Effective dialogue captures authentic speech patterns, revealing character emotions and advancing the plot naturally. Crafting meaningful exchanges requires balancing brevity with depth to maintain reader engagement and clarity. Discover how mastering dialogue can transform your storytelling by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
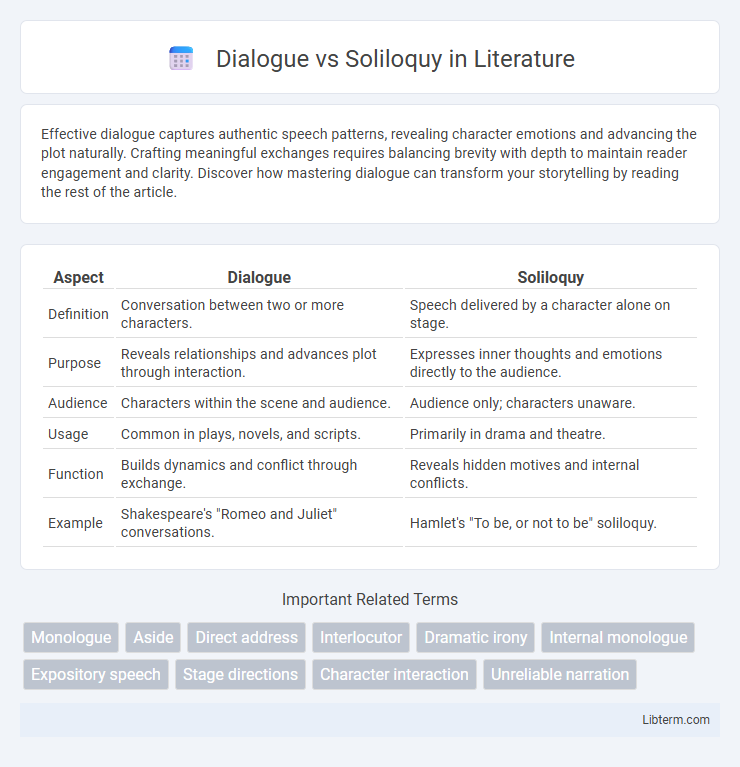
| Aspect | Dialogue | Soliloquy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conversation between two or more characters. | Speech delivered by a character alone on stage. |
| Purpose | Reveals relationships and advances plot through interaction. | Expresses inner thoughts and emotions directly to the audience. |
| Audience | Characters within the scene and audience. | Audience only; characters unaware. |
| Usage | Common in plays, novels, and scripts. | Primarily in drama and theatre. |
| Function | Builds dynamics and conflict through exchange. | Reveals hidden motives and internal conflicts. |
| Example | Shakespeare's "Romeo and Juliet" conversations. | Hamlet's "To be, or not to be" soliloquy. |
Understanding Dialogue and Soliloquy
Dialogue involves an exchange of spoken words between two or more characters, driving the plot and revealing relationships through interactive communication. Soliloquy is a dramatic device where a character speaks their inner thoughts aloud, often while alone on stage, offering deep insight into their emotions and motivations. Understanding the distinct functions of dialogue and soliloquy enhances the analysis of character development and narrative progression in literary and theatrical works.
Key Differences Between Dialogue and Soliloquy
Dialogue involves a conversation between two or more characters, driving the plot forward and revealing interpersonal dynamics. Soliloquy is a speech delivered by a single character who expresses inner thoughts and emotions directly to the audience. While dialogue emphasizes external communication, soliloquy focuses on internal reflection, providing insight into a character's motivations and psychological state.
Functions of Dialogue in Literature
Dialogue in literature serves multiple functions such as revealing character traits, advancing the plot, and creating conflict or tension between characters. It facilitates natural interaction that enhances realism and allows readers to infer relationships and emotions indirectly. Dialogue also provides exposition and background information, enriching the narrative without interrupting the story flow.
Purpose of Soliloquy in Drama
Soliloquy serves the crucial purpose of revealing a character's innermost thoughts, emotions, and conflicts directly to the audience, providing insight that dialogue between characters cannot convey. It allows playwrights to explore themes of internal struggle, conscience, and motivation, enhancing dramatic tension and character depth. Unlike dialogue, which facilitates interaction and plot progression, soliloquy offers a private moment of reflection that deepens understanding of the character's psyche.
Structural Elements of Dialogue
Dialogue consists of structured exchanges between two or more characters, featuring turn-taking where each speaker responds to the previous utterance, advancing the plot and revealing character relationships. It includes verbal interaction marked by question-answer sequences, interruptions, pauses, and overlapping speech, creating a dynamic rhythm that mimics real conversations. Unlike soliloquy, dialogue relies on interaction to develop dramatic tension and convey multiple perspectives simultaneously.
Characteristics of an Effective Soliloquy
An effective soliloquy reveals the character's innermost thoughts and emotions, offering deep psychological insight without the presence of other characters. It employs vivid, expressive language and maintains a natural flow that mirrors genuine contemplation, enhancing audience connection. The soliloquy drives the plot forward by exposing conflicts, motivations, or plans that remain hidden in dialogue.
Famous Examples of Dialogue in Plays
Dialogue in plays exemplifies dynamic character interaction and narrative progression, as seen in Shakespeare's "Hamlet," where Hamlet and Ophelia exchange revealing conversations that build emotional tension. Arthur Miller's "The Crucible" uses intense dialogue to explore themes of hysteria and integrity through characters like John Proctor and Abigail Williams. Samuel Beckett's "Waiting for Godot" features minimalist yet profound dialogue between Vladimir and Estragon, highlighting existential themes and human dependence on communication.
Iconic Soliloquies in Literary History
Iconic soliloquies, such as Hamlet's "To be or not to be" and Macbeth's "Tomorrow, and tomorrow, and tomorrow," reveal a character's inner turmoil through direct expression of thoughts, distinguishing them from dialogues, which involve interaction between characters. These soliloquies serve as pivotal moments in literary history, providing profound psychological insight and advancing the narrative without other characters' intervention. Shakespeare's mastery in crafting soliloquies highlights their significance as a dramatic device that deepens audience understanding of complex emotional and philosophical themes.
Impact on Character Development
Dialogue reveals character traits and emotional states through interactions and responses, allowing dynamic growth influenced by other characters. Soliloquy offers direct insight into a character's inner thoughts, emotions, and conflicts, providing a deep understanding of their motivations and psychological complexity. Both techniques enhance character development by showcasing external behavior and internal reflections, enriching narrative depth.
Dialogue vs Soliloquy: Which Drives the Story?
Dialogue drives the story by showcasing interactions between characters, advancing the plot through exchanges that reveal motivations, conflicts, and relationships. Soliloquy offers deep insight into a single character's inner thoughts and emotions, providing context but not direct plot movement. Effective storytelling balances dialogue's forward momentum with soliloquy's introspective depth to create a compelling narrative.
Dialogue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com