A straw man fallacy occurs when someone misrepresents an opponent's argument to make it easier to attack or refute. This tactic distorts the original position, leading to misunderstandings and weakening genuine debate. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to identify and counter straw man arguments effectively.
Table of Comparison
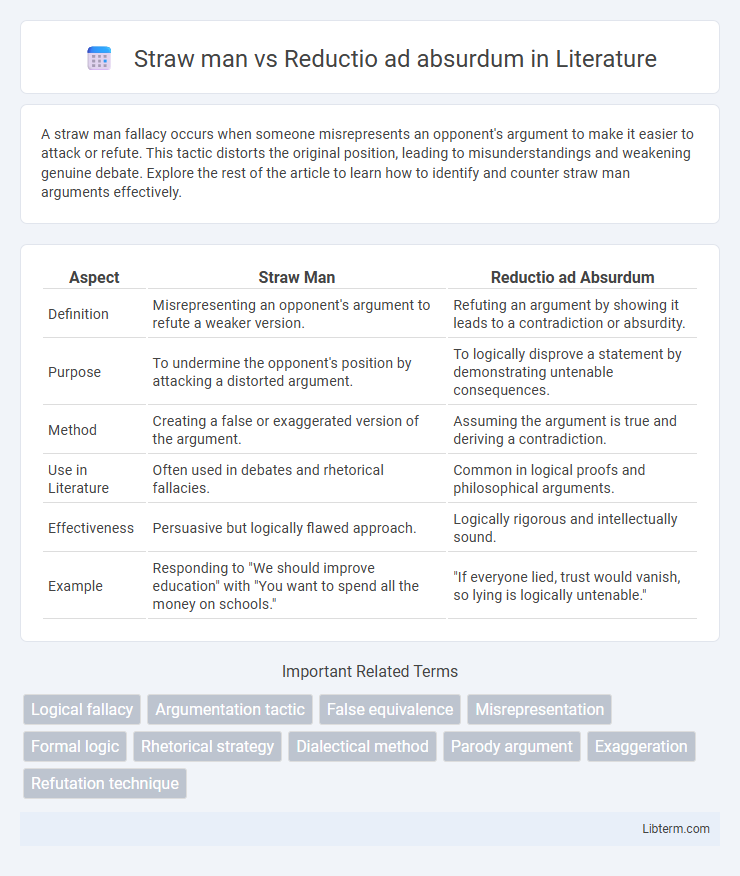
| Aspect | Straw Man | Reductio ad Absurdum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Misrepresenting an opponent's argument to refute a weaker version. | Refuting an argument by showing it leads to a contradiction or absurdity. |
| Purpose | To undermine the opponent's position by attacking a distorted argument. | To logically disprove a statement by demonstrating untenable consequences. |
| Method | Creating a false or exaggerated version of the argument. | Assuming the argument is true and deriving a contradiction. |
| Use in Literature | Often used in debates and rhetorical fallacies. | Common in logical proofs and philosophical arguments. |
| Effectiveness | Persuasive but logically flawed approach. | Logically rigorous and intellectually sound. |
| Example | Responding to "We should improve education" with "You want to spend all the money on schools." | "If everyone lied, trust would vanish, so lying is logically untenable." |
Introduction to Logical Fallacies
Straw man and reductio ad absurdum are distinct concepts in the study of logical fallacies, often encountered in critical thinking and argument analysis. The straw man fallacy involves misrepresenting or oversimplifying an opponent's argument to make it easier to attack, whereas reductio ad absurdum is a legitimate argumentative technique that demonstrates the absurdity of a claim by showing its logical consequences would be ridiculous or contradictory. Understanding the difference between these helps in identifying faulty reasoning and strengthening coherent, rational debates.
Defining the Straw Man Fallacy
The Straw Man fallacy occurs when someone misrepresents or oversimplifies an opponent's argument to make it easier to attack or refute. This distortion creates a weakened version of the original claim, diverting attention from the actual issue and misleading the audience. Unlike Reductio ad absurdum, which exposes logical contradictions within an argument, the Straw Man fallacy relies on deception rather than valid reasoning.
Mechanisms Behind Straw Man Arguments
Straw man arguments misrepresent an opponent's position by exaggerating, distorting, or oversimplifying it to create an easily attackable version. This mechanism involves intentionally construing a weakened or caricatured form of the original argument, making it simpler to refute while avoiding engagement with the genuine claims. Contrarily, reductio ad absurdum seeks to demonstrate that an argument leads to an absurd or contradictory conclusion by logically extending the original premise, rather than mischaracterizing it.
Understanding Reductio ad Absurdum
Reductio ad absurdum is a logical technique where an argument is disproven by showing that its premises lead to a contradiction or an absurd conclusion, highlighting the inconsistency within the original claim. Unlike the straw man fallacy, which misrepresents an opponent's position to easily refute it, reductio ad absurdum maintains the integrity of the argument while using rigorous logic to demonstrate its flaws. This method is fundamental in mathematical proofs and formal logic, reinforcing the importance of consistency and sound reasoning in argumentation.
Key Differences Between Straw Man and Reductio ad Absurdum
Straw man misrepresents an opponent's argument to easily refute it, often by exaggeration or distortion, while reductio ad absurdum demonstrates that a statement leads to absurd or contradictory conclusions, thereby disproving it logically. Straw man attacks a weakened version of a claim, whereas reductio ad absurdum relies on rigorous logical progression to show inconsistency. The key difference lies in Straw man's fallacious distortion versus reductio ad absurdum's legitimate logical technique.
Examples of Straw Man in Everyday Debate
Straw man examples in everyday debates include misrepresenting an opponent's argument by exaggerating or distorting their position, such as claiming someone who supports environmental regulations wants to eliminate all industry jobs. Another common instance is attacking a simplified or weakened version of a complex argument, like accusing a pro-healthcare reform advocate of wanting to completely nationalize all medical services without private options. These tactics divert attention from the original point, undermining genuine discussion and leading to misunderstandings.
Illustrative Cases of Reductio ad Absurdum
Reductio ad absurdum is a powerful argumentative technique used to demonstrate the falsity of a proposition by showing that its logical consequence leads to an absurd or contradictory outcome, such as in Zeno's paradoxes where infinite divisibility of space results in paradoxical conclusions about motion. Illustrative cases include Bertrand Russell's demonstration that naive set theory leads to paradoxes like Russell's paradox, thereby necessitating more rigorous axiomatic systems. Unlike the straw man fallacy, which misrepresents an opponent's argument for easy refutation, reductio ad absurdum rigorously derives contradictions to expose flaws in the original claim.
Common Misconceptions: Straw Man vs Reductio ad Absurdum
Common misconceptions often confuse straw man and reductio ad absurdum by incorrectly assuming both involve misrepresentation; straw man deliberately distorts an opponent's argument to easily refute it, while reductio ad absurdum logically demonstrates that an argument leads to absurd or contradictory conclusions. Straw man attacks a weakened or exaggerated version of the argument, undermining genuine debate, whereas reductio ad absurdum strengthens reasoning by revealing inherent flaws through contradiction. Understanding this distinction is essential for accurately analyzing critical thinking and rhetorical strategies.
Effectively Countering Straw Man and Misused Reductio
Effectively countering a Straw Man argument requires clearly restating your original position with precise evidence to expose the opponent's misrepresentation. Recognizing when Reductio ad absurdum is misused involves identifying exaggerated or illogical extensions of your argument that do not accurately reflect its true implications. Employing logical clarity and consistent definitions helps dismantle these fallacies while strengthening your argumentative stance.
Conclusion: Enhancing Critical Thinking Skills
Straw man and reductio ad absurdum are rhetorical techniques that critically impact logical argumentation. Recognizing a straw man fallacy, where an opponent's argument is misrepresented, prevents faulty reasoning and strengthens analytical skills. Employing reductio ad absurdum, which tests arguments by deriving contradictions, enhances the ability to evaluate the validity of claims and fosters deeper critical thinking.
Straw man Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com