Antithesis presents contrasting ideas in a balanced structure to emphasize differences and highlight key points effectively. This rhetorical device enhances your communication by creating a memorable impact through opposing concepts. Explore the article to discover how antithesis can sharpen your writing and speaking skills.
Table of Comparison
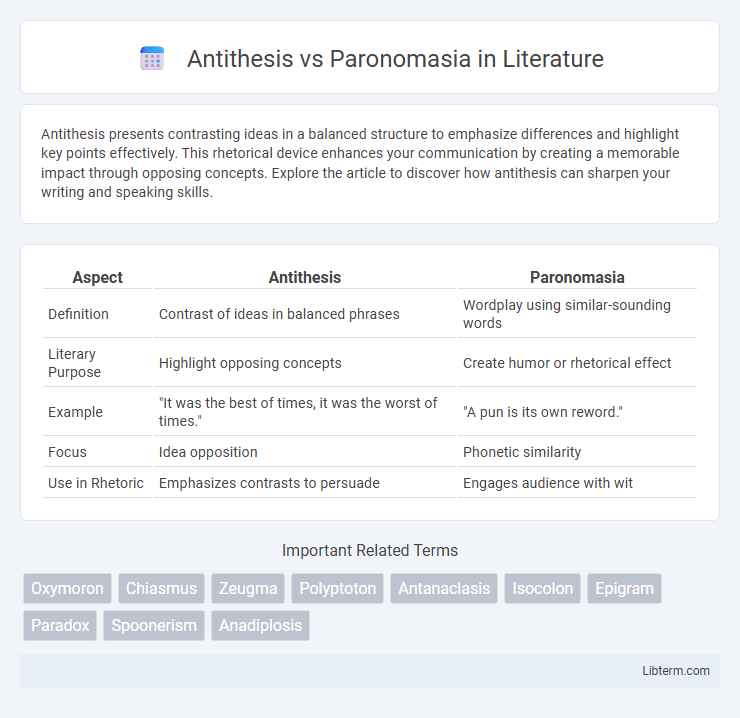
| Aspect | Antithesis | Paronomasia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contrast of ideas in balanced phrases | Wordplay using similar-sounding words |
| Literary Purpose | Highlight opposing concepts | Create humor or rhetorical effect |
| Example | "It was the best of times, it was the worst of times." | "A pun is its own reword." |
| Focus | Idea opposition | Phonetic similarity |
| Use in Rhetoric | Emphasizes contrasts to persuade | Engages audience with wit |
Introduction to Antithesis and Paronomasia
Antithesis is a rhetorical device that contrasts opposing ideas within a balanced structure to highlight their differences, enhancing clarity and emphasis in communication. Paronomasia, commonly known as a pun, exploits the similarity in sound between words with different meanings to create humor or a rhetorical effect. Both devices play distinct roles in language by engaging audiences through contrast and wordplay, enriching textual and spoken expression.
Defining Antithesis
Antithesis is a rhetorical device that juxtaposes contrasting ideas within a balanced structure to highlight their differences and create emphasis. Unlike paronomasia, which relies on wordplay through similar-sounding words or puns, antithesis emphasizes conceptual opposition to strengthen argument or artistic effect. Effective use of antithesis enhances clarity and memorability by presenting conflicting notions side by side.
Defining Paronomasia
Paronomasia, commonly known as a pun, is a rhetorical device that exploits the multiple meanings of a word or similar-sounding words for a humorous or rhetorical effect. Unlike antithesis, which contrasts opposing ideas within parallel structures to emphasize differences, paronomasia relies on wordplay and phonetic similarities to create ambiguity or wit. This stylistic choice enriches language by engaging listeners' cognitive and phonological processing through ingenious sound-based associations.
Key Differences Between Antithesis and Paronomasia
Antithesis involves contrasting ideas placed in parallel structures to highlight differences, whereas paronomasia relies on wordplay by using similar-sounding words with different meanings to create humor or emphasis. Antithesis is primarily a rhetorical device used to emphasize opposites in arguments or speeches, while paronomasia is commonly found in puns and witty language for entertainment. The key difference lies in antithesis focusing on conceptual contrast, while paronomasia centers on phonetic similarity and semantic ambiguity.
Literary Functions of Antithesis
Antithesis employs contrasting ideas or words within a balanced structure to highlight differences and create emphasis, thereby enhancing clarity and persuasion in literary works. It sharpens the reader's understanding by presenting opposing concepts side by side, often evoking strong emotional or intellectual responses. Unlike paronomasia, which relies on wordplay through similar sounds, antithesis functions primarily to structure arguments and themes effectively in rhetorical and poetic contexts.
Literary Functions of Paronomasia
Paronomasia, also known as a pun, functions as a literary device that exploits the multiple meanings or similar sounds of words to create humor or emphasize a particular point. It enhances reader engagement by adding layers of wit and wordplay, often leading to memorable and thought-provoking expressions. Unlike antithesis, which contrasts ideas for rhetorical effect, paronomasia enriches text through linguistic creativity and semantic ambiguity.
Examples of Antithesis in Literature
Antithesis in literature is exemplified by Charles Dickens' "It was the best of times, it was the worst of times," which contrasts opposing ideas to highlight their differences. Shakespeare's "To be, or not to be: that is the question" uses antithesis to present existential dilemmas through contrasting concepts. These examples demonstrate how antithesis enhances thematic depth by juxtaposing conflicting elements within a single sentence or phrase.
Examples of Paronomasia in Literature
Paronomasia, often known as a pun, employs words that sound alike but have different meanings to create humor or emphasis, as seen in Shakespeare's use of "grave" in *Hamlet*, blending the meanings of "serious" and "a burial place." Another classical example is in Lewis Carroll's *Through the Looking-Glass*, where the phrase "You are old, Father William," plays with double meanings and sound to generate a witty effect. These instances highlight paronomasia's power to engage readers through linguistic creativity, contrasting with antithesis, which juxtaposes opposing ideas for rhetorical impact.
When to Use Antithesis vs Paronomasia
Antithesis is best used when contrasting ideas or concepts need to be highlighted clearly to emphasize differences, often in persuasive or literary contexts. Paronomasia, or punning, is effective when wordplay or humor is desired to engage the audience through phonetic similarity or double meanings. Choose antithesis for clarity and impact in argumentation, while paronomasia suits creative expression and rhetorical wit.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rhetorical Device
Antithesis sharpens contrasts between opposing ideas to create a powerful impact, while paronomasia leverages wordplay and phonetic similarity for humor or emphasis. Selecting the right rhetorical device depends on the desired effect: use antithesis to highlight conflict or opposition, and paronomasia to engage audiences with wit or memorability. Effective communication arises from matching rhetorical strategies to the content's tone and purpose, enhancing clarity and persuasion.
Antithesis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com