Acrostic poems creatively use the first letters of each line to spell out a word or message, enhancing memorability and engagement. This poetic form allows you to express thoughts succinctly while adding a visual element to your writing. Explore the rest of this article to unlock unique techniques for crafting compelling acrostic poems.
Table of Comparison
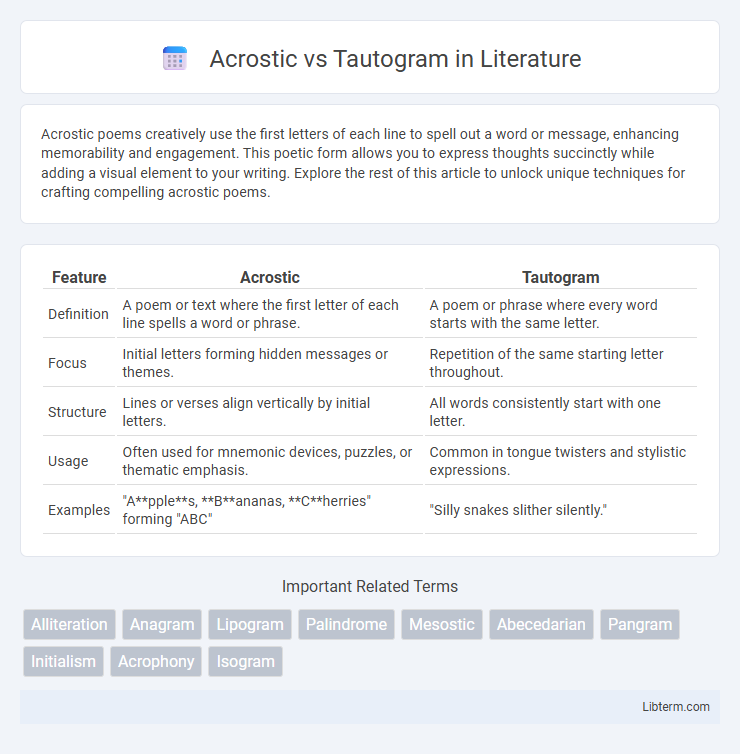
| Feature | Acrostic | Tautogram |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A poem or text where the first letter of each line spells a word or phrase. | A poem or phrase where every word starts with the same letter. |
| Focus | Initial letters forming hidden messages or themes. | Repetition of the same starting letter throughout. |
| Structure | Lines or verses align vertically by initial letters. | All words consistently start with one letter. |
| Usage | Often used for mnemonic devices, puzzles, or thematic emphasis. | Common in tongue twisters and stylistic expressions. |
| Examples | "Apples, Bananas, Cherries" forming "ABC" | "Silly snakes slither silently." |
Introduction to Acrostics and Tautograms
Acrostics are poems or texts where the first letter of each line spells out a word or message, often used for hidden meanings or mnemonic devices. Tautograms are compositions where every word begins with the same letter, creating a rhythmic and alliterative effect, common in tongue twisters and playful language exercises. Both poetic forms rely on letter patterns to enhance linguistic creativity and reader engagement.
Defining Acrostics: Structure and Purpose
Acrostics are a form of writing in which the first letters of each line or paragraph spell out a word or message, providing a hidden or emphasized meaning. The structure of an acrostic relies on this vertical arrangement, often used in poetry and puzzles to add layers of interpretation or mnemonic aid. The primary purpose is to create a memorable connection between the text and the spelled-out word, enhancing both aesthetic appeal and cognitive engagement.
Understanding Tautograms: Concept and Characteristics
Tautograms are a unique form of alliteration where every word in a phrase or sentence begins with the same letter, creating a rhythmic and memorable linguistic pattern. This constraint fosters creativity and challenges writers to convey coherent ideas while maintaining the repeated initial sound. Unlike acrostics, which use the first letters of lines to form words or messages, tautograms emphasize phonetic repetition without necessarily constructing hidden words or phrases.
Historical Origins of Acrostics and Tautograms
Acrostics trace their historical origins to ancient Greece, where poets like Simonides of Ceos used them as mnemonic devices and artistic expressions, with examples found in Classical literature and medieval manuscripts. Tautograms, on the other hand, emerged prominently within medieval Latin and Islamic poetry, emphasizing alliteration by repeating initial consonant sounds in each word of a line or phrase, serving as a stylistic and mnemonic technique. Both forms reflect early literary traditions aimed at enhancing memorability and aesthetic appeal in oral and written culture.
Key Differences Between Acrostics and Tautograms
Acrostics are poems or compositions where the first letter of each line or paragraph spells out a word or message vertically, emphasizing a hidden code or theme. Tautograms are verses or texts where every word in the line starts with the same letter, showcasing alliteration and phonetic harmony. The key difference is acrostics focus on the initial letters of lines forming a meaningful word, while tautograms concentrate on every word within a line beginning with the same letter.
Literary Significance of Both Forms
Acrostics and tautograms both hold distinct literary significance in creative expression and mnemonic function. Acrostics enhance textual depth by embedding hidden messages or thematic connections through the first letters of lines, enriching interpretative engagement. Tautograms emphasize phonetic artistry and rhythmic cohesion by using uniform initial sounds, contributing to memorability and artistic unity within poetic and rhetorical works.
Examples of Acrostics in Literature
Acrostics in literature appear prominently in works like Edgar Allan Poe's "An Acrostic," where the first letters of each line spell the name "Elizabeth." Another classic example is Lewis Carroll's poem "A Boat Beneath a Sunny Sky," which encodes the name "Alice" through its initial letters. These carefully crafted acrostics exemplify how authors embed hidden messages within poetic structures, contrasting with tautograms that rely solely on repetitive initial sounds.
Notable Tautogram Examples in Poetry
Notable tautogram examples in poetry include the alliterative verse of Edgar Allan Poe's "The Raven," where the repetition of initial consonant sounds creates a rhythmic, memorable effect. Classical poets like Geoffrey Chaucer utilized tautograms in Middle English literature, exemplifying the technique's historical significance. Modern poets also employ tautograms to emphasize thematic cohesion, demonstrating the enduring appeal of this stylistic device.
Creative Uses in Modern Writing
Acrostics creatively embed messages through the initial letters of lines or verses, enhancing poetic structure and enabling hidden communication in literature and digital media. Tautograms emphasize alliteration by starting every word with the same letter, enriching mnemonic devices and playful language in advertising and storytelling. Both forms engage readers' attention and memory, offering versatile tools for modern writers seeking to blend artistry with subtlety.
Choosing Between Acrostic and Tautogram for Your Work
Choosing between acrostic and tautogram depends on your creative goals and the impact you want to achieve. Acrostics emphasize hidden messages or themes by using the first letters of lines or verses, making them ideal for storytelling or encoding information. Tautograms focus on alliteration, with each word beginning with the same letter, creating rhythmic and phonetic patterns suited for poetry or catchy slogans.
Acrostic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com