Realism in art and literature emphasizes authentic representation of everyday life without idealization or romanticism. It focuses on truthful depiction of ordinary characters and situations, highlighting social issues and human experiences. Explore the article to understand how realism shapes your perception of the world through creative works.
Table of Comparison
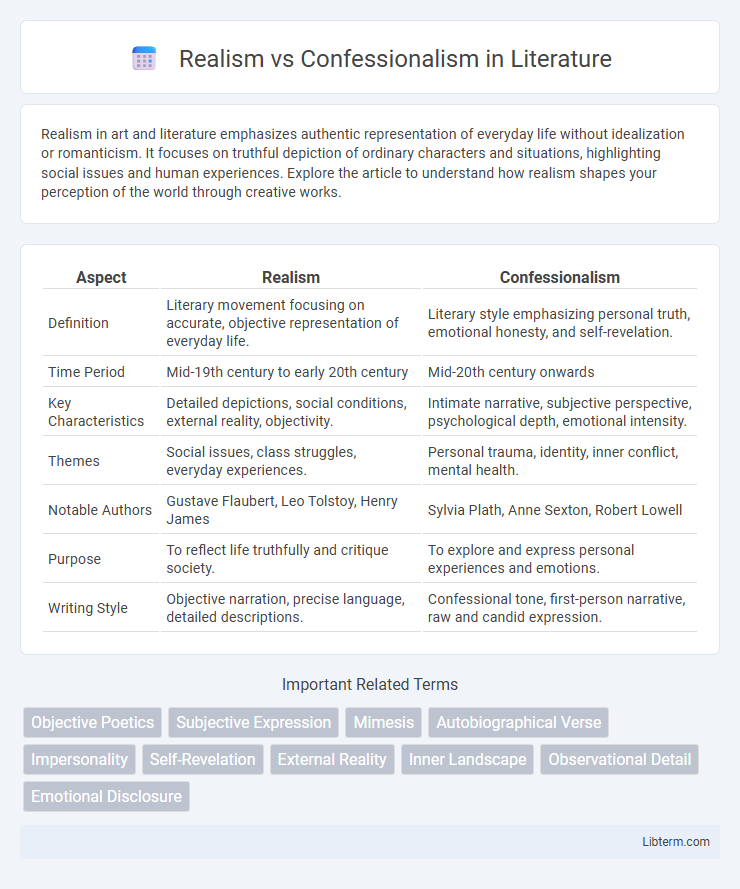
| Aspect | Realism | Confessionalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Literary movement focusing on accurate, objective representation of everyday life. | Literary style emphasizing personal truth, emotional honesty, and self-revelation. |
| Time Period | Mid-19th century to early 20th century | Mid-20th century onwards |
| Key Characteristics | Detailed depictions, social conditions, external reality, objectivity. | Intimate narrative, subjective perspective, psychological depth, emotional intensity. |
| Themes | Social issues, class struggles, everyday experiences. | Personal trauma, identity, inner conflict, mental health. |
| Notable Authors | Gustave Flaubert, Leo Tolstoy, Henry James | Sylvia Plath, Anne Sexton, Robert Lowell |
| Purpose | To reflect life truthfully and critique society. | To explore and express personal experiences and emotions. |
| Writing Style | Objective narration, precise language, detailed descriptions. | Confessional tone, first-person narrative, raw and candid expression. |
Understanding Realism: Core Principles and Origins
Realism, rooted in 19th-century literature, emphasizes accurate, detailed depictions of everyday life and society, rejecting romanticized or idealized portrayals. Core principles include a focus on characters' social conditions, ethical dilemmas, and the influence of environment and heredity on human behavior. Originating as a reaction to Romanticism, Realism seeks to present an objective, truthful representation of ordinary experiences.
Defining Confessionalism: Key Concepts and Historical Background
Confessionalism is a political system that allocates power among religious communities to ensure representation and prevent dominance by any single group, often rooted in the historical context of deeply divided societies like Lebanon. It emphasizes the recognition of distinct religious identities within governance structures, promoting coexistence through institutionalized power-sharing arrangements. The concept emerged as a response to sectarian conflict, aiming to maintain stability by embedding religious affiliations into political frameworks.
Realism vs Confessionalism: Theoretical Frameworks Compared
Realism and Confessionalism represent two distinct theoretical frameworks in international relations, with Realism emphasizing power dynamics, state interests, and survival in an anarchic international system. Confessionalism, rooted in religious and sectarian identities, shapes political behavior and governance structures by prioritizing communal representation and power-sharing among different confessional groups. The contrast lies in Realism's focus on material power and strategic interests versus Confessionalism's emphasis on identity politics and institutionalized sectarian balance.
Influences on International Relations: Realist and Confessionalist Perspectives
Realism in international relations emphasizes the role of state power, security, and national interest in a competitive anarchic global system, with key thinkers like Hans Morgenthau and Kenneth Waltz shaping its principles. Confessionalism, rooted in sectarian identities and power-sharing arrangements, influences state behavior by prioritizing internal religious or ethnic group interests, particularly evident in Lebanon's political framework. These perspectives diverge in explaining state actions: realists focus on strategic calculations for survival and dominance, while confessionalists highlight the impact of internal communal dynamics and sectarian loyalties on foreign policy decisions.
Policy Implications: Realism’s Approach vs Confessionalism’s Solutions
Realism's approach to policy emphasizes state sovereignty, power balance, and national interest, often prioritizing security and strategic alliances over ideological or moral considerations. Confessionalism advocates power-sharing arrangements and institutional inclusivity based on sectarian or religious identity, aiming to mitigate conflict through proportional representation and guaranteed group rights. Policy implications differ as Realism favors pragmatic, often unilateral actions to maintain order, whereas Confessionalism seeks consensus-driven governance to ensure stability in divided societies.
Case Studies: Realism and Confessionalism in Historical Context
Realism in political science emphasizes state-centric analysis and power dynamics, exemplified by the Cold War US-Soviet rivalry where national interest and security dominated policy decisions. Confessionalism, particularly in Lebanon, is rooted in power-sharing among religious communities to maintain political stability and manage sectarian diversity, as seen in the National Pact and Taif Agreement. These case studies highlight Realism's focus on external threats and state survival, contrasting with Confessionalism's emphasis on internal coexistence and institutionalized sectarian representation.
Strengths and Limitations of Realism
Realism emphasizes state sovereignty, power dynamics, and national interest, providing a clear framework for analyzing international relations through balance-of-power mechanisms. Its strength lies in explaining conflict and cooperation based on rational actors prioritizing security, but it often overlooks ethical considerations, non-state actors, and the influence of domestic politics, limiting its explanatory power. Realism's focus on material power can understate the role of ideas, identities, and international institutions in shaping global outcomes.
Advantages and Critiques of Confessionalism
Confessionalism promotes political stability by ensuring power-sharing among diverse religious or ethnic groups, which helps prevent domination by a single group and reduces conflict. Critics argue that confessionalism entrenches sectarian divisions, limits national unity, and hampers political reform by prioritizing group interests over merit and common citizenship. While it fosters inclusion, confessionalism often leads to political gridlock and may incentivize corruption within sectarian parties.
Modern Impact: Realism and Confessionalism in Contemporary Issues
Realism, emphasizing state interests and power politics, shapes contemporary international relations by prioritizing national security and pragmatic diplomacy, influencing policies on issues like trade, conflict, and security alliances. Confessionalism, centered on power-sharing based on religious or ethnic identities, impacts governance models in countries with diverse populations, as seen in Lebanon and Bosnia, where it aims to maintain peace but often complicates political stability. The modern impact of both ideologies is evident in their roles in addressing conflicts and fostering cooperation, reflecting the tension between pragmatic statecraft and identity-based political arrangements.
Choosing an Approach: Realism or Confessionalism for Today’s Challenges
Choosing between Realism and Confessionalism in today's political landscape depends on prioritizing either pragmatic state interests or ideological and moral commitments. Realism emphasizes power dynamics, national security, and practical diplomacy, essential for navigating global conflicts and geopolitical competition. Confessionalism advocates for governance grounded in religious or ethical identity, fostering social cohesion and legitimacy in societies with diverse cultural or sectarian groups.
Realism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com