Prose offers a straightforward and natural form of writing that mirrors everyday speech, making it easy to understand and relatable. It encompasses various genres including novels, essays, and short stories, providing rich avenues for expression and creativity. Dive deeper into the article to explore how prose can enhance your communication and storytelling skills.
Table of Comparison
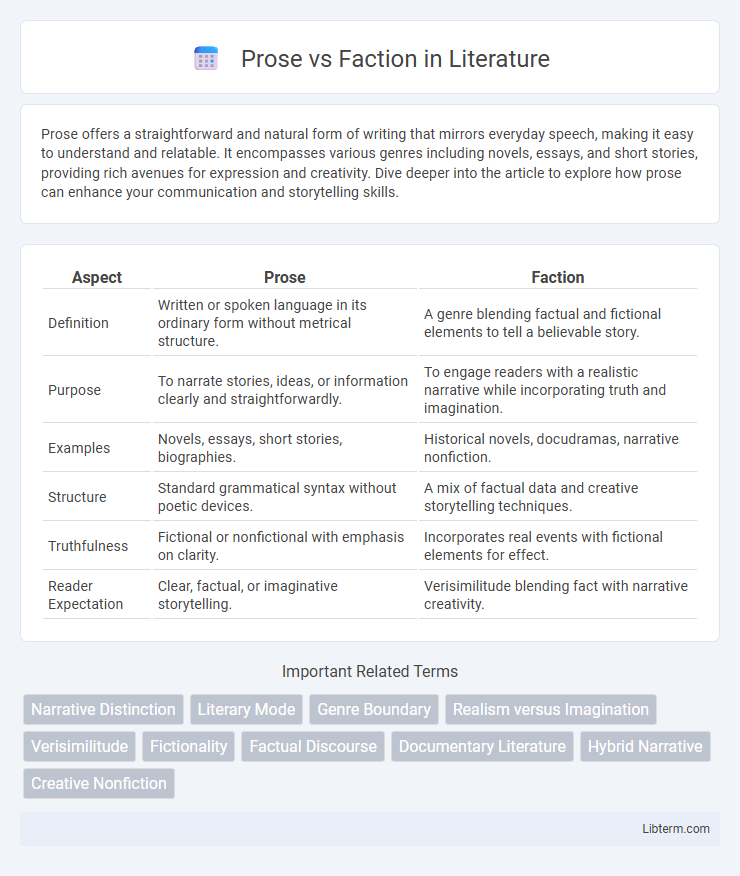
| Aspect | Prose | Faction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Written or spoken language in its ordinary form without metrical structure. | A genre blending factual and fictional elements to tell a believable story. |
| Purpose | To narrate stories, ideas, or information clearly and straightforwardly. | To engage readers with a realistic narrative while incorporating truth and imagination. |
| Examples | Novels, essays, short stories, biographies. | Historical novels, docudramas, narrative nonfiction. |
| Structure | Standard grammatical syntax without poetic devices. | A mix of factual data and creative storytelling techniques. |
| Truthfulness | Fictional or nonfictional with emphasis on clarity. | Incorporates real events with fictional elements for effect. |
| Reader Expectation | Clear, factual, or imaginative storytelling. | Verisimilitude blending fact with narrative creativity. |
Understanding Prose and Faction
Prose refers to written or spoken language in its ordinary form, characterized by natural flow and grammatical structure without metrical patterns, commonly used in novels, essays, and articles. Faction represents a literary genre blending fact and fiction, where real historical events or figures are intertwined with imaginative storytelling to enhance engagement and insight. Understanding prose involves recognizing its role in clear communication, while grasping faction requires appreciating the balance between factual accuracy and creative narrative.
Key Differences Between Prose and Faction
Prose is a form of writing characterized by ordinary language and grammatical structure, primarily used in fiction and non-fiction narratives without metrical patterns. Faction blends factual information with fictional storytelling, often incorporating real events or characters while adding imaginative details for narrative effect. The key differences lie in prose's adherence to either purely imaginative or purely factual content, whereas faction deliberately merges truth and fiction to enhance engagement and convey deeper insights.
Historical Origins of Prose and Faction
Prose originated in ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Egypt, where narratives and records were composed in straightforward, structured language to preserve history and culture. Faction, a blend of fact and fiction, emerged notably in the 20th century as authors intertwined real historical events with imaginative storytelling to enhance narrative depth and engagement. The historical development of prose laid the foundation for faction, enabling writers to manipulate factual frameworks creatively while maintaining authenticity.
Narrative Techniques in Prose vs Faction
Prose utilizes narrative techniques such as detailed character development, immersive descriptions, and fictional plot structures to evoke imagination and emotional engagement. Faction blends factual information with storytelling elements, employing real events and authentic details while incorporating narrative devices like dialogue, scene-setting, and pacing to enhance readability and impact. The key difference lies in prose prioritizing imaginative creation, whereas faction integrates reality with creative narration for informative storytelling.
Common Genres for Prose and Faction
Common genres for prose include novels, short stories, essays, and biographies, characterized by continuous, flowing text without structured meter or rhyme. Faction, a blend of fact and fiction, frequently appears in historical novels, creative nonfiction, and docudramas, merging factual events with imaginative storytelling. Both prose and faction use narrative techniques but differ in their emphasis on factual accuracy versus creative embellishment.
Impact on Reader Engagement
Prose offers immersive storytelling through carefully crafted language that fosters emotional connections and deepens reader engagement. Faction blends factual accuracy with narrative techniques, increasing credibility while maintaining interest by merging education and entertainment. This combination enhances trust and stimulates curiosity, effectively sustaining readers' attention.
Famous Prose and Faction Works
Famous prose works such as Jane Austen's "Pride and Prejudice" and George Orwell's "1984" showcase the art of fictional storytelling grounded in character development and narrative style. Faction, a blend of fact and fiction, is exemplified by Truman Capote's "In Cold Blood," which combines rigorous investigative journalism with literary techniques to create a compelling true crime narrative. These works highlight the distinct yet overlapping boundaries where factual accuracy meets creative interpretation.
Writing Styles Compared
Prose consists of straightforward, continuous text that emphasizes clarity and narrative flow, often used in fiction, non-fiction, and everyday communication. Faction blends factual information with fictional storytelling, creating a hybrid style that combines real events with imaginative elements to engage readers while informing them. Both styles manipulate language and structure, but prose prioritizes coherence and realism, whereas faction allows creative liberties to enhance the narrative impact.
Relevance in Modern Literature
Prose remains a dominant form in modern literature, prized for its clarity and expansive storytelling capabilities, which allow authors to explore complex characters and intricate plots. Faction, blending fact and fiction, gains relevance by offering readers immersive narratives grounded in real events, enhancing engagement and critical reflection. This hybrid approach appeals to contemporary audiences seeking both entertainment and insight, bridging the gap between historical accuracy and creative expression.
Choosing Between Prose and Faction
Choosing between prose and faction depends heavily on the intent and audience of the writing. Prose emphasizes imaginative storytelling and character development, ideal for creative expression and entertainment. Faction combines factual accuracy with narrative elements, making it suitable for readers seeking engaging yet informative content that blurs the line between history and storytelling.
Prose Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com