Realism captures life with genuine detail and authentic representation, emphasizing everyday experiences and social realities. It seeks to portray characters and settings as they truly are, avoiding idealization or romanticism. Explore the rest of this article to deepen your understanding of how realism shapes art and literature.
Table of Comparison
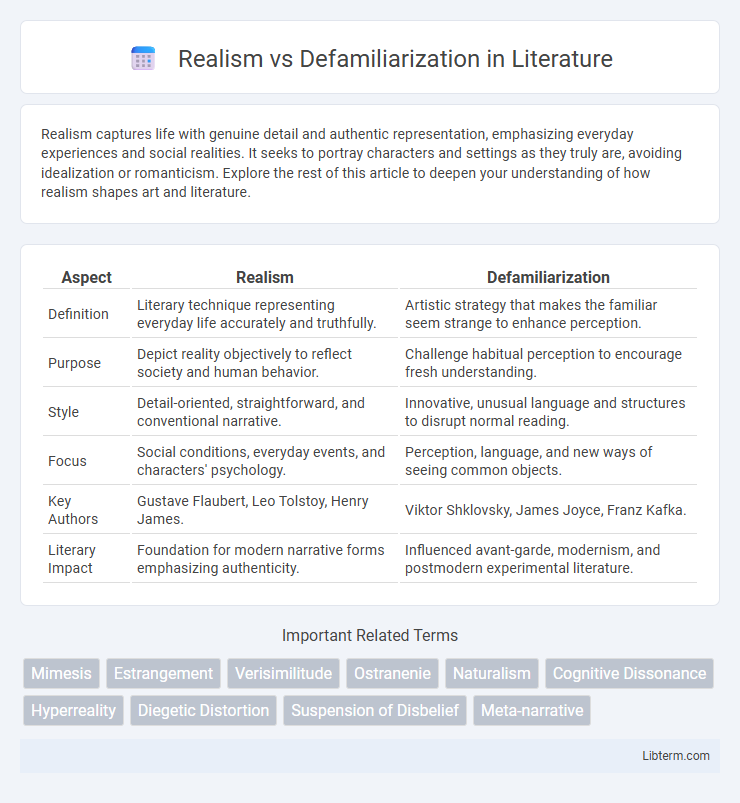
| Aspect | Realism | Defamiliarization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Literary technique representing everyday life accurately and truthfully. | Artistic strategy that makes the familiar seem strange to enhance perception. |
| Purpose | Depict reality objectively to reflect society and human behavior. | Challenge habitual perception to encourage fresh understanding. |
| Style | Detail-oriented, straightforward, and conventional narrative. | Innovative, unusual language and structures to disrupt normal reading. |
| Focus | Social conditions, everyday events, and characters' psychology. | Perception, language, and new ways of seeing common objects. |
| Key Authors | Gustave Flaubert, Leo Tolstoy, Henry James. | Viktor Shklovsky, James Joyce, Franz Kafka. |
| Literary Impact | Foundation for modern narrative forms emphasizing authenticity. | Influenced avant-garde, modernism, and postmodern experimental literature. |
Introduction to Realism and Defamiliarization
Realism emphasizes representing everyday life with accuracy and detail, aiming to portray characters, settings, and situations in a familiar, relatable way. Defamiliarization disrupts this familiarity by presenting ordinary objects or experiences in an unfamiliar or strange manner, encouraging readers to see them from a new perspective. This technique challenges conventional perceptions and enhances literary depth by making the familiar seem extraordinary.
Historical Origins of Realism
Realism emerged in the mid-19th century as a literary and artistic movement grounded in the accurate, detailed depiction of everyday life, reacting against Romanticism's idealism and emotional excess. Key figures like Gustave Flaubert and Honore de Balzac shaped Realism by emphasizing social context, class struggles, and ordinary characters to reflect contemporary society. This historical shift marked a commitment to objective observation and a truthful representation of human experience, laying the foundation for modern narrative techniques.
The Concept of Defamiliarization in Literature
Defamiliarization in literature disrupts habitual perception by presenting familiar objects or experiences in an unfamiliar way, enhancing readers' engagement with the text. Unlike Realism, which aims to depict life accurately and objectively, defamiliarization challenges readers to see the ordinary through a fresh perspective, provoking deeper reflection and emotional response. This technique, rooted in Russian Formalism and notably advanced by Viktor Shklovsky, emphasizes the artifice of language to break automatic, routine interpretations.
Key Principles of Realism
Realism prioritizes accurate, detailed representation of everyday life, emphasizing characters, settings, and situations that reflect ordinary experiences and social conditions. It employs objective narration and psychological depth to create authentic, believable narratives that resonate with readers' perceptions of reality. The principles of plausibility and causality ensure that events unfold logically, enhancing the work's credibility and fostering empathy through relatable, multidimensional characters.
Techniques and Methods of Defamiliarization
Defamiliarization techniques disrupt ordinary perception by presenting common subjects in unfamiliar ways, such as through unexpected metaphors, unconventional narrative structures, or distorted imagery. Methods include estrangement strategies like Verfremdungseffekt, which alienates the audience to provoke critical reflection, and defamiliarized language that forces readers to reevaluate automatic interpretations. These approaches contrast realism's emphasis on straightforward representation by foregrounding the artifice and complexity of experience.
Realism vs Defamiliarization: Core Differences
Realism aims to depict life and ordinary experiences with accurate, detailed representation, emphasizing familiar settings and characters to evoke recognition and relatability. Defamiliarization, on the other hand, breaks conventional perceptions by presenting common objects or scenarios in unfamiliar or strange ways, forcing the audience to see them anew and question routine understanding. The core difference lies in realism's goal of mirroring reality versus defamiliarization's purpose to disrupt and reframe reality through unexpected perspectives.
Impact on Reader Perception
Realism grounds the narrative in familiar contexts, enabling readers to connect through relatable characters and settings, which fosters empathy and clarity. Defamiliarization disrupts ordinary perceptions by presenting the familiar in an unfamiliar way, prompting readers to question assumptions and engage more critically with the text. This contrast intensifies reader awareness, with realism providing comfort and defamiliarization provoking deeper reflection.
Notable Authors and Works: Case Studies
Notable authors in Realism include Gustave Flaubert, whose novel *Madame Bovary* exemplifies detailed, truthful representation of everyday life, and George Eliot, known for *Middlemarch*, highlighting social realism and character complexity. Defamiliarization is prominently employed by writers like Viktor Shklovsky, who theorized the technique, and Franz Kafka, whose *The Metamorphosis* disrupts ordinary perception to reveal deeper psychological truths. These case studies demonstrate how Realism emphasizes ordinary experience while Defamiliarization challenges readers to experience the familiar as strange, thereby enhancing literary understanding.
Contemporary Relevance and Evolution
Realism emphasizes accurate representation of everyday life, grounding narratives in familiar experiences to foster relatability and social critique. Defamiliarization disrupts habitual perception by presenting ordinary objects or scenarios in unfamiliar ways, prompting deeper reflection and critical thinking. Contemporary literature and art increasingly blend these approaches, evolving to challenge audience complacency while maintaining accessibility amid digital and postmodern cultural shifts.
Conclusion: Future Directions in Literary Theory
Realism continues to anchor literary theory by emphasizing authentic representation of everyday life, while defamiliarization challenges readers to perceive the familiar through innovative linguistic and narrative techniques. Future directions in literary theory increasingly integrate cognitive science and digital media to explore how defamiliarization can reshape reader engagement and meaning-making processes. Embracing interdisciplinary approaches will enhance understanding of how realism and defamiliarization interact to expand literary expression in contemporary contexts.
Realism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com