Paronomasia, commonly known as a pun, plays on the multiple meanings or similar sounds of words to create humor or rhetorical effect. This linguistic device enriches communication by engaging your audience with clever wordplay that can lighten the mood or emphasize a point. Discover more about how paronomasia can enhance your writing and speech throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
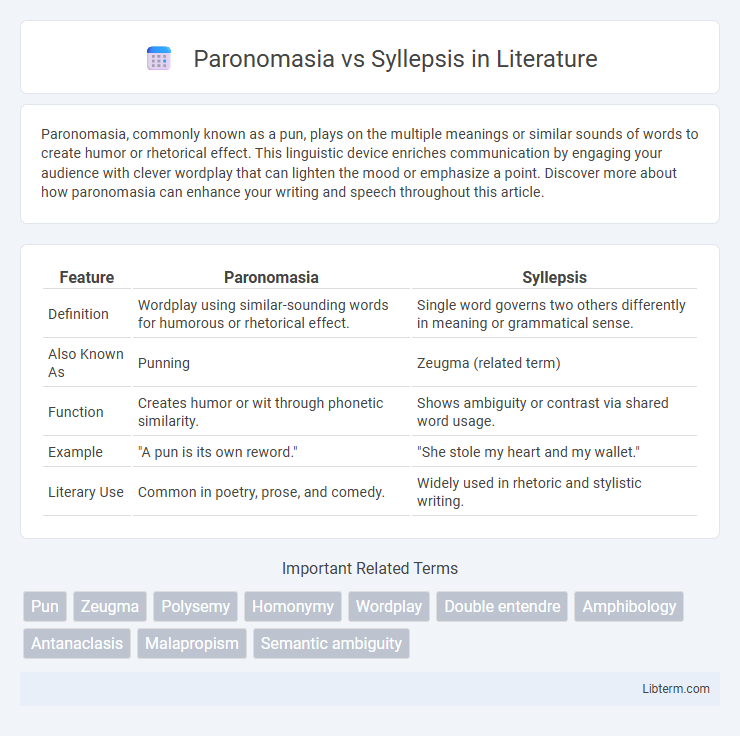
| Feature | Paronomasia | Syllepsis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Wordplay using similar-sounding words for humorous or rhetorical effect. | Single word governs two others differently in meaning or grammatical sense. |
| Also Known As | Punning | Zeugma (related term) |
| Function | Creates humor or wit through phonetic similarity. | Shows ambiguity or contrast via shared word usage. |
| Example | "A pun is its own reword." | "She stole my heart and my wallet." |
| Literary Use | Common in poetry, prose, and comedy. | Widely used in rhetoric and stylistic writing. |
Understanding Paronomasia: Definition and Examples
Paronomasia is a rhetorical device involving the use of words that sound similar but have different meanings, creating a pun that enhances humor or emphasis. Examples include Shakespeare's "Ask for me tomorrow, and you shall find me a grave man," where "grave" plays on seriousness and a burial site. This stylistic technique leverages phonetic similarity to engage audiences and enrich language with layered meanings.
What is Syllepsis? Key Concepts Explained
Syllepsis is a figure of speech where a single word, usually a verb or adjective, governs or modifies two or more words in different senses or meanings simultaneously. This linguistic device creates a nuanced or humorous effect by exploiting the ambiguity of the shared word. Unlike paronomasia, which relies on wordplay through similar sounds, syllepsis emphasizes semantic flexibility within one grammatical structure.
Historical Origins of Paronomasia and Syllepsis
Paronomasia, rooted in ancient Greek rhetoric, traces its origins to classical poets and orators who used wordplay to enhance memorability and wit. Syllepsis emerged from literature in the 17th century, influenced by both classical and Renaissance styles, characterized by a single word governing multiple others in different senses or grammatical contexts. These rhetorical devices served distinct historical roles, with paronomasia emphasizing phonetic similarity for puns, while syllepsis highlighted syntactic and semantic ambiguity.
Linguistic Differences: Paronomasia vs Syllepsis
Paronomasia involves wordplay exploiting similar sounds or homophones to create a pun, emphasizing phonetic resemblance and lexical ambiguity. Syllepsis merges a single word with multiple meanings or grammatical roles, applying it differently to two or more parts of a sentence, often blending semantic incongruity and syntactic variation. The primary linguistic difference lies in paronomasia's phonological manipulation versus syllepsis's syntactic and semantic duality in word usage.
Common Uses of Paronomasia in Literature
Paronomasia, commonly known as a pun, is widely used in literature to create humor, emphasize double meanings, and engage readers by playing on word similarities. Shakespeare frequently employed paronomasia in his plays to enrich dialogue with wit and layered meanings, exemplified in works like "Romeo and Juliet" and "Hamlet." Unlike syllepsis, which involves a single word applying to multiple meanings or objects, paronomasia hinges on sound-alike words or phrases to achieve its rhetorical effect.
Notable Syllepsis in Classic and Modern Texts
Notable syllepsis in classic texts includes Shakespeare's use in "The Rape of Lucrece," where a single word governs multiple meanings for dramatic effect. In modern literature, Sylvia Plath's poetry often employs syllepsis to juxtapose emotional and literal interpretations within a concise phrase. Both classic and contemporary examples highlight syllepsis' capacity to enrich language through layered meanings and stylistic complexity.
Cognitive Effects: How Paronomasia and Syllepsis Shape Meaning
Paronomasia exploits phonetic similarity between words to create playful ambiguity, triggering multiple interpretations that enhance cognitive engagement and humor. Syllepsis relies on a single word governing multiple parts of a sentence, often leading to a semantic twist that challenges expectations and deepens comprehension. Both devices manipulate language structures to activate different layers of meaning, influencing how readers mentally process and derive significance from text.
Paronomasia and Syllepsis in Rhetoric and Humor
Paronomasia, or punning, exploits the phonetic similarity between words to create humor and rhetorical emphasis, often enriching texts with playful ambiguity. Syllepsis involves a single word governed by two or more words in different senses, generating surprise or irony that intensifies comedic or persuasive effects. Both devices serve as powerful rhetorical tools by engaging audiences through clever wordplay and layered meanings in literature and speech.
Writing Techniques: Crafting Clever Paronomasia and Syllepsis
Paronomasia leverages wordplay by exploiting phonetic similarities between words with different meanings, creating clever puns that engage readers through witty ambiguity. Syllepsis intertwines a single word with two or more parts of a sentence, applying different meanings to each, which enriches text with layered semantic effects. Mastering these writing techniques involves understanding phonetics, semantic flexibility, and context to craft nuanced, memorable expressions that elevate literary style.
Paronomasia vs Syllepsis: Impact on Reader Engagement
Paronomasia, or punning, leverages wordplay through similar sounds to create humor or emphasize meaning, enhancing reader engagement by sparking curiosity and amusement. Syllepsis involves using a single word in different senses or linking two concepts, prompting readers to think critically and appreciate linguistic dexterity. The impact of paronomasia on engagement lies in its playful interaction with language, while syllepsis deepens cognitive involvement by challenging interpretation.
Paronomasia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com