Deliberative communication involves thoughtful decision-making and careful consideration of all possible outcomes before choosing a course of action. It plays a crucial role in personal and professional settings, enabling you to weigh pros and cons effectively. Explore the rest of the article to understand how deliberative strategies can enhance your decision-making skills.
Table of Comparison
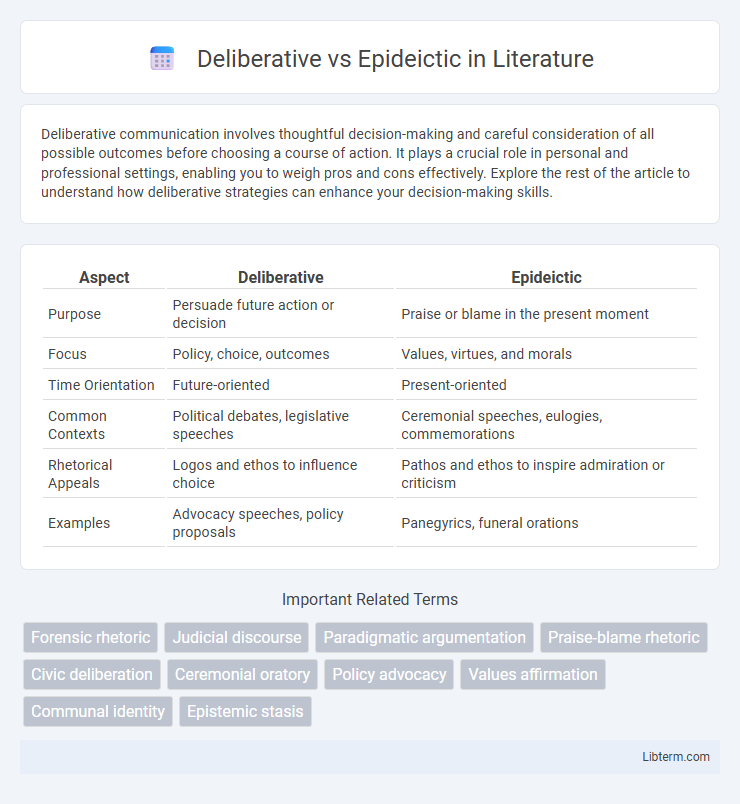
| Aspect | Deliberative | Epideictic |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Persuade future action or decision | Praise or blame in the present moment |
| Focus | Policy, choice, outcomes | Values, virtues, and morals |
| Time Orientation | Future-oriented | Present-oriented |
| Common Contexts | Political debates, legislative speeches | Ceremonial speeches, eulogies, commemorations |
| Rhetorical Appeals | Logos and ethos to influence choice | Pathos and ethos to inspire admiration or criticism |
| Examples | Advocacy speeches, policy proposals | Panegyrics, funeral orations |
Introduction to Deliberative and Epideictic Rhetoric
Deliberative rhetoric centers on persuasion regarding future actions, often employed in political or legislative contexts where decisions impact upcoming events. Epideictic rhetoric, by contrast, focuses on praise or blame, typically used in ceremonial settings to reinforce shared values and beliefs. Understanding these distinct rhetorical styles enhances effective communication by aligning the message with the audience's expectations and situational context.
Defining Deliberative Rhetoric: Purpose and Context
Deliberative rhetoric aims to persuade an audience toward future actions by emphasizing practical benefits or consequences, commonly used in political debates and policy discussions. Its purpose revolves around urging decisions that promote the common good or avoid harm, relying on evidence-based appeals and logical reasoning. This form of rhetoric typically contrasts with epideictic rhetoric, which centers on praise or blame in ceremonial contexts rather than decision-making.
Epideictic Rhetoric Explained: Meaning and Function
Epideictic rhetoric, also known as ceremonial rhetoric, focuses on praising or blaming during special occasions and aims to reinforce shared values and community bonds. It emphasizes the present moment, appealing to emotions by celebrating virtues such as honor, bravery, or justice through vivid language and stylistic devices. This form of rhetoric plays a critical role in shaping cultural identity and collective memory by highlighting exemplary behavior and moral standards.
Historical Roots of Deliberative and Epideictic Forms
Deliberative rhetoric traces its historical roots to the political assemblies of ancient Athens, where speakers aimed to influence future policy decisions through persuasion and argumentation. Epideictic rhetoric, originating from public ceremonies and festivals, focused on praise or blame to reinforce communal values and social cohesion in classical Greek society. Both forms, foundational to Aristotelian rhetoric, shaped public communication by addressing practical governance and ceremonial expression respectively.
Key Differences: Deliberative vs Epideictic Rhetoric
Deliberative rhetoric centers on future-oriented decision-making, aiming to persuade an audience toward a specific course of action based on potential outcomes, commonly used in political or legislative contexts. Epideictic rhetoric, by contrast, focuses on the present, emphasizing praise or blame to reinforce communal values and celebrate virtues or condemn vices, often found in ceremonial speeches. Key differences include their temporal focus--future versus present--their primary purpose--persuasion for action versus celebration or condemnation--and typical settings such as policy debates for deliberative and commemorative events for epideictic rhetoric.
Typical Audiences for Deliberative and Epideictic Speech
Typical audiences for deliberative speech include policymakers, legislators, or community members who must decide on future actions or policies based on arguments about potential benefits and consequences. Epideictic speech usually targets a broader, often more general audience such as attendees at ceremonies, celebrations, or commemorations, where the focus is on praise, values, and shared beliefs rather than decision-making. Understanding these audience contexts helps speakers tailor their message to effectively persuade or inspire according to the rhetorical purpose.
Common Strategies in Deliberative Rhetoric
Deliberative rhetoric often employs strategies such as appealing to future consequences, emphasizing benefits and harms, and using logical reasoning to persuade audiences toward action or policy decisions. Speakers commonly use examples and analogies to forecast potential outcomes, reinforcing the urgency or feasibility of proposed measures. Ethical appeals that highlight justice and the common good also play a crucial role in motivating deliberative arguments.
Persuasive Techniques in Epideictic Rhetoric
Epideictic rhetoric relies heavily on persuasive techniques such as vivid imagery, emotional appeals, and the use of ethos to establish credibility and inspire admiration or condemnation. It emphasizes values and virtues through praise or blame, aiming to reinforce communal beliefs and cultural ideals. By appealing to shared emotions and moral standards, epideictic speeches strengthen social bonds and influence audience attitudes.
Real-World Examples Illustrating Both Forms
Deliberative rhetoric is often seen in political debates where legislators argue for future policies, such as climate change legislation or economic reform, emphasizing consequences and benefits. Epideictic rhetoric appears prominently in ceremonial speeches, like eulogies or award presentations, where the focus is on praising or blaming individuals to reaffirm communal values. Businesses also use deliberative rhetoric in strategic planning meetings to decide future directions, while epideictic rhetoric is common in brand storytelling to build emotional connections with consumers.
Choosing Between Deliberative and Epideictic Approaches
Choosing between deliberative and epideictic approaches depends on the communication goal: deliberative rhetoric aims to persuade an audience toward future action by weighing benefits and consequences, making it ideal for policy debates or decision-making contexts. Epideictic rhetoric focuses on praising or blaming, strengthening community values and shared beliefs, often used in ceremonial speeches to reinforce social cohesion. Selecting the appropriate approach hinges on whether the emphasis is on influencing practical decisions or celebrating collective ideals.
Deliberative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com