Dialogue enhances communication by fostering understanding and collaboration between individuals. It allows you to express thoughts clearly while actively listening to others, promoting mutual respect and problem-solving. Explore the rest of this article to discover effective dialogue techniques and their impact on relationships.
Table of Comparison
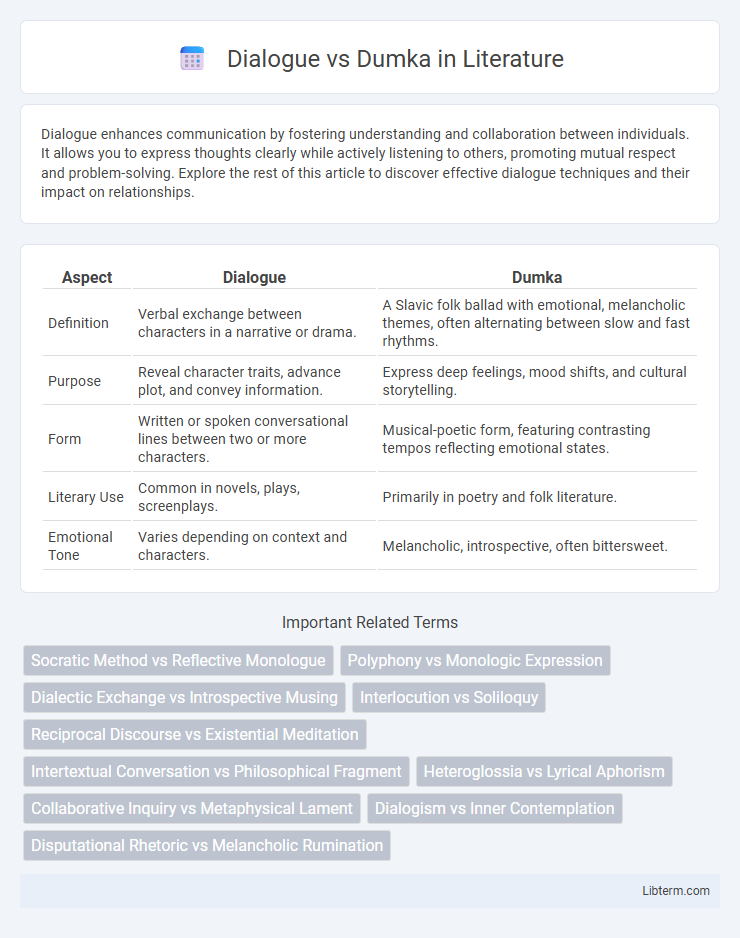
| Aspect | Dialogue | Dumka |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verbal exchange between characters in a narrative or drama. | A Slavic folk ballad with emotional, melancholic themes, often alternating between slow and fast rhythms. |
| Purpose | Reveal character traits, advance plot, and convey information. | Express deep feelings, mood shifts, and cultural storytelling. |
| Form | Written or spoken conversational lines between two or more characters. | Musical-poetic form, featuring contrasting tempos reflecting emotional states. |
| Literary Use | Common in novels, plays, screenplays. | Primarily in poetry and folk literature. |
| Emotional Tone | Varies depending on context and characters. | Melancholic, introspective, often bittersweet. |
Introduction to Dialogue and Dumka
Dialogue is a conversational exchange between two or more characters that drives narratives, reveals character traits, and advances plotlines, commonly used in literature, theater, and film. Dumka, originating from Ukrainian folk music, is a form of lyrical lament or mournful song characterized by alternating slow, melancholic passages and lively, upbeat sections. While dialogue structures communication and interaction in storytelling, Dumka conveys emotional contrasts through its musical composition.
Defining Dialogue: Meaning and Features
Dialogue is a structured conversation between two or more characters that serves to advance the plot, reveal character relationships, and convey themes within literary works. It is characterized by its interactive nature, realistic speech patterns, and the use of direct quotations to represent spoken words. Essential features include clarity, conciseness, and the ability to reflect distinct character voices and emotions.
Understanding Dumka: Concept and Origins
Dumka is a musical form rooted in Slavic folk traditions, characterized by its alternating melancholic and lively tempos, reflecting a deep emotional narrative. Originating from Ukrainian folk music, dumka originally served as a vocal lament or reflective ballad before being adapted into instrumental compositions by classical composers like Antonin Dvorak. This form contrasts with dialogue-based structures by emphasizing mood shifts and thematic storytelling rather than conversational exchanges between voices or instruments.
Key Differences Between Dialogue and Dumka
Dialogue is a conversational exchange between two or more characters, serving to reveal personality, advance the plot, or provide information within a narrative. Dumka is a specific type of literary or musical composition, originating from Eastern European folk traditions, characterized by alternating slow, melancholic sections and faster, lively passages, often expressing emotional contrast. The key difference lies in dialogue's function as a narrative device in prose or drama, while dumka is a form with distinct rhythmic and emotional patterns used in music and poetry.
Purposes and Functions in Literature
Dialogue serves to develop character relationships, reveal motivations, and advance the plot by showcasing direct verbal exchanges between characters. Dumka, a lyrical and melancholic form originating from Eastern European folk music, functions in literature to convey deep emotional states, often reflecting introspection and sorrow through poetic or musical narrative. While dialogue emphasizes interaction and dynamic storytelling, dumka centers on mood, atmosphere, and the internal emotional landscape.
Structural Elements: Dialogue vs Dumka
Dialogue and Dumka differ significantly in structural elements, as Dialogue typically features a back-and-forth exchange between characters that drives the narrative or reveals conflict, emphasizing conversational rhythm and pacing. Dumka, rooted in Slavic folk tradition, combines contrasting moods within a single composition, alternating between melancholic and lively sections to evoke emotional depth and cultural expression. While Dialogue relies on interactive speech patterns and character dynamics, Dumka focuses on mood shifts and musical phrasing to convey its thematic essence.
Role in Enhancing Narrative and Theme
Dialogue sharpens character development and advances the plot by revealing motivations, conflicts, and relationships through spoken exchanges, making the narrative more dynamic and relatable. Dumka, a musical form rooted in Slavic folklore, enhances thematic depth by conveying emotional contrasts and introspective moods, often reflecting internal struggles within the narrative structure. Together, dialogue and Dumka enrich storytelling by combining verbal interaction with evocative emotional expression, deepening audience engagement and thematic resonance.
Examples of Dialogue in Literature
Dialogue in literature often brings characters to life by showcasing their interactions and emotions directly, as exemplified in Shakespeare's *Hamlet*, where exchanges between Hamlet and Ophelia reveal deep psychological conflict. Jane Austen's *Pride and Prejudice* uses witty dialogue between Elizabeth Bennet and Mr. Darcy to develop character and social themes. In Arthur Miller's *The Crucible*, confrontations through dialogue expose the hysteria and moral struggles of the Salem witch trials.
Notable Instances of Dumka in Writing
Dumka, a Slavic-origin musical and literary form characterized by alternating melancholy and lively sections, appears notably in the works of composers like Antonin Dvorak, who popularized it in chamber music and symphonies, as well as in classical literature where it conveys emotional contrast. Unlike dialogue, which directly presents conversational exchanges between characters, dumka serves as an expressive, often lyrical narrative device reflecting inner turmoil and cultural themes. Prominent literary examples include the 19th-century Ukrainian and Czech writers who infused dumka into poetry and prose to evoke national identity and emotional depth.
Choosing Between Dialogue and Dumka: Tips for Writers
Writers should choose dialogue to reveal character emotions and advance the plot through direct speech, creating immediacy and engagement. Dumka offers a reflective, lyrical narrative style that explores internal thoughts and moods, ideal for introspective moments or cultural themes. Balancing dialogue's dynamic interaction with dumka's poetic depth enhances storytelling by blending action with emotional resonance.
Dialogue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com