Effective time management boosts productivity by prioritizing tasks and minimizing distractions, enabling you to achieve goals efficiently. Techniques such as the Pomodoro method and time blocking help maintain focus and reduce burnout. Explore the rest of the article to master practical strategies for optimizing your daily schedule.
Table of Comparison
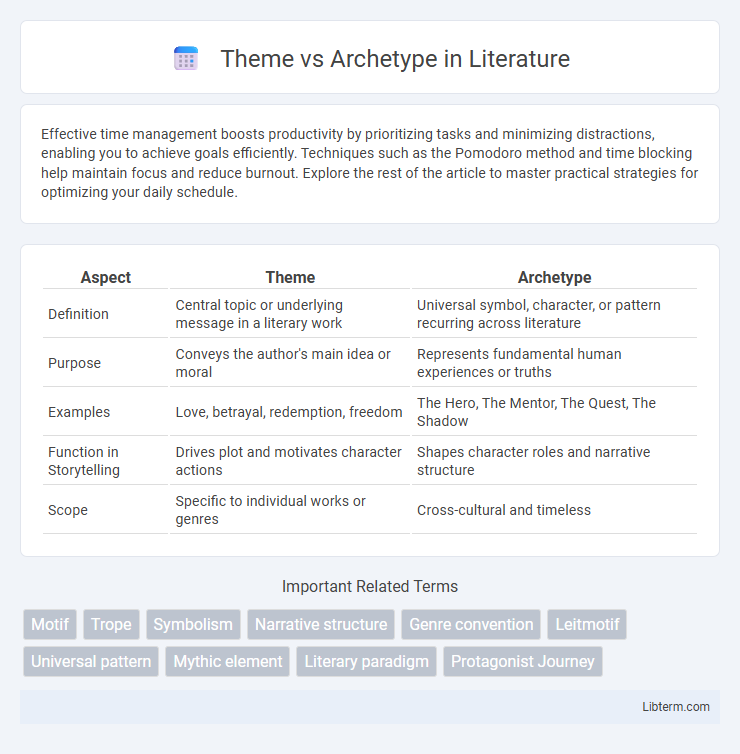
| Aspect | Theme | Archetype |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Central topic or underlying message in a literary work | Universal symbol, character, or pattern recurring across literature |
| Purpose | Conveys the author's main idea or moral | Represents fundamental human experiences or truths |
| Examples | Love, betrayal, redemption, freedom | The Hero, The Mentor, The Quest, The Shadow |
| Function in Storytelling | Drives plot and motivates character actions | Shapes character roles and narrative structure |
| Scope | Specific to individual works or genres | Cross-cultural and timeless |
Understanding Theme and Archetype
Theme represents the central idea or underlying message conveyed in a literary work, reflecting universal human experiences such as love, conflict, or identity. Archetypes are recurring symbols, characters, or motifs that embody fundamental human patterns, like the Hero, the Mentor, or the Journey. Understanding theme and archetype enables deeper analysis of narratives by revealing the shared emotional truths and cultural values embedded within stories.
Defining Theme in Literature
Theme in literature represents the central topic, subject, or message explored by a story, often reflecting universal truths or underlying ideas about human nature and society. It differs from an archetype, which is a recurring symbol, character type, or pattern that embodies fundamental human experiences. Defining theme involves identifying the main concept or moral that the narrative communicates through plot, character development, and setting.
Exploring the Nature of Archetypes
Archetypes represent universal, symbolic characters or motifs deeply embedded in the human psyche, transcending cultures and historical periods. Unlike themes, which convey the central ideas or messages within a narrative, archetypes embody fundamental human experiences and instincts, such as the Hero, the Mentor, or the Shadow. Exploring the nature of archetypes reveals how these primal patterns shape storytelling, influence character development, and resonate with audiences on a subconscious level.
Key Differences Between Theme and Archetype
Themes represent the central ideas or messages explored throughout a narrative, revealing the author's underlying commentary on life, society, or human nature. Archetypes are universally recognized symbols, characters, or motifs that recur across various stories and cultures, serving as foundational templates for storytelling. While themes convey abstract concepts and moral lessons, archetypes provide concrete figures and patterns that embody these ideas in literature and mythology.
Common Themes in Storytelling
Common themes in storytelling include love, betrayal, redemption, and the hero's journey, each embodying universal human experiences that resonate across cultures. Themes serve as the underlying messages or central ideas, while archetypes represent recurring character types or symbols, such as the mentor, the hero, or the shadow. Identifying common themes helps writers create meaningful narratives, as these themes connect deeply with audiences by reflecting fundamental emotions and moral dilemmas.
Universal Archetypes Across Cultures
Universal archetypes transcend cultural boundaries, embodying fundamental human experiences such as the Hero, the Mentor, and the Shadow. These archetypes serve as symbolic figures that resonate deeply within collective unconscious minds, shaping narratives and moral frameworks worldwide. Unlike themes, which express central ideas or messages in stories, archetypes provide the structural foundation and recognizable character patterns that appear consistently across diverse cultures.
How Themes Influence Plot Development
Themes shape plot development by providing underlying messages that guide character decisions and conflicts, creating coherence throughout the story. Archetypes serve as recurring character or plot patterns that embody these themes, helping readers quickly grasp the narrative's deeper significance. By integrating themes with archetypal elements, writers craft engaging plots that resonate emotionally and intellectually with audiences.
The Role of Archetypes in Character Creation
Archetypes serve as foundational blueprints in character creation, embodying universal patterns that resonate across cultures and narratives, such as the Hero, Mentor, or Shadow. These archetypal roles provide writers with recognizable character frameworks that facilitate emotional connection and thematic depth within a story. Integrating archetypes enables consistent character development and supports the exploration of underlying themes through their interactions and growth.
Interplay Between Theme and Archetype
Themes shape the overarching message or moral of a story, while archetypes serve as universal character or situational patterns that embody these themes. The interplay between theme and archetype enhances narrative depth by using familiar archetypal figures--such as the Hero, Mentor, or Shadow--to explore complex thematic concepts like redemption, sacrifice, or good versus evil. This dynamic allows storytellers to communicate profound ideas through recognizable patterns, making the narrative resonate on both personal and collective levels.
Analyzing Theme and Archetype in Popular Works
Theme explores the central message or underlying idea in popular works, revealing insights into human nature and societal norms. Archetypes are recurring symbols or character types that resonate universally, such as the Hero, the Mentor, or the Journey, providing a structural foundation for narrative interpretation. Analyzing theme and archetype together enhances understanding of a work's deeper meaning and cultural significance across genres and time periods.
Theme Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com