A metaphor is a powerful figure of speech that directly compares two unrelated things to highlight a shared quality, enriching language with vivid imagery and deeper meaning. By transforming abstract concepts into relatable visuals, metaphors engage your imagination and enhance understanding. Explore the rest of the article to discover how metaphors shape communication and creativity.
Table of Comparison
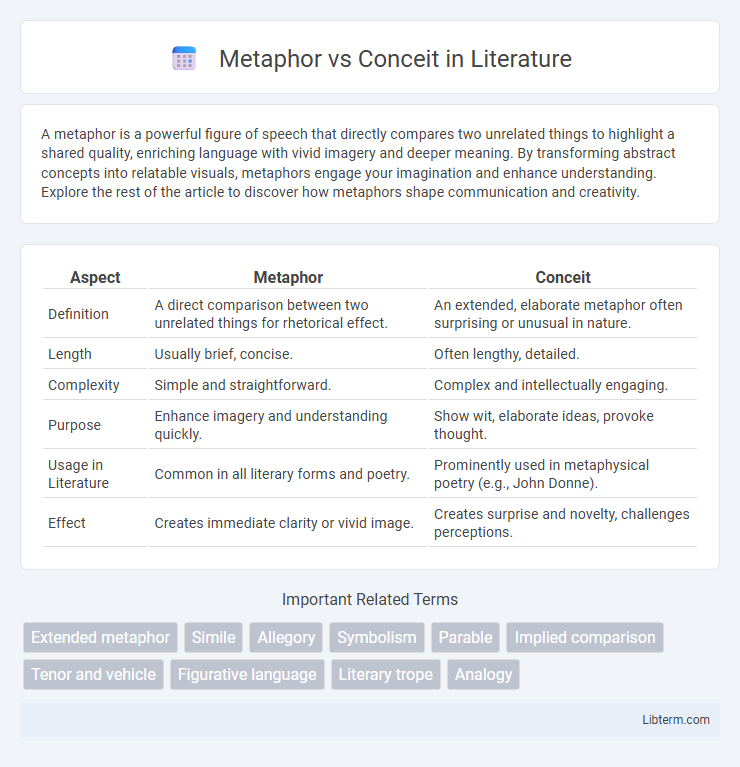
| Aspect | Metaphor | Conceit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A direct comparison between two unrelated things for rhetorical effect. | An extended, elaborate metaphor often surprising or unusual in nature. |
| Length | Usually brief, concise. | Often lengthy, detailed. |
| Complexity | Simple and straightforward. | Complex and intellectually engaging. |
| Purpose | Enhance imagery and understanding quickly. | Show wit, elaborate ideas, provoke thought. |
| Usage in Literature | Common in all literary forms and poetry. | Prominently used in metaphysical poetry (e.g., John Donne). |
| Effect | Creates immediate clarity or vivid image. | Creates surprise and novelty, challenges perceptions. |
Introduction to Metaphor and Conceit
A metaphor is a figure of speech that directly compares two unrelated things, highlighting their shared qualities to create vivid imagery. Conceit, a more elaborate or extended metaphor, often involves complex and ingenious comparisons that span multiple lines or an entire poem. Both devices enrich language by drawing imaginative connections, but conceits typically showcase greater intellectual complexity and originality.
Defining Metaphor: Meaning and Examples
Metaphor is a figure of speech that directly compares two unrelated things by stating one thing is another, enhancing meaning through symbolic representation. Examples include phrases like "Time is a thief" or "The world is a stage," where abstract concepts gain vivid imagery. Unlike conceit, which extends a metaphor with complex and elaborate comparisons, metaphors are typically concise and widely understood.
Understanding Conceit: Meaning and Examples
Conceit is an extended metaphor that establishes a strikingly elaborate or unusual comparison between two seemingly unrelated subjects, often found in poetry and literature. Unlike a simple metaphor that makes a brief direct comparison, a conceit develops the analogy throughout a passage or entire work, enhancing thematic depth and provoking thought. Famous examples include John Donne's comparison of lovers to a compass in "A Valediction: Forbidding Mourning" and Shakespeare's depiction of the world as a stage.
Historical Evolution of Metaphors
Metaphors have evolved from simple comparisons in ancient rhetoric to complex devices that shape cognitive frameworks across cultures. Conceits, emerging prominently in Renaissance and Baroque poetry, intensify metaphoric expression through elaborate and often surprising analogies. The historical evolution highlights metaphors' shift from straightforward linguistic tools to intricate conceptual constructs within literary traditions.
Evolution and Significance of Conceits
Conceits evolved during the Renaissance as elaborate, extended metaphors that juxtapose seemingly unrelated ideas to provoke deeper intellectual engagement and emotional response. Unlike simple metaphors, conceits emphasize ingenuity and complexity, often shaping the thematic framework of literary works, especially in metaphysical poetry. The significance of conceits lies in their ability to challenge conventional perceptions, enriching literary expression and expanding interpretive possibilities.
Key Differences between Metaphor and Conceit
Metaphor is a figure of speech that directly compares two unrelated things to highlight a shared quality, often brief and straightforward. Conceit, a more elaborate and extended form of metaphor, creates an intricate and far-fetched comparison, commonly found in poetry like John Donne's works. The key difference lies in the scope and complexity: metaphors are concise and implicit, while conceits develop a sustained and detailed analogy that invites deeper intellectual engagement.
Function of Metaphors in Literature
Metaphors in literature function as powerful tools to convey complex ideas and emotions by creating vivid imagery and enhancing readers' understanding through implicit comparisons. They facilitate deeper connections between abstract concepts and tangible experiences, enriching narrative layers and thematic depth. Conceits, as extended and elaborate metaphors, intensify this function by drawing striking and often unconventional parallels that challenge readers to engage more critically with the text.
Role of Conceits in Poetry and Prose
Conceits play a vital role in poetry and prose by creating elaborate and striking comparisons that deepen meaning and engage the reader's imagination more intensively than simple metaphors. They often link seemingly unrelated ideas in surprising ways, enhancing the emotional and intellectual impact of the text while highlighting the writer's creativity. Used skillfully, conceits can transform abstract concepts into vivid, memorable imagery that enriches narrative and poetic expression.
Metaphor vs. Conceit: Comparative Analysis
Metaphor and conceit both serve as figures of speech that draw comparisons, yet metaphors offer brief and straightforward analogies while conceits extend through elaborate and often surprising comparisons. Metaphors typically operate within the natural scope of understanding, linking two unlike things in a way that enhances meaning without extensive elaboration. Conceits, commonly found in metaphysical poetry, employ far-fetched or highly inventive parallels that provoke deeper reflection, emphasizing complexity and intellectual engagement over simplicity.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Metaphor and Conceit
Selecting between metaphor and conceit depends on the depth of comparison and complexity desired in literary expression. Metaphors provide concise, straightforward imagery that enhances clarity and immediate understanding, ideal for accessible communication. Conceits, often elaborate and extended, suit intricate themes requiring intellectual engagement and layered interpretation.
Metaphor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com