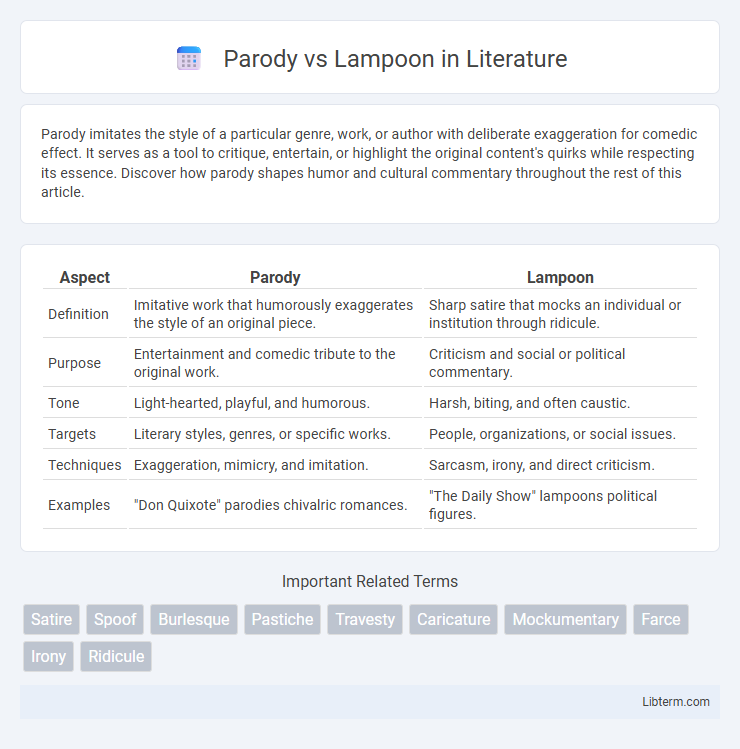
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Parody | Lampoon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Imitative work that humorously exaggerates the style of an original piece. | Sharp satire that mocks an individual or institution through ridicule. |
| Purpose | Entertainment and comedic tribute to the original work. | Criticism and social or political commentary. |
| Tone | Light-hearted, playful, and humorous. | Harsh, biting, and often caustic. |
| Targets | Literary styles, genres, or specific works. | People, organizations, or social issues. |
| Techniques | Exaggeration, mimicry, and imitation. | Sarcasm, irony, and direct criticism. |
| Examples | "Don Quixote" parodies chivalric romances. | "The Daily Show" lampoons political figures. |
Understanding Parody and Lampoon
Parody imitates the style or content of a work to create humor or critique through exaggeration and playful mimicry, often highlighting the original's distinctive features. Lampoon targets individuals, groups, or institutions with sharp, satirical ridicule aimed at exposing flaws or absurdities, frequently using irony and sarcasm. Understanding parody involves recognizing affectionate imitation, while lampoon involves direct, often harsh social or political criticism.
Defining Parody: Key Characteristics
Parody is a creative work that humorously imitates the style or content of an original piece, often exaggerating distinctive features to entertain or critique. Key characteristics include mimicry, exaggeration, and a clear reference to the source material, enabling audiences to recognize the original while enjoying its humorous twist. Unlike lampoon, parody leans more on playful imitation rather than direct satire or harsh criticism.
What is Lampoon? Core Features
A lampoon is a form of satire that sharply criticizes individuals, groups, or institutions through humor, irony, and exaggeration, often intended to ridicule or mock its target. Core features of a lampoon include its direct and aggressive tone, use of biting sarcasm, and a focus on exposing flaws or hypocrisy in a memorable and impactful manner. Unlike parody, which mimics style for humorous effect, a lampoon aims to provoke thought and highlight societal issues through pointed critique.
Historical Origins: Parody vs Lampoon
Parody originated in ancient Greece as a literary device used by poets like Aristophanes to mimic and humorously critique classical works, emphasizing imitation with exaggeration. Lampoon traces back to Renaissance Europe, emerging as satirical writings designed to publicly mock individuals or institutions through sharp, often biting commentary. Both forms developed as tools for social and political commentary, with parody relying on stylistic imitation and lampoon focusing on direct, scathing criticism.
Techniques Used in Parody
Parody employs techniques such as exaggeration, imitation, and irony to mimic and humorously critique the style or content of an original work, often enhancing recognizable features to highlight absurdities. It utilizes structural mimicry, including replicating narrative styles, character archetypes, or specific dialogues, to create a comedic effect that relies on audience familiarity with the source material. The technique of juxtaposition is common in parody, presenting exaggerated or incongruous elements side-by-side to emphasize the original work's flaws or peculiarities.
Satirical Tools of Lampoon
Lampoon employs sharp satire to mock or criticize individuals, institutions, or societal norms by exaggerating flaws and exposing absurdities with biting humor. Unlike parody, which mimics a specific work's style for comedic effect, lampoon uses direct, often scathing commentary as a satirical tool to provoke reflection or social change. This method relies on irony, sarcasm, and caricature to highlight hypocrisy and folly, making lampoon a powerful vehicle for cultural and political critique.
Famous Examples of Parody and Lampoon
Famous examples of parody include *Weird Al* Yankovic's music videos, which mimic popular songs with humorous twists, and the film *Scary Movie*, which parodies horror movie tropes. Iconic lampoons include Jonathan Swift's *A Modest Proposal*, a satirical essay lambasting social issues, and the TV show *Saturday Night Live*, known for its sharp political and celebrity lampooning. Both parody and lampoon use humor to critique, but parody imitates style while lampoon employs biting satire.
Impact on Society and Culture
Parody and lampoon both serve as powerful tools in shaping society and culture by critiquing and challenging prevailing norms, yet their impacts differ in tone and intention. Parody often employs humor and imitation to entertain while subtly provoking thought, making complex social issues more accessible and fostering cultural reflection. Lampoon, with its sharp and biting satire, aggressively exposes flaws and hypocrisy, prompting public discourse and sometimes sparking reform or social change.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Parody and lampoon both critique subjects through humor, but legal protections vary significantly, with parody often safeguarded under fair use doctrine due to its transformative nature, while lampoon may face higher risks of defamation claims because it targets personal character more aggressively. Ethical considerations emphasize respecting individuals' reputations and avoiding harm, making parody a generally accepted form of social commentary, whereas lampooning can cross ethical lines by promoting ridicule or malice. Courts evaluate intent, accuracy, and impact when determining legality, underscoring the fine balance creators must maintain between freedom of expression and responsible communication.
Choosing Between Parody and Lampoon
Choosing between parody and lampoon depends on the intent and tone of the critique. Parody mimics the style or content of the original work humorously to entertain while indirectly critiquing, often relying on exaggeration and imitation. Lampoon delivers a sharper, more biting satire aimed at exposing flaws or hypocrisy, frequently using ridicule and sarcasm for a more pointed social or political commentary.
Parody Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com