Expert commentary offers insightful analysis that deepens your understanding of complex topics by highlighting key perspectives and trends. These thoughtful interpretations connect facts with broader implications, enriching your knowledge base. Explore the full article to discover detailed insights that will enhance your grasp of the subject.
Table of Comparison
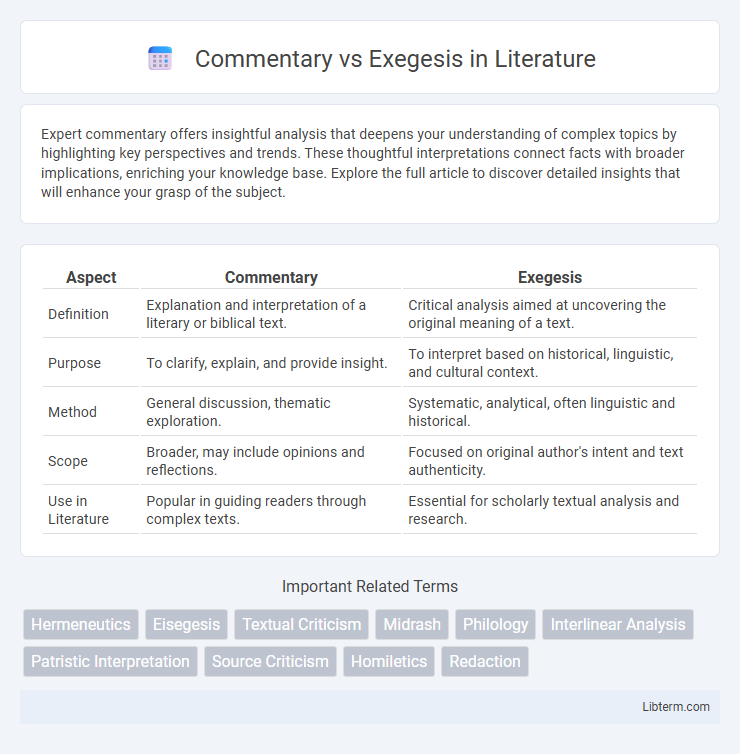
| Aspect | Commentary | Exegesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Explanation and interpretation of a literary or biblical text. | Critical analysis aimed at uncovering the original meaning of a text. |
| Purpose | To clarify, explain, and provide insight. | To interpret based on historical, linguistic, and cultural context. |
| Method | General discussion, thematic exploration. | Systematic, analytical, often linguistic and historical. |
| Scope | Broader, may include opinions and reflections. | Focused on original author's intent and text authenticity. |
| Use in Literature | Popular in guiding readers through complex texts. | Essential for scholarly textual analysis and research. |
Understanding Commentary and Exegesis
Commentary involves explanation and interpretation of a text, often blending historical context, linguistic analysis, and theological insights to clarify meaning. Exegesis specifically refers to the critical examination and systematic analysis of a text, aiming to uncover the original intent and meaning based on language, culture, and historical background. Understanding commentary requires recognizing it as a broader, often more interpretive, approach, while exegesis demands a precise, scholarly method focused on textual fidelity and context.
Defining Commentary in Biblical Studies
Commentary in biblical studies refers to a detailed explanation and interpretation of scriptural texts, often written by scholars to clarify meaning, historical context, and theological significance. It provides verse-by-verse analysis, addressing linguistic, cultural, and doctrinal elements to enhance understanding for readers and students. Unlike exegesis, which is a critical and systematic process of extracting original meaning from the text, commentary compiles and communicates these insights for broader educational purposes.
What is Exegesis?
Exegesis is the critical interpretation and explanation of a biblical text, aiming to uncover the original meaning intended by the author within its historical, cultural, and linguistic context. It involves detailed linguistic analysis, examination of the original languages such as Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek, and consideration of relevant historical background to provide an accurate understanding of scripture. Unlike general commentary, exegesis relies heavily on scholarly methods and primary sources to produce precise and objective biblical interpretation.
Historical Development of Commentary and Exegesis
The historical development of commentary and exegesis reflects distinct but overlapping scholarly traditions aimed at interpreting texts, particularly religious scriptures. Commentary evolved as detailed scholarly notes accompanying a text, serving to explain language, context, and interpretative nuances, prominently seen in Greco-Roman and medieval biblical scholarship. Exegesis developed as a systematic, critical method focused on uncovering the original meaning of a text through historical, linguistic, and cultural analysis, gaining prominence during the Enlightenment and modern biblical studies.
Purpose and Goals: Commentary vs Exegesis
Commentary aims to explain and interpret a text by providing historical context, linguistic analysis, and thematic insights to enhance understanding. Exegesis seeks to uncover the original meaning and intent of the text through critical examination and contextual study, often focusing on theological or doctrinal accuracy. Both serve to illuminate scriptures, but commentary integrates broader reflections while exegesis concentrates on precise, scholarly interpretation.
Methods Used in Commentary
Commentary methods typically involve a detailed, line-by-line analysis of a text, integrating historical context, linguistic study, and theological interpretation to clarify meaning. Scholars use comparative analysis with other texts and consider the author's intent, cultural background, and literary style to provide insight. This method contrasts with exegesis, which primarily focuses on extracting the original meaning from the text through critical examination and contextual understanding.
Techniques of Exegesis
Techniques of exegesis include textual analysis, examining the original language and context to uncover deeper meanings within the scripture. Historical-critical methods assess the cultural, historical, and literary background to provide accurate interpretation. Intertextual comparison and theological reflection are also essential for connecting scriptural passages and understanding their implications comprehensively.
Key Differences Between Commentary and Exegesis
Commentary provides an interpretative explanation of a text, often reflecting the author's perspectives and broader theological or historical context, while exegesis involves a critical, systematic analysis aimed at uncovering the original meaning of the text based on linguistic, cultural, and textual evidence. Exegesis emphasizes precise examination of grammar, syntax, and semantic nuances of the original language, whereas commentary tends to synthesize these findings with practical applications and doctrinal insights. The key difference lies in exegesis's objective approach to interpreting the text itself, contrasted with commentary's more subjective and explanatory nature.
Importance in Modern Theological Studies
Commentary and exegesis play crucial roles in modern theological studies by providing detailed analysis and interpretation of sacred texts. Exegesis systematically uncovers the original meaning through linguistic and historical context, enabling accurate theological insights. Commentary synthesizes exegetical findings, offering contemporary application and deeper understanding, essential for informed doctrinal development and interfaith dialogue.
Choosing Between Commentary and Exegesis
Choosing between commentary and exegesis depends on the depth of biblical analysis needed; commentary offers concise explanations and practical applications, making it suitable for general study or sermon preparation. Exegesis provides a detailed, word-for-word examination of the original texts, ideal for academic research and in-depth theological work. Scholars and students should assess their goals and the complexity of the passage to determine whether a broad interpretative overview or rigorous textual analysis is required.
Commentary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com