Bard is an advanced AI language model designed to generate human-like text, assist with creative writing, and answer complex questions effectively. It uses cutting-edge natural language processing techniques to provide accurate and contextually relevant responses. Discover how Bard can enhance your productivity and creativity by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
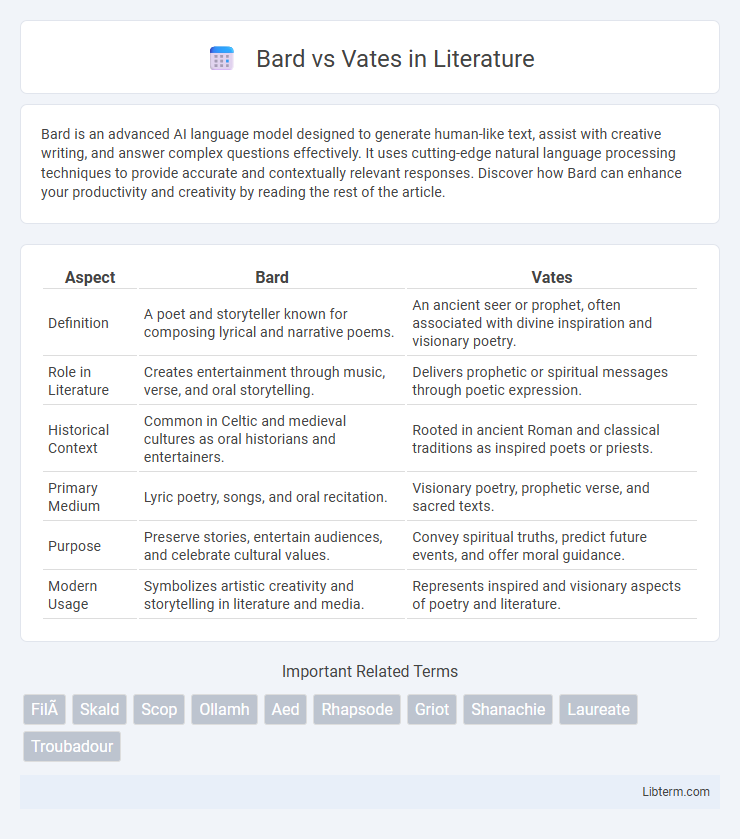
| Aspect | Bard | Vates |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A poet and storyteller known for composing lyrical and narrative poems. | An ancient seer or prophet, often associated with divine inspiration and visionary poetry. |
| Role in Literature | Creates entertainment through music, verse, and oral storytelling. | Delivers prophetic or spiritual messages through poetic expression. |
| Historical Context | Common in Celtic and medieval cultures as oral historians and entertainers. | Rooted in ancient Roman and classical traditions as inspired poets or priests. |
| Primary Medium | Lyric poetry, songs, and oral recitation. | Visionary poetry, prophetic verse, and sacred texts. |
| Purpose | Preserve stories, entertain audiences, and celebrate cultural values. | Convey spiritual truths, predict future events, and offer moral guidance. |
| Modern Usage | Symbolizes artistic creativity and storytelling in literature and media. | Represents inspired and visionary aspects of poetry and literature. |
Introduction to Bard vs Vates
Bard and Vates represent distinct roles rooted in ancient Celtic culture, each serving unique societal functions. Bards were primarily poets and musicians who preserved history and tradition through oral storytelling and song. Vates, often considered prophets or seers, emphasized spiritual guidance and divination, shaping cultural and religious beliefs.
Defining Bard: Origins and Meanings
Bard originates from the Gaelic word "baird," referring to a poet or minstrel in ancient Celtic cultures, primarily responsible for composing and reciting epic poetry and songs that preserve oral history. Bards were revered as historians, genealogists, and entertainers, often attached to royal courts or tribal communities. Unlike the Latin-derived term vates, which means prophet or seer, bard emphasizes artistic storytelling and musical tradition.
Understanding Vates: Historical Context
Vates were ancient Roman seers and prophets known for their divinatory abilities, often linked to poetic and religious functions within the society. Unlike bards, who primarily served as storytellers and musicians preserving oral tradition, vates played a crucial role in spiritual guidance and interpreting omens during the Roman Republic and early Empire. Their prophecies were integral to decision-making processes in both public and private rites, emphasizing their importance in historical and religious contexts.
Bard in Literature and Culture
Bard in literature and culture represents poets or storytellers celebrated for composing and reciting epic works, often preserving oral traditions and cultural heritage. The term "Bard" is closely associated with figures like William Shakespeare, symbolizing creative genius and the power of narrative to shape societal values. In contrast to "Vates," which implies a seer or prophet, the Bard emphasizes artistic expression and communal storytelling as a means of cultural identity and memory.
Vates in Ancient Traditions
Vates were revered seers and prophets in ancient traditions, often regarded as intermediaries between the divine and human realms, possessing spiritual insight and the ability to foretell future events. Unlike bards, who primarily served as poets and musicians preserving oral history and culture, vates held a more mystical role centered on ritualistic prophecy and divination practices within Celtic and Roman societies. Their influence extended into religious ceremonies, shaping decision-making and reinforcing societal values through visionary guidance.
Key Differences Between Bard and Vates
Bard traditionally refers to a poet and storyteller who composes and recites epic or lyrical poetry, often preserving oral history and legends, while Vates in ancient contexts denotes a seer or prophet with a focus on divine inspiration and prophecy rather than narrative creation. The Bard emphasizes artistic expression and cultural transmission through poetry and music, whereas the Vates plays a critical role in spiritual guidance and foretelling future events based on divine insight. Key differences lie in their functions: Bards maintain cultural heritage through creative storytelling, whereas Vates serve as intermediaries between the divine and human realms, delivering prophetic wisdom.
Roles and Functions in Society
Bards served as poets, musicians, and storytellers, preserving history and cultural heritage through oral traditions in Celtic and medieval societies. Vates, often seen as seers or prophets in Roman and early Celtic contexts, fulfilled spiritual and divinatory roles, interpreting omens and guiding communal decisions. Both figures held significant influence, with bards shaping social memory and vates providing religious and ideological direction.
Evolution of Bard and Vates Over Time
Bard and Vates both originate from ancient roles of poetic and prophetic tradition, with Bard evolving as a Celtic storyteller and musician, while Vates served as a Roman seer and poet. Over time, the Bard transitioned into a symbol of cultural preservation and artistic expression, especially in Scottish and Irish history. The Vates role shifted towards religious and political prophecy, influencing Roman literature and later Renaissance humanism.
Influence on Modern Storytelling
Bard and Vates represent distinct archetypes that have shaped modern storytelling by influencing narrative structure and thematic depth. The Bard, often seen as a charismatic storyteller and entertainer, popularized oral tradition and melodic poetry, embedding emotional resonance and cultural values into stories. In contrast, the Vates, as a prophetic and visionary figure, introduced elements of mysticism and foresight, inspiring modern narratives that explore existential themes and moral complexity.
Conclusion: Bard vs Vates in Contemporary Perspective
Bard and Vates represent distinct archetypes within ancient literary and prophetic traditions, with the Bard typically embodying artistic expression and cultural storytelling, while the Vates serves as a seer or visionary with spiritual insight. Contemporary perspectives emphasize the Bard's role in preserving cultural identity through narrative and performance, contrasting with the Vates' function of interpreting divine or mystical messages. Both figures remain influential in modern interpretations of myth and literature, highlighting the intersection of creativity and prophecy in human understanding.
Bard Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com