Discourse encompasses the structured ways of speaking, writing, and thinking that shape communication within social contexts, influencing how ideas and beliefs are constructed and understood. Analyzing discourse reveals underlying power dynamics, cultural norms, and social identities embedded in language use. Explore the rest of this article to deepen your understanding of how discourse shapes human interaction and meaning.
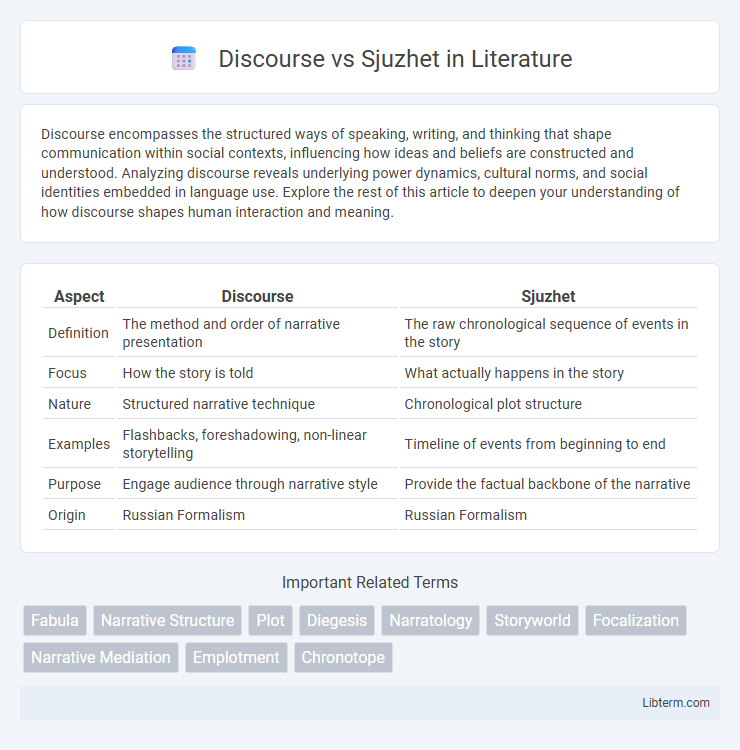
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Discourse | Sjuzhet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The method and order of narrative presentation | The raw chronological sequence of events in the story |
| Focus | How the story is told | What actually happens in the story |
| Nature | Structured narrative technique | Chronological plot structure |
| Examples | Flashbacks, foreshadowing, non-linear storytelling | Timeline of events from beginning to end |
| Purpose | Engage audience through narrative style | Provide the factual backbone of the narrative |
| Origin | Russian Formalism | Russian Formalism |
Understanding Discourse and Sjuzhet
Discourse refers to the way a story is presented, including the structure, perspective, and narrative techniques, while Sjuzhet denotes the chronological sequence of events as they occur in the story's world. Understanding Discourse involves analyzing narrative style, manipulation of time, and thematic emphasis to reveal deeper meanings beyond the plot. Mastery of Sjuzhet emphasizes grasping cause-effect relationships and temporal order, crucial for interpreting the story's underlying message.
The Origins of Discourse and Sjuzhet in Literary Theory
Discourse and Sjuzhet originate from Russian Formalism, where Sjuzhet refers to the narrative structure or the way events are presented, while Fabula denotes the raw chronological sequence of events. The analysis of discourse examines how narrative techniques manipulate time and information to create meaning beyond the basic story. Understanding these concepts is crucial for dissecting narrative strategies and the transformation of plot in literary theory.
Defining Discourse: Structure and Function
Discourse refers to the structured way information is presented, shaping how a narrative is organized and understood beyond the mere sequence of events, known as sjuzhet. It encompasses techniques such as flashbacks, pacing, and perspective shifts that influence audience interpretation and engagement. The function of discourse is to control the delivery and emphasis of the story's elements, thus constructing meaning and emotional impact distinct from the raw chronological plot.
Decoding Sjuzhet: Narrative Construction
Decoding sjuzhet involves analyzing the narrative construction techniques that determine how story events are presented, structured, and temporally arranged, influencing audience perception and engagement. While discourse focuses on the mode of telling, sjuzhet refers to the specific organization and selection of events that form the narrative timeline. Understanding sjuzhet enables a deeper insight into narrative manipulation, highlighting how plot sequencing shapes thematic development and character motivations.
Discourse vs Sjuzhet: Key Differences
Discourse refers to the way a narrative is presented, emphasizing the structure, order, and style of storytelling, while Sjuzhet (or story) encompasses the raw sequence of events and their chronological progression. The key difference lies in Discourse's manipulation of time, perspective, and narrative techniques, whereas Sjuzhet remains the fundamental storyline without alterations. Understanding Discourse versus Sjuzhet highlights how narratives transform simple plots into complex, engaging experiences through deliberate narrative construction.
Impact on Storytelling and Reader Perception
Discourse shapes storytelling by structuring narrative delivery, influencing reader engagement and interpretation through techniques such as flashbacks, pacing, and viewpoint shifts. Sjuzhet refers to the chronological sequence of events, providing a clear framework that guides reader understanding of the story's plot. The interplay between discourse and sjuzhet creates layered narratives that affect emotional impact and thematic depth in reader perception.
Practical Examples: Discourse and Sjuzhet in Literature
Discourse and sjuzhet represent distinct narrative structures where discourse refers to the way a story is told, and sjuzhet denotes the chronological sequence of events in the plot. In Fyodor Dostoevsky's "Crime and Punishment," the sjuzhet follows Raskolnikov's timeline, but the discourse manipulates time through flashbacks and internal monologues to reveal psychological depth. Similarly, in Vladimir Nabokov's "Lolita," the sjuzhet presents a linear sequence, yet the discourse utilizes unreliable narration and fragmented memories to shape the reader's perception of the story.
Analysis of Discourse and Sjuzhet in Modern Media
Discourse and sjuzhet function as pivotal components in analyzing narrative structures within modern media, where discourse represents the way a story is communicated and sjuzhet refers to the chronological sequence of events. In film and digital storytelling, the manipulation of discourse can reshape audience perception by altering pacing, perspective, and emphasis, while the sjuzhet maintains the foundational plot progression. Understanding the interplay between discourse and sjuzhet enhances critical media literacy and reveals how narrative techniques influence emotional engagement and thematic interpretation.
Theoretical Implications for Writers and Critics
Discourse and sjuzhet represent distinct narrative structures that shape storytelling and critical analysis by emphasizing how stories are told versus what is told. Writers and critics leverage discourse theory to explore the manipulation of temporal order, narrative perspective, and language style, enriching character development and thematic depth. Understanding sjuzhet facilitates a focus on chronological plot events, enabling clearer narrative coherence and aiding critics in dissecting story causality and structure for deeper interpretive insights.
Conclusion: Mastering Narrative through Discourse and Sjuzhet
Mastering narrative involves understanding the interplay between discourse--the presentation and structure of the story--and sjuzhet, the chronological sequence of events. Effective storytelling leverages discourse to manipulate time, perspective, and emphasis, enriching the audience's engagement and interpretation. Mastery of both concepts enables storytellers to craft compelling narratives that resonate through deliberate plot arrangement and thematic depth.
Discourse Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com