Direct discourse captures a character's exact speech, allowing readers to experience conversations vividly and authentically. Using quotation marks and precise punctuation, it differentiates spoken words from narrative text, enhancing clarity and engagement. Explore the rest of the article to master direct discourse techniques that will bring your writing to life.
Table of Comparison
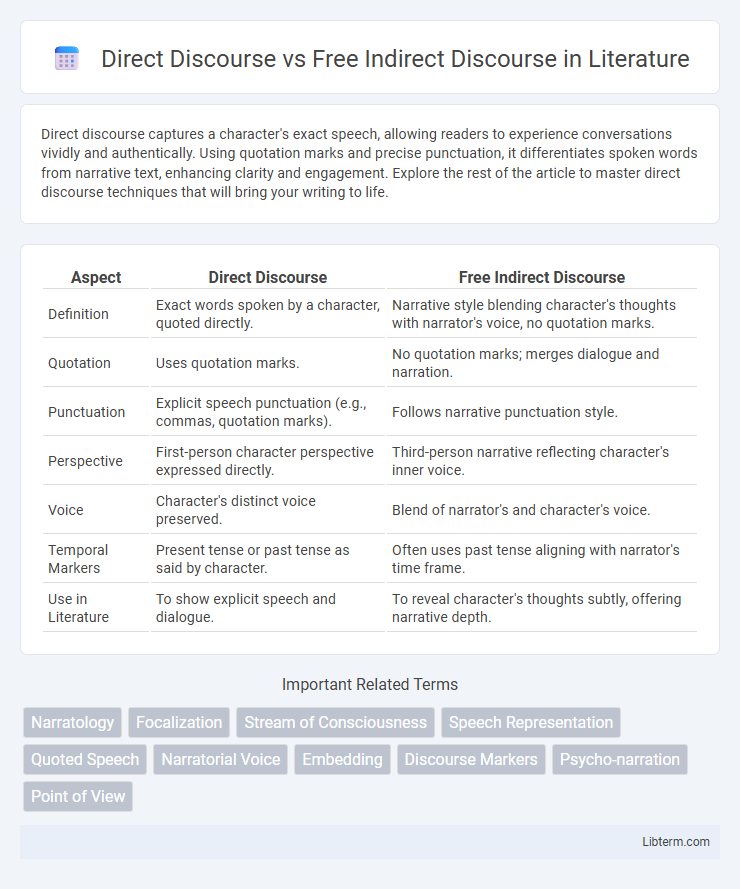
| Aspect | Direct Discourse | Free Indirect Discourse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exact words spoken by a character, quoted directly. | Narrative style blending character's thoughts with narrator's voice, no quotation marks. |
| Quotation | Uses quotation marks. | No quotation marks; merges dialogue and narration. |
| Punctuation | Explicit speech punctuation (e.g., commas, quotation marks). | Follows narrative punctuation style. |
| Perspective | First-person character perspective expressed directly. | Third-person narrative reflecting character's inner voice. |
| Voice | Character's distinct voice preserved. | Blend of narrator's and character's voice. |
| Temporal Markers | Present tense or past tense as said by character. | Often uses past tense aligning with narrator's time frame. |
| Use in Literature | To show explicit speech and dialogue. | To reveal character's thoughts subtly, offering narrative depth. |
Introduction to Discourse Styles in Narrative
Direct discourse presents characters' speech verbatim, using quotation marks to convey exact words and tone, creating immediacy and vividness in narrative. Free indirect discourse blends a character's thoughts or speech into the third-person narration without quotation marks, reflecting their perspective while maintaining narrative voice and temporal fluidity. This style enables seamless psychological insight and nuanced portrayal of consciousness within the narrative framework.
What is Direct Discourse?
Direct Discourse presents a character's exact spoken or thought words enclosed in quotation marks, maintaining the original syntax and style of the utterance. This narrative technique allows readers to experience the character's voice authentically and immediately, revealing emotions and intentions explicitly. It contrasts with Free Indirect Discourse by clearly distinguishing the character's speech from the narrator's voice.
Defining Free Indirect Discourse
Free Indirect Discourse blends a character's thoughts or speech seamlessly into third-person narration without quotation marks or explicit attribution, creating a fluid narrative voice that merges subjective experience with the narrator's perspective. Unlike Direct Discourse, which reproduces exact words within quotation marks, Free Indirect Discourse captures the essence of a character's internal voice while maintaining grammatical structures of third-person narration. This technique enhances psychological depth and immediacy by conveying personal perceptions and emotions subtly within the ongoing narrative flow.
Key Differences Between Direct and Free Indirect Discourse
Direct Discourse presents characters' spoken words verbatim, enclosed in quotation marks and often marked by a reporting verb, maintaining clear narrative distance. Free Indirect Discourse merges the narrator's voice with the character's thoughts and speech, eliminating quotation marks and blending perspectives without explicit attribution. This technique creates a seamless switch between third-person narration and subjective experience, offering deeper psychological insight while preserving narrative fluidity.
Stylistic Features of Direct Discourse
Direct Discourse directly quotes a character's speech or thoughts, maintaining the exact wording and punctuation, often enclosed in quotation marks to signal the character's voice vividly. This stylistic choice enhances immediacy and realism, allowing readers to experience the narrative through the character's personal perspective and emotional tone. The use of first-person pronouns, present tense, and precise lexical choices in Direct Discourse distinguishes it sharply from the narrator's voice, emphasizing individual expression within the text.
Narrative Advantages of Free Indirect Discourse
Free indirect discourse offers narrative advantages by seamlessly blending a character's thoughts and feelings with the third-person narrative voice, creating a more intimate and immersive experience. This technique allows for subtle shifts in perspective without explicit markers, enhancing psychological depth and maintaining narrative fluidity. It enables authors to convey subjective viewpoints while preserving narrative control, enriching character development and emotional nuance.
Effects on Characterization and Voice
Direct discourse presents a character's speech verbatim, preserving their unique voice and allowing readers to engage directly with their emotions and intentions, which sharpens characterization. Free indirect discourse blends the character's thoughts and speech into the narrator's voice, creating a subtle merge that reveals internal states without explicit quotations, enhancing psychological depth. This narrative technique fosters intimacy between the character and reader by conveying subjective perspectives while maintaining narrative cohesion.
Reader Engagement and Perspective
Direct discourse presents characters' exact words, enhancing reader engagement by offering immediate access to their thoughts and emotions. Free indirect discourse blends narrator's voice with character's inner thoughts, creating a seamless shift in perspective that deepens reader connection without explicit quotation. This narrative technique allows readers to perceive subjective experience while maintaining narrative flow, enriching interpretative depth and emotional involvement.
Common Examples in Literature
Direct discourse presents characters' exact words using quotation marks, as seen in Shakespeare's plays where dialogues explicitly reveal thoughts and conversations. Free indirect discourse blends the narrator's voice with the character's inner thoughts without quotation marks, exemplified by Jane Austen's novels like "Emma," where the narrative seamlessly reflects characters' perspectives. This technique creates a subtle shift between third-person narration and personal consciousness, enriching the reader's connection to character psychology.
Choosing the Right Discourse for Your Story
Direct discourse provides clear, character-specific dialogue that immerses readers in authentic conversations, making it ideal for revealing personality and emotions explicitly. Free indirect discourse blends a character's thoughts and voice with the narrator's, offering a subtle, intimate perspective without breaking narrative flow, perfect for maintaining a close yet omniscient viewpoint. Selecting between them depends on narrative style and emotional impact; direct discourse enhances immediacy, while free indirect discourse deepens psychological insight.
Direct Discourse Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com