Bard is an advanced AI chatbot developed by Google, designed to provide accurate and context-aware responses across various topics. Leveraging cutting-edge natural language processing technology, it enhances user interactions by understanding and generating human-like text. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Bard can elevate your digital communication experience.
Table of Comparison
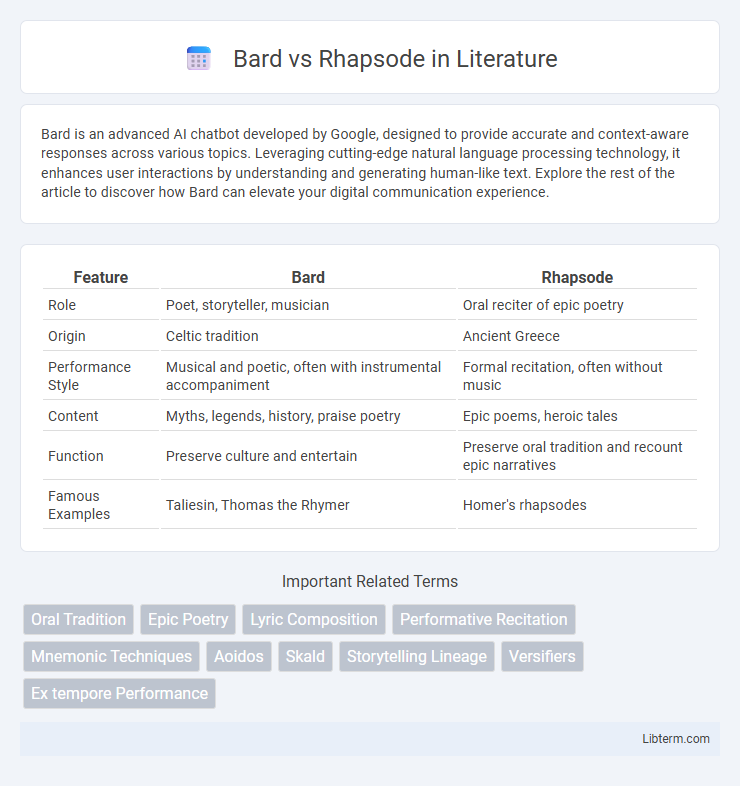
| Feature | Bard | Rhapsode |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Poet, storyteller, musician | Oral reciter of epic poetry |
| Origin | Celtic tradition | Ancient Greece |
| Performance Style | Musical and poetic, often with instrumental accompaniment | Formal recitation, often without music |
| Content | Myths, legends, history, praise poetry | Epic poems, heroic tales |
| Function | Preserve culture and entertain | Preserve oral tradition and recount epic narratives |
| Famous Examples | Taliesin, Thomas the Rhymer | Homer's rhapsodes |
Introduction to Bards and Rhapsodes
Bards and rhapsodes were ancient performers central to Greek oral tradition, with bards typically known for composing and singing epic poetry that preserved cultural heritage. Rhapsodes specialized in reciting and performing established poetic works, often engaging audiences through dramatic delivery and memorization techniques. Both roles were instrumental in maintaining and transmitting mythology, history, and cultural values in pre-literate societies.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Bards originated in ancient Celtic cultures as oral poets and storytellers preserving history and genealogies through song, while rhapsodes emerged in ancient Greece specializing in the performance of epic poetry such as Homer's Iliad and Odyssey. The evolution of bards was closely tied to the Gaelic tradition, where they became esteemed figures in medieval courts, whereas rhapsodes functioned primarily as itinerant performers whose role diminished with the advent of written literature. Both roles illustrate the transition from oral to written cultural transmission but reflect distinct regional practices and artistic forms in the preservation and dissemination of early literature.
Cultural Significance in Ancient Societies
Bards and rhapsodes played crucial roles in preserving and transmitting oral traditions in ancient societies, with bards often serving as cultural historians and genealogists in Celtic regions. Rhapsodes, primarily active in ancient Greece, specialized in reciting epic poetry like Homer's Iliad and Odyssey, thereby reinforcing communal values and collective identity through performance. Both figures embodied the cultural significance of storytelling, ensuring the continuity of mythology, history, and moral lessons across generations.
Roles and Functions in Storytelling
Bards serve as poetic storytellers who preserve cultural heritage through songs and epic tales, often incorporating music to engage audiences emotionally. Rhapsodes specialize in reciting and performing existing narratives with dramatic expression, primarily focusing on oral transmission rather than original composition. Both roles maintain oral traditions but differ in their creative input and performance styles within storytelling.
Performance Styles and Techniques
Bards employ a narrative performance style that combines storytelling with music, using lyrical poetry, song, and instrumental accompaniment to evoke emotion and preserve cultural history. Rhapsodes specialize in declamatory recitations of epic poetry, emphasizing rhythmic speech, dramatic pauses, and vocal modulation to engage listeners through oral tradition. Both utilize mnemonic devices, but bards integrate melody and harmony, whereas rhapsodes focus primarily on poetic meter and verbal artistry.
Key Differences Between Bard and Rhapsode
Bards are storytellers and musicians who blend poetry, music, and performance to preserve and transmit cultural history, often personalizing tales with emotional expression. Rhapsodes specialize in the oral recitation of epic poetry, emphasizing standardized, formalized presentations of established works like Homeric epics. While bards engage audiences through creative adaptation and musical accompaniment, rhapsodes prioritize faithful, rhythmic narration of canonical texts without significant alteration.
Famous Bards and Renowned Rhapsodes
Famous bards such as William Shakespeare and Robert Burns are celebrated for their poetic storytelling and musical compositions that have influenced literature and culture for centuries. Renowned rhapsodes like Homer, traditionally credited with composing the Iliad and the Odyssey, specialized in oral recitations of epic poetry, preserving ancient myths and histories. While bards often combined poetry and music, rhapsodes primarily focused on the memorization and live performance of lengthy narrative verses, shaping the way stories were shared in the classical world.
Influence on Literature and Oral Tradition
Bards shaped literature and oral tradition by preserving epic stories and genealogies through melodic recitations, ensuring cultural continuity across generations in Celtic and medieval societies. Rhapsodes, prominent in ancient Greece, performed and composed epic poetry, notably Homeric epics, advancing literary forms and public entertainment through their authoritative interpretations. Both roles significantly impacted narrative transmission, with bards emphasizing communal memory and rhapsodes influencing literary canons and performance styles.
Modern Interpretations and Legacy
Modern interpretations of Bard and Rhapsode highlight contrasting approaches to oral tradition and performance in literature. Bards are often seen as versatile storytellers preserving cultural memory through song and poetry, while Rhapsodes are recognized for their specialized recitations of epic poetry, emphasizing accuracy and dramatic delivery. The legacy of both roles shapes contemporary understandings of narrative art, influencing modern authors, performers, and scholars in their exploration of oral history and literary expression.
Conclusion: Bard vs Rhapsode in Context
Bard and Rhapsode both serve as performers of epic poetry, with the Bard often integrating music and storytelling, while the Rhapsode emphasizes recitation of literary works. In historical and cultural contexts, the Bard acts as a creative storyteller, shaping narratives through song, whereas the Rhapsode preserves and delivers fixed poetic texts. Understanding their distinct roles highlights variations in oral tradition and cultural transmission across ancient societies.
Bard Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com