Empiricism emphasizes that knowledge is primarily derived from sensory experience and evidence rather than innate ideas or pure reason. This philosophical approach has shaped modern scientific methods by prioritizing observation and experimentation. Discover how empiricism influences your understanding of knowledge and how it applies to various fields in the full article.
Table of Comparison
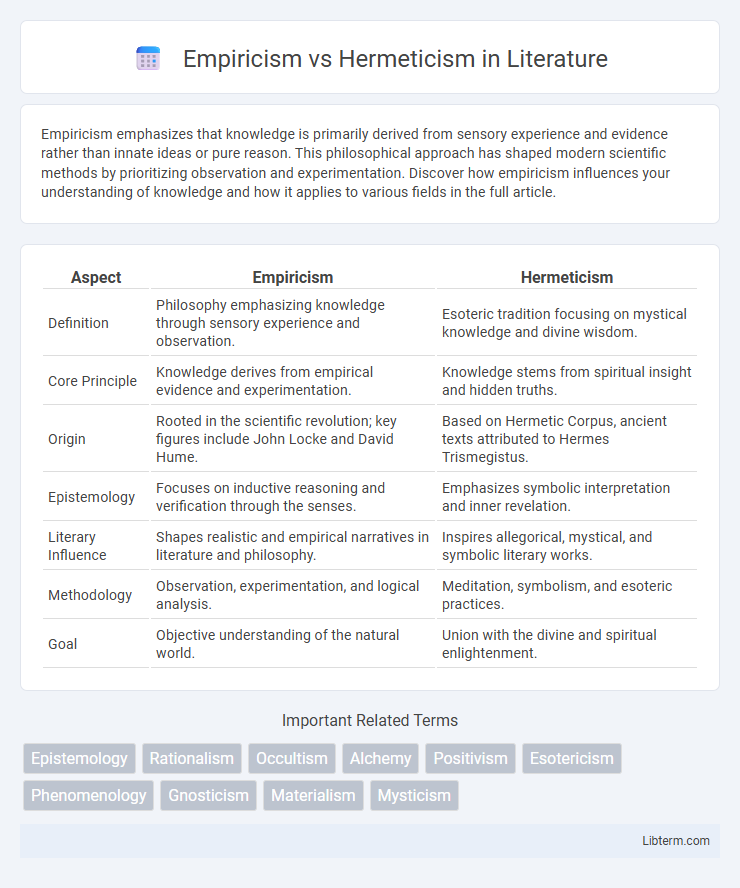
| Aspect | Empiricism | Hermeticism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophy emphasizing knowledge through sensory experience and observation. | Esoteric tradition focusing on mystical knowledge and divine wisdom. |
| Core Principle | Knowledge derives from empirical evidence and experimentation. | Knowledge stems from spiritual insight and hidden truths. |
| Origin | Rooted in the scientific revolution; key figures include John Locke and David Hume. | Based on Hermetic Corpus, ancient texts attributed to Hermes Trismegistus. |
| Epistemology | Focuses on inductive reasoning and verification through the senses. | Emphasizes symbolic interpretation and inner revelation. |
| Literary Influence | Shapes realistic and empirical narratives in literature and philosophy. | Inspires allegorical, mystical, and symbolic literary works. |
| Methodology | Observation, experimentation, and logical analysis. | Meditation, symbolism, and esoteric practices. |
| Goal | Objective understanding of the natural world. | Union with the divine and spiritual enlightenment. |
Introduction to Empiricism and Hermeticism
Empiricism emphasizes knowledge derived from sensory experience and observation, promoting scientific inquiry based on evidence and experimentation. Hermeticism centers on esoteric wisdom from ancient texts attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, highlighting spiritual transformation and metaphysical insights. Both frameworks offer distinct approaches to understanding reality: empirical methods stress measurable data, while Hermeticism explores symbolic and mystical interpretations.
Historical Origins and Development
Empiricism originated during the Scientific Revolution in the 16th and 17th centuries, emphasizing knowledge through sensory experience and observation, with key figures like Francis Bacon and John Locke shaping its principles. Hermeticism traces back to the early centuries of the Common Era, rooted in mystical and esoteric teachings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, influencing Renaissance thinkers and alchemists seeking spiritual and hidden knowledge. Both traditions significantly impacted Western philosophy and science, with empiricism forming the basis of modern scientific methodology while Hermeticism inspired occult and philosophical explorations throughout history.
Core Philosophical Principles
Empiricism centers on knowledge derived from sensory experience and observation, emphasizing evidence and experimentation as the foundations of understanding. Hermeticism, rooted in ancient esoteric traditions, relies on mystical insights, symbolic interpretation, and the belief in hidden correspondences between the macrocosm and microcosm. While empiricism values measurable data and scientific methods, Hermeticism prioritizes spiritual unity and the pursuit of inner knowledge through metaphysical principles.
Key Figures and Influencers
Empiricism, championed by key figures like John Locke, David Hume, and Francis Bacon, emphasizes knowledge derived from sensory experience and scientific observation. Hermeticism, rooted in ancient texts attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, influenced Renaissance thinkers such as Marsilio Ficino and Giordano Bruno, who integrated mystical and esoteric wisdom into their philosophies. The empirical tradition laid the foundation for modern science, while Hermeticism shaped early modern metaphysical and alchemical thought.
Methods of Knowledge Acquisition
Empiricism emphasizes knowledge acquisition through sensory experience and observation, relying on experimentation and evidence to validate theories. Hermeticism advocates for esoteric insight and spiritual revelation as primary methods, emphasizing intuitive understanding and mystical practices. These contrasting approaches reflect the empirical focus on external reality versus Hermeticism's inward, transcendental exploration of truth.
Science and the Empirical Tradition
Empiricism emphasizes knowledge derived from sensory experience and experimental evidence, forming the foundation of the modern scientific method. Hermeticism, rooted in esoteric and mystical traditions, prioritizes symbolic interpretation and inner revelation over observable phenomena. The empirical tradition's reliance on reproducibility and falsifiability contrasts sharply with Hermeticism's emphasis on spiritual insights, influencing the development of objective science.
Mysticism and Hermetic Wisdom
Empiricism emphasizes knowledge through sensory experience and scientific observation, while Hermeticism centers on mystical traditions and esoteric wisdom derived from ancient texts like the Hermetica. Hermetic wisdom explores the nature of the divine, the cosmos, and the interconnectedness of all things through symbolic interpretation and spiritual practices. Mysticism in Hermeticism seeks direct personal experience of the divine, transcending empirical evidence to access hidden truths beyond physical reality.
Points of Convergence and Divergence
Empiricism and Hermeticism converge in their pursuit of knowledge, yet empiricism relies on sensory experience and scientific methods, while Hermeticism emphasizes mystical insight and esoteric wisdom. Both traditions seek to understand the nature of reality, but empiricism values empirical evidence and experimentation, whereas Hermeticism focuses on spiritual transformation and metaphysical truths. The divergence is marked by empiricism's foundation in observable phenomena contrasted with Hermeticism's grounding in symbolic interpretation and occult practices.
Contemporary Relevance and Applications
Empiricism drives contemporary scientific methods by emphasizing observation and experimentation as foundations for knowledge, crucial in fields like medicine, technology, and data science. Hermeticism influences modern spiritual and psychological practices through its focus on inner transformation, symbolism, and the interconnectedness of the universe, impacting areas such as holistic healing and metaphysical philosophy. Both paradigms offer complementary approaches in understanding reality, blending empirical research with mystical insights for a more integrated worldview.
Conclusion: Bridging Reason and Mysticism
Empiricism emphasizes knowledge through sensory experience and scientific inquiry, while Hermeticism centers on esoteric wisdom and mystical insight. Bridging reason and mysticism requires integrating empirical evidence with symbolic interpretation to enrich understanding beyond purely rational or spiritual frameworks. This synthesis fosters a holistic worldview where objective analysis and inner exploration coexist, advancing both knowledge and inner transformation.
Empiricism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com