A monologue is a powerful theatrical device where a single character speaks aloud, revealing inner thoughts or advancing the plot. It often provides deep insight into the character's emotions, motivations, and conflicts, captivating the audience's attention. Discover how mastering monologues can elevate your performance by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
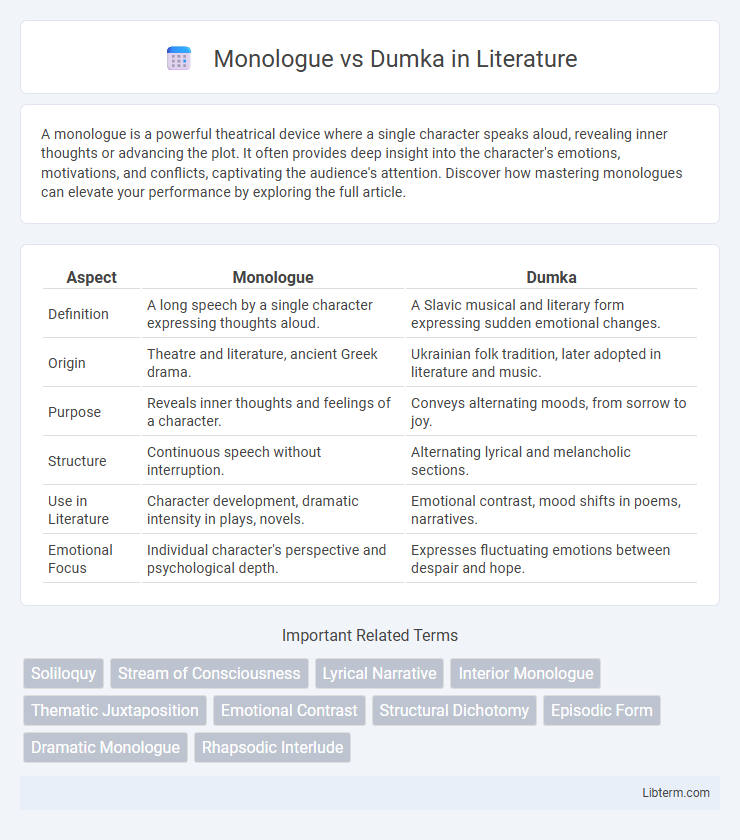
| Aspect | Monologue | Dumka |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A long speech by a single character expressing thoughts aloud. | A Slavic musical and literary form expressing sudden emotional changes. |
| Origin | Theatre and literature, ancient Greek drama. | Ukrainian folk tradition, later adopted in literature and music. |
| Purpose | Reveals inner thoughts and feelings of a character. | Conveys alternating moods, from sorrow to joy. |
| Structure | Continuous speech without interruption. | Alternating lyrical and melancholic sections. |
| Use in Literature | Character development, dramatic intensity in plays, novels. | Emotional contrast, mood shifts in poems, narratives. |
| Emotional Focus | Individual character's perspective and psychological depth. | Expresses fluctuating emotions between despair and hope. |
Understanding Monologue: Definition and Features
A monologue is a dramatic speech delivered by a single character, expressing inner thoughts or emotions directly to the audience or other characters. Key features include extended length, narrative depth, and the ability to reveal motivation, conflict, and personality. Unlike a dumka, which is a musical form marked by contrasting moods and folk influences, a monologue centers on verbal expression and psychological insight.
Defining Dumka: Historical and Cultural Context
Dumka, a musical form rooted in Eastern European folk traditions, originated as a sorrowful, narrative ballad characterized by alternating slow, melancholic verses and faster, lively sections. Historically associated with Ukrainian and Slavic cultures, dumkas convey deep emotional contrasts and storytelling, often expressing themes of longing, struggle, and hope. Unlike a monologue, which is a single-speaker dramatic or literary speech, dumka integrates this rich cultural heritage into musical expression, blending narrative depth with melodic variation.
Structural Differences Between Monologue and Dumka
Monologue typically consists of a single speaker presenting a continuous speech or narrative, often structured with a clear beginning, middle, and end, emphasizing character development and emotional expression. Dumka, originating from Slavic folk traditions, features alternating slow, melancholic sections and faster, lively passages, creating a contrasting, episodic structure that highlights shifts in mood and tempo. The primary structural difference lies in Monologue's linear, singular narrative flow versus Dumka's cyclical alternation between contrasting musical themes and emotional states.
Emotional Expression: Monologue vs Dumka
Monologue emphasizes a singular emotional perspective, allowing deep exploration of one character's inner thoughts and feelings. Dumka, rooted in Slavic folk tradition, features contrasting moods within a single piece, blending melancholy with moments of joy or nostalgia. This dynamic emotional interplay in Dumka creates a more varied and dramatic expression compared to the focused intensity of a monologue.
Origins and Evolution: From Stage to Slavic Roots
Monologue, rooted in ancient Greek theater, evolved from solo performance art emphasizing individual expression and introspection on stage. Dumka, originating in Slavic musical traditions, is a melancholic folk song form reflecting emotional storytelling and cultural heritage. Both forms transformed through time, with monologues shaping dramatic literature and dumkas influencing classical compositions by composers like Dvorak and Bartok.
Common Themes in Monologue and Dumka
Monologues and Dumkas often explore inner emotions and personal reflections, revealing the speaker's psychological depth. Both forms emphasize themes of solitude, emotional conflict, and introspection, highlighting the complexity of individual experience. This shared focus allows audiences to connect intimately with the character's thoughts and feelings.
Linguistic and Stylistic Characteristics Compared
Monologue typically features a single speaker expressing inner thoughts or narrating events, characterized by a coherent, continuous speech with a consistent tone and formal or informal language depending on context. Dumka, derived from Slavic musical and literary traditions, combines alternating moods of melancholy and exuberance, reflected in its fragmented, often rhythmic and lyrical stylistic shifts that evoke emotional contrasts. Linguistically, monologues rely on extended, uninterrupted discourse promoting clarity and depth, while Dumka employs stylistic variances and tonal modulation to create dynamic, mood-driven narratives.
Use in Literature, Music, and Art
Monologue serves as a powerful literary device, enabling deep exploration of a character's thoughts and emotions in plays and novels. Dumka, originating as a Slavic musical form, blends melancholic verses with lively refrains, influencing Eastern European classical compositions and folk music. In art, monologue-inspired works emphasize introspection and solitude, while dumka-themed pieces often capture the contrasting moods of melancholy and spirited joy.
Impact on Audience: Engaging Through Words and Melody
Monologue captivates audiences through direct, intense verbal expression, allowing deep insight into a character's emotions and thoughts, creating a powerful psychological impact. Dumka, with its melancholic Slavic folk roots and alternating slow and fast tempos, engages listeners emotionally through evocative melodies that convey sorrow and hope simultaneously. The blend of spoken drama in monologues and the lyrical musicality in dumkas offers unique immersive experiences that resonate differently but profoundly with audiences.
Modern Adaptations and Influences
Modern adaptations of the monologue emphasize internal conflict and character psychology, often integrating multimedia elements to enhance narrative depth. Dumka, originally a Slavic folk lament, influences contemporary classical and fusion music by blending melancholic melodies with modern orchestration techniques. Both forms inspire innovative storytelling in theater and music, reflecting evolving cultural expressions and emotional complexities.
Monologue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com