A motto captures the core values and guiding principles that drive an individual or organization, serving as a concise statement of purpose and inspiration. It helps align actions with goals, reinforcing commitment and motivation in challenging situations. Discover how crafting the perfect motto can empower your journey by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
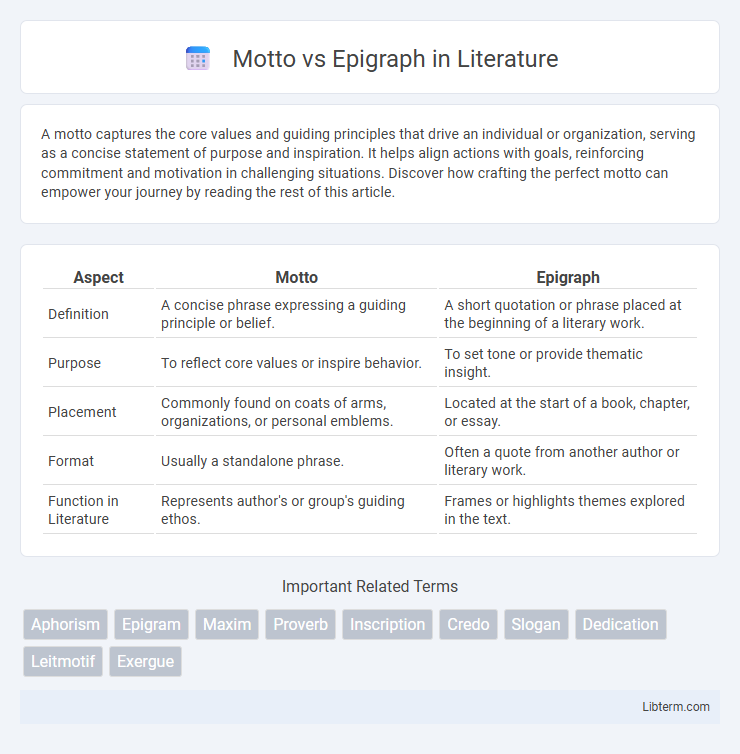
| Aspect | Motto | Epigraph |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A concise phrase expressing a guiding principle or belief. | A short quotation or phrase placed at the beginning of a literary work. |
| Purpose | To reflect core values or inspire behavior. | To set tone or provide thematic insight. |
| Placement | Commonly found on coats of arms, organizations, or personal emblems. | Located at the start of a book, chapter, or essay. |
| Format | Usually a standalone phrase. | Often a quote from another author or literary work. |
| Function in Literature | Represents author's or group's guiding ethos. | Frames or highlights themes explored in the text. |
Introduction to Mottos and Epigraphs
Mottos are concise phrases or sentences expressing the guiding principles or beliefs of an individual, group, or institution, often encapsulating core values in a memorable way. Epigraphs, by contrast, are brief quotations or excerpts placed at the beginning of a book, chapter, or essay, intended to set a thematic tone or provide insight into the content. Both serve distinct purposes in literature and culture, with mottos emphasizing identity and epigraphs enhancing thematic depth.
Defining a Motto
A motto is a concise phrase or sentence that encapsulates the core values, guiding principles, or mission of an individual, organization, or group, often used to inspire or motivate. It serves as a personal or collective creed, reflecting identity and purpose in a memorable form. Unlike an epigraph, which is a quotation or phrase placed at the beginning of a text to set a thematic tone, a motto functions as a permanent emblem of belief or ambition.
Understanding Epigraphs
Epigraphs are brief quotations or sayings engraved or printed at the beginning of a book or chapter to suggest its theme or underlying message. Unlike mottos, which express guiding principles or beliefs often associated with individuals, organizations, or families, epigraphs serve as literary devices to frame the reader's interpretation of the text. Understanding epigraphs involves analyzing their source, context, and relevance to the work's central ideas, enriching the reader's engagement with the narrative.
Key Differences Between Motto and Epigraph
Mottos are concise phrases embodying the core values or guiding principles of individuals, organizations, or nations, serving as lifelong commitments. Epigraphs are short quotations or sayings placed at the beginning of literary works to set the theme or tone, often attributed to other authors. While mottos express enduring identity or mission, epigraphs function as thematic introductions influencing readers' interpretations.
Historical Origins of Mottos
Mottos trace their origins to ancient heraldry, serving as concise expressions of family values or ideals often inscribed on coats of arms during medieval Europe. These phrases encapsulated guiding principles or aspirations, providing identity and inspiration for noble lineages. Unlike epigraphs, which originated mainly as literary or monumental inscriptions, mottos evolved as personal or institutional emblems with deep historical significance tied to lineage and tradition.
The Role of Epigraphs in Literature
Epigraphs serve as concise literary devices that provide thematic insight or set the tone for a work by quoting a relevant text, often from another author or source. Unlike mottos, which express guiding principles or beliefs, epigraphs function as interpretive lenses, enriching readers' understanding of the narrative or its underlying ideas. Authors use epigraphs strategically to foreshadow themes, establish context, and create intertextual connections that deepen the reading experience.
Purposes and Functions in Writing
Mottos serve as concise, memorable phrases encapsulating core values or guiding principles, often used by individuals, organizations, or communities to establish identity and inspire action. Epigraphs function as brief quotations placed at the beginning of literary works or chapters, setting thematic tone, offering insight, or framing the reader's understanding. Both devices enhance writing by reinforcing purpose: mottos emphasize enduring ideals, while epigraphs provide contextual or interpretive cues.
Famous Examples of Mottos and Epigraphs
Mottos like "In God We Trust" on the U.S. currency embody national values and identity, while epigraphs such as the opening quote of Gabriel Garcia Marquez's *One Hundred Years of Solitude* set thematic tones for literary works. Famous epigraphs often derive from classical literature or philosophical texts, adding depth and context before the main text begins, exemplified by T.S. Eliot's use of Dante in *The Waste Land*. Mottos typically function as succinct, guiding principles for organizations or countries, whereas epigraphs serve as interpretive aids, bridging the author's vision with readers' expectations.
Choosing Between a Motto and an Epigraph
Choosing between a motto and an epigraph depends on the intended purpose and placement in a text or organization. A motto serves as a concise statement embodying core values or guiding principles, often used by institutions, families, or individuals to inspire identity and commitment. An epigraph functions as a brief quotation or phrase placed at the beginning of a literary work or chapter, providing thematic framing or context that enriches the reader's understanding.
Conclusion: Enhancing Meaning through Mottos and Epigraphs
Mottos and epigraphs both enrich texts by encapsulating core values or themes in concise phrases, often guiding readers' interpretation and framing the narrative's message. Mottos typically express enduring principles or ideals associated with a person, group, or institution, while epigraphs set the tone or provide thematic context, often quoting another work. Using mottos and epigraphs strategically enhances meaning by inviting reflection, deepening understanding, and connecting the audience to broader cultural or philosophical ideas.
Motto Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com