Naturalism emphasizes the portrayal of reality through detailed observation and a focus on the environment's influence on human behavior. This literary and artistic movement highlights the deterministic aspects of life, often illustrating how social conditions and heredity shape individuals. Explore the rest of this article to understand how Naturalism continues to impact contemporary storytelling and art.
Table of Comparison
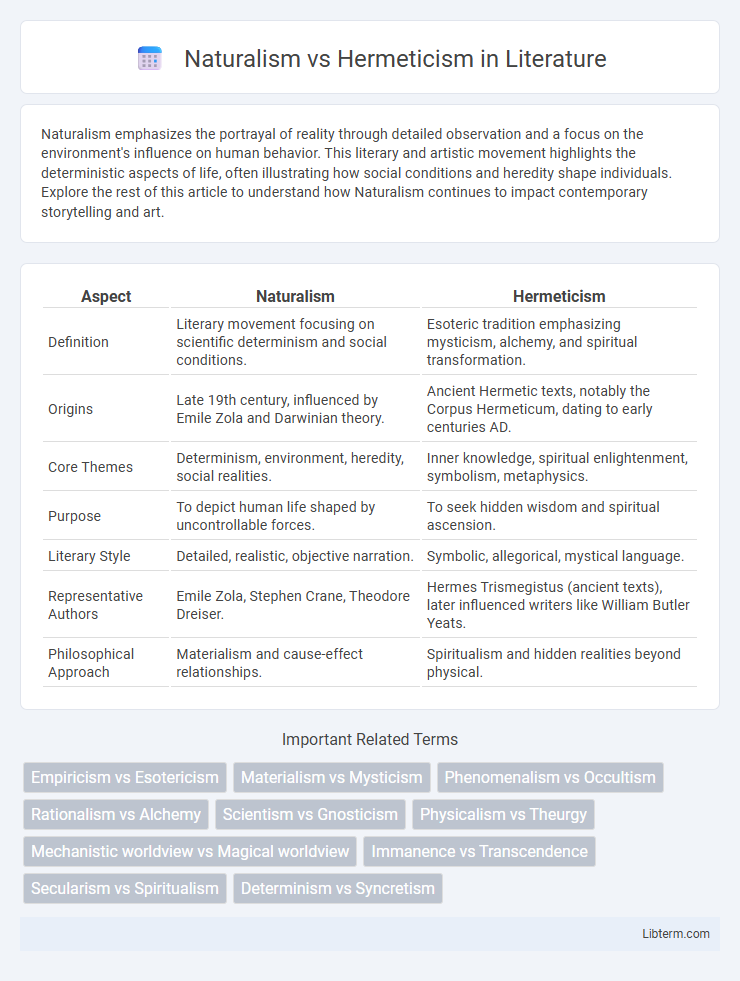
| Aspect | Naturalism | Hermeticism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Literary movement focusing on scientific determinism and social conditions. | Esoteric tradition emphasizing mysticism, alchemy, and spiritual transformation. |
| Origins | Late 19th century, influenced by Emile Zola and Darwinian theory. | Ancient Hermetic texts, notably the Corpus Hermeticum, dating to early centuries AD. |
| Core Themes | Determinism, environment, heredity, social realities. | Inner knowledge, spiritual enlightenment, symbolism, metaphysics. |
| Purpose | To depict human life shaped by uncontrollable forces. | To seek hidden wisdom and spiritual ascension. |
| Literary Style | Detailed, realistic, objective narration. | Symbolic, allegorical, mystical language. |
| Representative Authors | Emile Zola, Stephen Crane, Theodore Dreiser. | Hermes Trismegistus (ancient texts), later influenced writers like William Butler Yeats. |
| Philosophical Approach | Materialism and cause-effect relationships. | Spiritualism and hidden realities beyond physical. |
Introduction to Naturalism and Hermeticism
Naturalism asserts that all phenomena can be explained through natural causes and laws without invoking supernatural elements, emphasizing empirical observation and scientific reasoning as foundations for understanding reality. Hermeticism, rooted in esoteric traditions and ancient texts credited to Hermes Trismegistus, explores mystical knowledge, spiritual transformation, and the interconnectedness of the cosmos through symbolic teachings and alchemical principles. These contrasting worldviews shape foundational beliefs about existence, knowledge, and the nature of the universe, influencing diverse philosophical and spiritual practices.
Historical Origins and Development
Naturalism, rooted in ancient Greek philosophy, emphasizes understanding the universe through observable phenomena and empirical evidence, with early proponents like Democritus and Epicurus shaping its foundation. Hermeticism, originating from Hellenistic Egypt and attributed to the mythic figure Hermes Trismegistus, blends Greco-Egyptian spiritual traditions with alchemical, astrological, and mystical knowledge, influencing Renaissance esotericism. The development of Naturalism advanced through scientific methods during the Enlightenment, while Hermeticism persisted as a mystical framework intertwining spirituality and occult sciences.
Core Philosophical Principles
Naturalism asserts that reality is exclusively composed of natural elements and forces, emphasizing empirical observation and scientific inquiry as the means to understand existence. Hermeticism centers on esoteric wisdom, spiritual transformation, and the interconnectedness of the cosmos, advocating for hidden knowledge accessible through mystical practices. The core philosophical divergence lies in Naturalism's reliance on observable phenomena versus Hermeticism's focus on metaphysical and symbolic interpretation of reality.
Views on Nature and the Cosmos
Naturalism views nature as a self-sustaining system governed by physical laws, where the cosmos operates without supernatural intervention, emphasizing empirical observation and scientific explanation. Hermeticism perceives the cosmos as a manifestation of divine principles, where nature is interconnected through mystical correspondences and spiritual forces that transcend material reality. This contrast highlights naturalism's reliance on observable phenomena against hermeticism's focus on hidden, esoteric knowledge linking the microcosm and macrocosm.
Understanding Human Existence
Naturalism explains human existence through physical processes, emphasizing biological evolution, neuroscience, and empirical evidence to understand consciousness and behavior. Hermeticism interprets human existence as a spiritual journey, stressing the connection between the microcosm and macrocosm, and the pursuit of inner knowledge and cosmic harmony. This contrast highlights the material basis of Naturalism versus the metaphysical focus of Hermeticism in exploring the nature of being.
Naturalism’s Emphasis on Science and Empiricism
Naturalism prioritizes science and empiricism by asserting that all phenomena can be explained through natural causes and observable evidence, rejecting supernatural or mystical explanations commonly found in Hermeticism. This philosophical approach relies on systematic observation, experimentation, and the scientific method to understand reality, emphasizing materialism and physical laws. In contrast, Hermeticism centers on esoteric knowledge, spiritual insights, and metaphysical principles that transcend empirical verification.
Hermeticism’s Mystical and Esoteric Teachings
Hermeticism emphasizes mystical and esoteric teachings rooted in ancient wisdom, focusing on the transcendence of ordinary reality through divine knowledge and spiritual alchemy. Its core principles include the unity of the cosmos, the interconnectedness of mind and matter, and the pursuit of gnosis to unlock hidden truths within the self and the universe. Hermetic texts like the Corpus Hermeticum explore these mystical concepts, contrasting sharply with Naturalism's empirical and materialistic worldview.
Key Figures and Texts
Naturalism is prominently associated with figures like Democritus and Epicurus, whose works such as "On Nature" emphasize a materialistic universe governed by natural laws. Hermeticism centers on writings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, including the "Corpus Hermeticum," which explores cosmic principles and spiritual transformation through esoteric knowledge. The key texts in Naturalism prioritize empirical observation and rationalism, while Hermeticism focuses on mystical wisdom and metaphysical insights.
Influence on Modern Thought
Naturalism's emphasis on empirical evidence and scientific methodology profoundly shaped modern scientific inquiry and secular philosophy, promoting a worldview grounded in observable phenomena. Hermeticism contributed to the development of esoteric traditions and influenced Renaissance humanism, leaving a legacy in metaphysical thought and the exploration of inner spirituality. The interplay between Naturalism's rationalism and Hermeticism's mystical insights continues to inform contemporary debates on the nature of reality and consciousness.
Comparative Analysis: Similarities and Differences
Naturalism emphasizes a materialistic worldview where all phenomena arise from natural causes without supernatural intervention, while Hermeticism is a spiritual philosophy centered on esoteric knowledge, mysticism, and the belief in occult forces governing the universe. Both systems explore the nature of reality and human existence but diverge fundamentally in approach, with Naturalism relying on empirical evidence and scientific method, and Hermeticism embracing metaphysical principles and symbolic interpretation. The comparative analysis reveals that while Naturalism focuses on observable facts and reproducibility, Hermeticism prioritizes hidden wisdom and spiritual transformation, highlighting the contrast between rational inquiry and mystical experience.
Naturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com