Surrealism explores the unconscious mind through unexpected juxtapositions and dreamlike imagery, challenging traditional perceptions of reality. This artistic movement influences literature, visual arts, and film, encouraging you to embrace imagination beyond logic. Discover how surrealism reshapes creativity and thought as you read the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
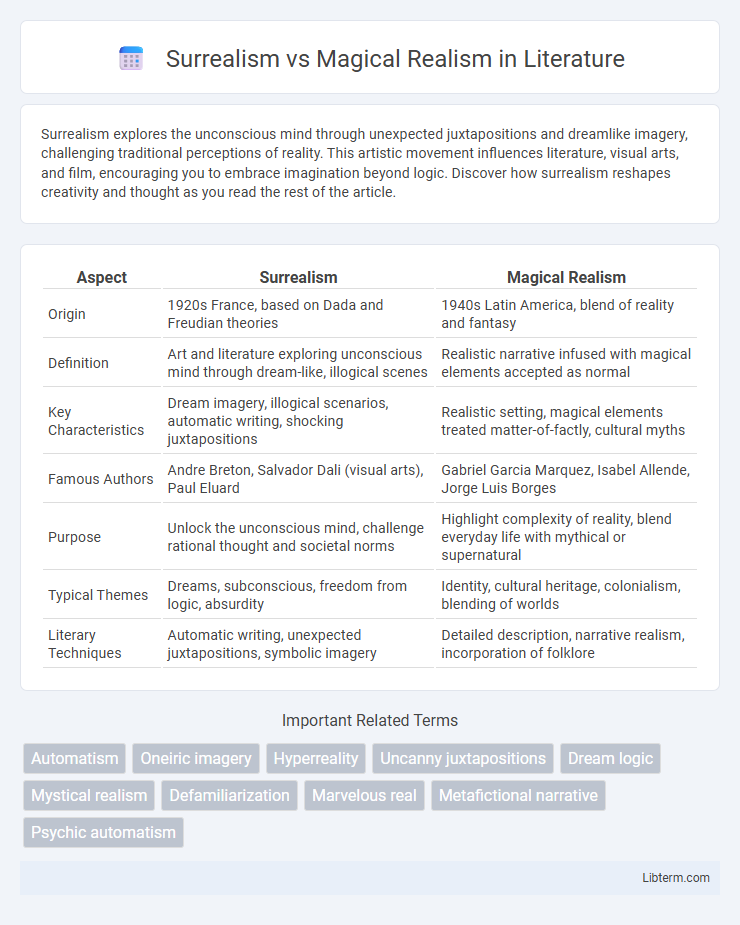
| Aspect | Surrealism | Magical Realism |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | 1920s France, based on Dada and Freudian theories | 1940s Latin America, blend of reality and fantasy |
| Definition | Art and literature exploring unconscious mind through dream-like, illogical scenes | Realistic narrative infused with magical elements accepted as normal |
| Key Characteristics | Dream imagery, illogical scenarios, automatic writing, shocking juxtapositions | Realistic setting, magical elements treated matter-of-factly, cultural myths |
| Famous Authors | Andre Breton, Salvador Dali (visual arts), Paul Eluard | Gabriel Garcia Marquez, Isabel Allende, Jorge Luis Borges |
| Purpose | Unlock the unconscious mind, challenge rational thought and societal norms | Highlight complexity of reality, blend everyday life with mythical or supernatural |
| Typical Themes | Dreams, subconscious, freedom from logic, absurdity | Identity, cultural heritage, colonialism, blending of worlds |
| Literary Techniques | Automatic writing, unexpected juxtapositions, symbolic imagery | Detailed description, narrative realism, incorporation of folklore |
Introduction to Surrealism and Magical Realism
Surrealism emerged in the early 20th century as an avant-garde movement emphasizing the unconscious mind, dream imagery, and illogical scenes to challenge reality and traditional aesthetics. Magical Realism originated in Latin American literature, blending realistic narratives with magical elements presented as ordinary, creating a seamless fusion of fantasy and everyday life. Both styles disrupt conventional representation but differ in intent and cultural context, with Surrealism seeking to unlock the subconscious and Magical Realism embedding the mystical within the fabric of reality.
Historical Origins and Influences
Surrealism, emerging in the early 1920s from the Dada movement, was heavily influenced by Freudian psychoanalysis and aimed to unleash the unconscious mind through dream-like, illogical imagery. Magical Realism, developing in Latin America during the mid-20th century, blends realistic narrative with fantastical elements, rooted in indigenous mythology and postcolonial cultural identity. Both movements reflect reactions to historical upheaval but diverge in their cultural origins: Surrealism is European and avant-garde, while Magical Realism integrates local traditions with modern storytelling.
Defining Characteristics of Surrealism
Surrealism is defined by its emphasis on unlocking the unconscious mind through dream-like, illogical scenes and bizarre, often unsettling imagery that defies rational explanation. It frequently employs automatic writing, unexpected juxtapositions, and symbolic motifs to challenge conventional perceptions of reality. The movement aims to transcend reality by blending reality with the irrational, creating a distorted yet psychologically rich experience.
Defining Characteristics of Magical Realism
Magical Realism is characterized by the seamless integration of fantastical elements into a realistic narrative, where extraordinary occurrences are accepted as normal within the story's world. This genre often portrays ordinary settings infused with magical or supernatural details that reflect cultural, social, or historical contexts, emphasizing the coexistence of reality and magic. Unlike Surrealism's dream-like disjointedness, Magical Realism maintains coherent and detailed depictions of everyday life, blending myth and reality to explore human experience.
Key Themes in Surrealism
Surrealism explores themes of the unconscious mind, dream imagery, and the irrational, often emphasizing automatic writing and spontaneous creativity to unlock hidden desires and fears. Key motifs include juxtapositions of unrelated objects, distorted realities, and symbolic representations challenging conventional perception. This movement seeks to disrupt logical reasoning and tap into deeper psychological truths beyond everyday experience.
Key Themes in Magical Realism
Magical Realism emphasizes the coexistence of the magical and the mundane, blending fantastical elements with everyday reality to highlight cultural and political contradictions, especially in Latin American contexts. Key themes include the fluidity of time, the interplay between myth and history, and the exploration of identity through a fusion of the supernatural and the real. This genre challenges traditional narrative structures by presenting extraordinary phenomena as part of ordinary life.
Leading Figures and Iconic Works
Surrealism, led by figures such as Andre Breton and Salvador Dali, is defined by dream-like, illogical scenes exemplified in Dali's painting "The Persistence of Memory" and Breton's "Manifesto of Surrealism." Magical Realism, championed by Gabriel Garcia Marquez and Isabel Allende, blends fantastical elements with reality, with Marquez's novel "One Hundred Years of Solitude" standing as an iconic work. Both movements challenge conventional perceptions, but Surrealism dives into unconscious mind imagery while Magical Realism integrates magical aspects into everyday life narratives.
Artistic Techniques and Narrative Styles
Surrealism employs dreamlike, illogical scenes and unexpected juxtapositions to explore the unconscious mind, often using techniques like automatic drawing and collage to disrupt reality. Magical Realism integrates fantastical elements into otherwise realistic settings, maintaining a matter-of-fact narrative style that normalizes the extraordinary within everyday life. While Surrealism challenges perceptions with abstract and fragmented narratives, Magical Realism blends magical details seamlessly into coherent, culturally rich stories.
Impact on Literature and Visual Arts
Surrealism revolutionized literature and visual arts through its emphasis on unlocking the unconscious mind, leading to dreamlike imagery and non-linear narratives that challenged traditional reality. Magical realism blended fantastical elements with everyday settings, enriching storytelling by exploring cultural and social realities through the extraordinary, influencing Latin American literature and global art movements. Both movements expanded artistic expression, with Surrealism inspiring avant-garde experimentation and Magical realism fostering a synthesis of myth and reality, deeply impacting narrative structures and visual symbolism.
Surrealism vs Magical Realism: Core Differences
Surrealism emphasizes the unconscious mind, dream-like imagery, and irrational juxtapositions to challenge reality and provoke emotional responses. Magical Realism incorporates magical elements seamlessly into a realistic environment, blending the ordinary with the fantastical to explore cultural and social realities. The core difference lies in Surrealism's intent to disrupt logical perception versus Magical Realism's integration of supernatural events as normal aspects of everyday life.
Surrealism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com