Interpretation involves analyzing and explaining the meaning behind data, texts, or situations to provide clarity and insight. It plays a crucial role in fields like literature, law, and data science, enabling you to derive meaningful conclusions from complex information. Explore the article to deepen your understanding of effective interpretation techniques.
Table of Comparison
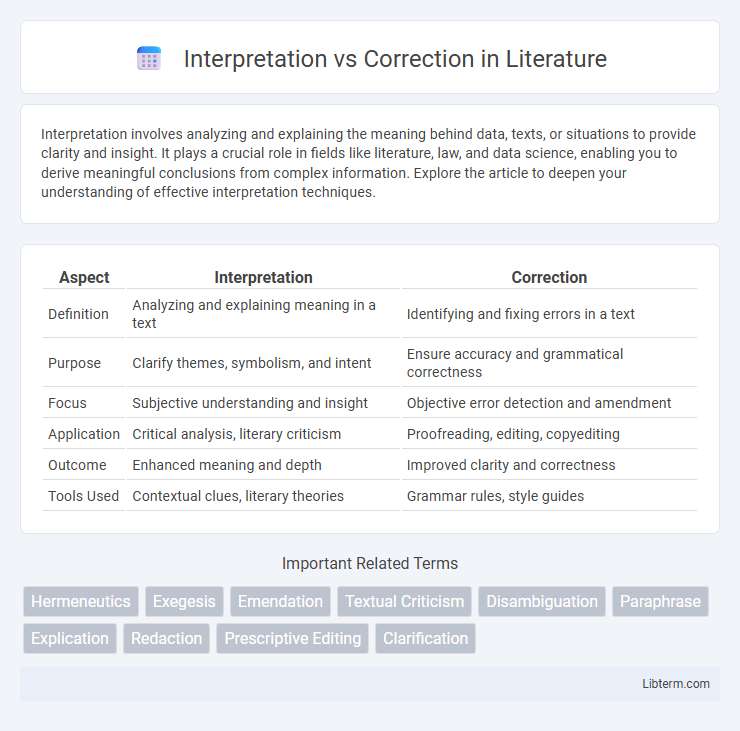
| Aspect | Interpretation | Correction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzing and explaining meaning in a text | Identifying and fixing errors in a text |
| Purpose | Clarify themes, symbolism, and intent | Ensure accuracy and grammatical correctness |
| Focus | Subjective understanding and insight | Objective error detection and amendment |
| Application | Critical analysis, literary criticism | Proofreading, editing, copyediting |
| Outcome | Enhanced meaning and depth | Improved clarity and correctness |
| Tools Used | Contextual clues, literary theories | Grammar rules, style guides |
Understanding Interpretation and Correction
Interpretation involves analyzing and explaining meanings within data or text, while correction focuses on identifying and fixing errors to improve accuracy. Understanding interpretation requires recognizing context, nuances, and intended messages, whereas correction demands attention to detail and adherence to established standards. Both processes are essential for enhancing clarity and reliability in communication and information processing.
Key Differences Between Interpretation and Correction
Interpretation involves understanding and explaining the meaning of information, whereas correction focuses on identifying and rectifying errors or inaccuracies. Interpretation aims to provide clarity and insight, while correction ensures accuracy and compliance with standards. Key differences include their objectives, with interpretation centered on comprehension and correction targeting improvement or error resolution.
The Role of Interpretation in Communication
Interpretation plays a crucial role in communication by enabling individuals to derive meaning from messages based on context, tone, and cultural nuances. Effective interpretation bridges gaps in understanding, facilitating clearer and more accurate exchanges of information. Misinterpretation often leads to communication breakdowns, highlighting the importance of contextual awareness and active listening in the interpretive process.
When is Correction Necessary?
Correction is necessary when errors significantly impact understanding or accuracy, such as in technical documents, legal texts, or academic papers. It ensures clarity and maintains the integrity of the original message by addressing factual inaccuracies, grammatical mistakes, or typographical errors. Interpretation, on the other hand, deals with conveying the intended meaning without altering the source material, making correction essential only when miscommunication risks arise.
Factors Influencing Interpretation
Factors influencing interpretation include cultural background, context, and individual experiences, which shape how information is perceived and understood. Language nuances and the clarity of communication also impact the accuracy of interpretation, often leading to varied meanings. External elements such as tone, body language, and prior knowledge further modulate how an interpreter deciphers messages.
Common Situations Requiring Correction
Common situations requiring correction include misreading legal terms, grammatical errors in formal documents, and discrepancies in financial statements. Interpretation errors often arise from ambiguous language or cultural differences, while correction demands precise adjustments to ensure clarity and accuracy. Proper correction safeguards the integrity of contracts, reports, and official records, preventing costly misunderstandings and legal disputes.
Benefits and Limitations of Interpretation
Interpretation offers the benefit of understanding meaning within context, enabling nuanced comprehension of language, culture, and intent. Its limitations include the potential for subjective bias and ambiguity, which can lead to misunderstandings or misrepresentations. Unlike correction, interpretation emphasizes conveying speaker intent rather than enforcing strict accuracy or error-free content.
Risks of Over-Correction
Over-correction in language interpretation can lead to significant miscommunication and distortion of the original message, impacting both the speaker's intent and listener's understanding. Excessive correction often suppresses natural language variations and cultural nuances, resulting in a loss of authenticity and potential alienation of the audience. Balancing accurate interpretation with minimal interference preserves the integrity and clarity of communication while mitigating risks associated with over-correction.
Improving Interpretation and Correction Skills
Enhancing interpretation skills requires active listening, contextual understanding, and cultural awareness to accurately convey meaning between languages. Correction skills improve through targeted feedback, error analysis, and consistent practice in identifying and rectifying inaccuracies in translation or speech. Leveraging technology such as computer-assisted translation tools and interactive language platforms accelerates proficiency in both interpreting and correcting complex linguistic nuances.
Balancing Interpretation and Correction Effectively
Balancing interpretation and correction effectively involves understanding the context and nuances of communication while providing precise feedback to improve clarity and accuracy. Effective interpretation requires active listening and cultural awareness, whereas correction demands sensitivity to avoid discouragement and maintain engagement. Integrating these skills enhances both comprehension and learning outcomes in educational and professional settings.
Interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com