Paradise Lost explores the epic struggle between good and evil through the poetic retelling of the biblical Fall of Man, revealing profound themes of temptation, free will, and redemption. John Milton's masterful use of language and vivid imagery immerses readers in a timeless narrative that challenges perceptions of authority and morality. Discover how this classic work continues to influence literature and thought by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
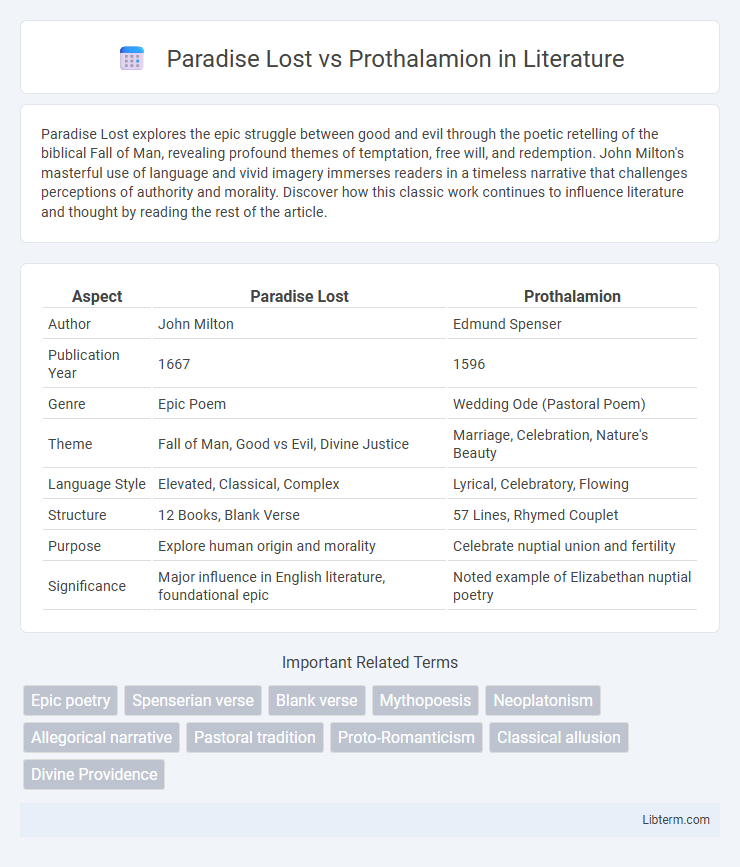
| Aspect | Paradise Lost | Prothalamion |
|---|---|---|
| Author | John Milton | Edmund Spenser |
| Publication Year | 1667 | 1596 |
| Genre | Epic Poem | Wedding Ode (Pastoral Poem) |
| Theme | Fall of Man, Good vs Evil, Divine Justice | Marriage, Celebration, Nature's Beauty |
| Language Style | Elevated, Classical, Complex | Lyrical, Celebratory, Flowing |
| Structure | 12 Books, Blank Verse | 57 Lines, Rhymed Couplet |
| Purpose | Explore human origin and morality | Celebrate nuptial union and fertility |
| Significance | Major influence in English literature, foundational epic | Noted example of Elizabethan nuptial poetry |
Introduction: Comparing Literary Giants
Paradise Lost, John Milton's epic masterpiece published in 1667, explores themes of divine justice, free will, and the Fall of Man through complex blank verse narrative. Prothalamion, composed by Edmund Spenser in 1596, is a lyrical poem celebrating marriage with vivid nature imagery and classical allusions, blending pastoral and mythological elements. The introduction of both works showcases the authors' command of language and their distinct approaches to profound human experiences within the Renaissance literary tradition.
Historical Context: Milton and Spenser
John Milton's *Paradise Lost* (1667) reflects the turbulent political and religious upheaval of 17th-century England, particularly the aftermath of the English Civil War and the Restoration, emphasizing themes of authority, obedience, and individual conscience. Edmund Spenser's *Prothalamion* (1596), composed during the Elizabethan era, celebrates an idealized vision of harmony and social order, embodying the optimism and cultural nationalism of late 16th-century England. These works illustrate the shift from Renaissance humanism and courtly celebration in Spenser's time to Milton's engagement with Puritan ideology and republicanism in a monarchy-restored England.
Thematic Contrasts: Epic vs. Celebration
Paradise Lost explores grand themes of cosmic struggle, free will, and the fall of humanity through an epic lens, emphasizing moral complexity and divine justice. Prothalamion centers on celebratory themes of love, marriage, and renewal, reflecting a pastoral and joyful atmosphere that contrasts with the epic's somber tone. These works exemplify Milton's versatility in addressing both profound theological questions and the joyous rites of human life.
Structure and Form: Epic Poem vs. Marriage Song
Paradise Lost, an epic poem by John Milton, employs a grand, formal structure with blank verse to explore profound themes of creation, fall, and redemption through a vast, heroic narrative. In contrast, Edmund Spenser's Prothalamion is a celebratory marriage song composed in lyrical, musical stanzas that evoke joy and harmony, focusing on a specific social event--the nuptial ceremony of noble brides. The epic form's complexity and elevated style starkly contrast with the marriage song's concise, melodic, and ritualistic composition, highlighting distinct poetic purposes and audience engagement.
Religious Undertones and Symbolism
Paradise Lost by John Milton uses rich religious undertones and symbolism to explore themes of sin, redemption, and divine justice, portraying the biblical fall of man with epic imagery and theological depth. Prothalamion by Edmund Spenser employs Christian motifs subtly intertwined with classical symbolism, celebrating nuptial harmony and divine blessing while emphasizing innocence and purity. The two works contrast in their theological focus, with Milton's epic delving into cosmic spiritual conflict and Spenser's lyric highlighting sacred matrimonial joy.
Portrayal of Love and Human Experience
Paradadise Lost explores love through the prism of divine and tragic dimensions, emphasizing obedience, sacrifice, and redemption in the human experience. In contrast, Prothalamion celebrates love as joyous, ceremonial, and harmonious, capturing the innocence and idealism of human emotions. Both works reveal the multifaceted nature of love, juxtaposing the spiritual and earthly realms within the larger context of human existence.
Use of Imagery and Language
Paradise Lost employs grandiose, vivid imagery rooted in biblical and classical references to evoke the cosmic struggle between good and evil, using elevated, formal language that reflects its epic scope. Prothalamion, by contrast, utilizes pastoral and celebratory imagery drawn from nature and nuptial symbolism, with lyrical and delicate language that creates a sense of joy and harmony. Both texts exemplify Milton's mastery of imagery and diction, yet they serve distinct thematic purposes shaped by their respective genres.
Representation of Nature and the Divine
Paradise Lost portrays nature as a reflection of divine order and cosmic hierarchy, emphasizing the fallen world's separation from God's original creation, while Prothalamion celebrates nature's harmonious beauty as a symbol of divine grace and renewal. Milton's epic uses vivid natural imagery to illustrate spiritual conflict and redemption, whereas Spenser's lyric poem infuses natural elements with themes of innocence and blessed union. Both works intertwine the divine presence with the natural world but diverge in tone: the former underscores loss and cosmic struggle, and the latter, joy and hope.
Lasting Influence on English Literature
Paradise Lost by John Milton and Prothalamion by Edmund Spenser have left a profound and lasting influence on English literature through their pioneering use of language and thematic depth. Milton's epic poem reshaped the possibilities of poetic form and theological exploration, inspiring generations of writers with its complex portrayal of rebellion and redemption. Spenser's Prothalamion, with its lyrical celebration of marriage and nature, contributed to the development of English pastoral poetry and influenced the sonnet tradition.
Conclusion: Legacy and Relevance Today
Paradadise Lost, John Milton's epic poem, remains a seminal work influencing modern interpretations of theology, free will, and human nature, emphasizing the eternal struggle between good and evil. Prothalamion, by Edmund Spenser, celebrates union and hope, its lyrical beauty sustaining its relevance in studies of Renaissance poetry and nuptial symbolism. Both works continue to inspire contemporary literary criticism, reflecting enduring themes that shape cultural and philosophical discourse today.
Paradise Lost Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com