Genetic analysis uncovers vital information about your DNA, identifying inherited traits and potential health risks through advanced sequencing techniques. By decoding genetic markers, researchers can provide personalized insights that enhance medical decisions and lifestyle choices. Discover how genetic analysis can transform your understanding of health in the full article.
Table of Comparison
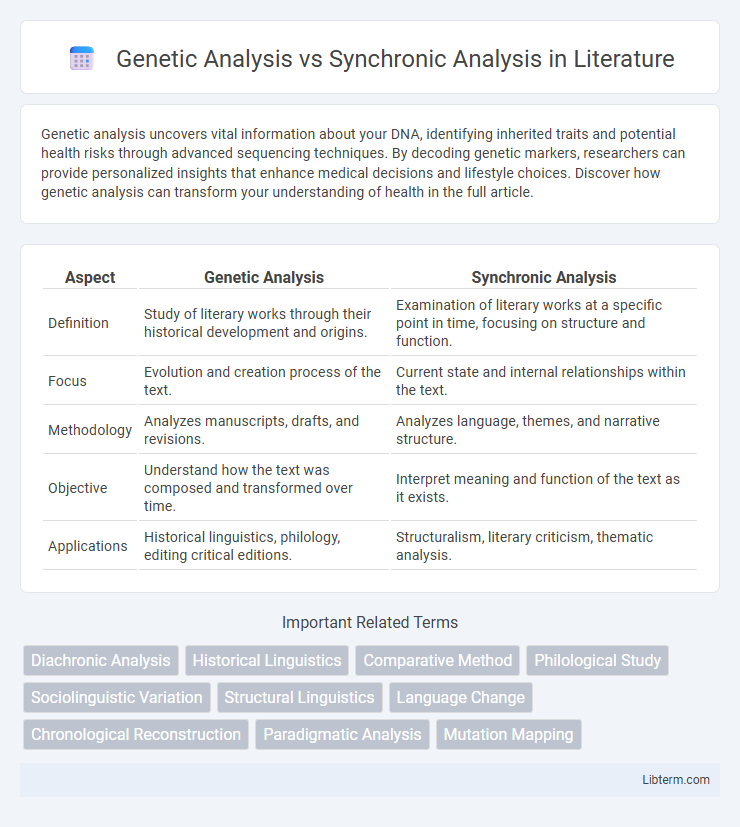
| Aspect | Genetic Analysis | Synchronic Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of literary works through their historical development and origins. | Examination of literary works at a specific point in time, focusing on structure and function. |
| Focus | Evolution and creation process of the text. | Current state and internal relationships within the text. |
| Methodology | Analyzes manuscripts, drafts, and revisions. | Analyzes language, themes, and narrative structure. |
| Objective | Understand how the text was composed and transformed over time. | Interpret meaning and function of the text as it exists. |
| Applications | Historical linguistics, philology, editing critical editions. | Structuralism, literary criticism, thematic analysis. |
Introduction to Genetic and Synchronic Analysis
Genetic analysis examines the historical development and evolution of linguistic elements to understand their origins and transformations over time. Synchronic analysis, in contrast, focuses on the structure and function of language at a specific point without considering historical context. Understanding the differences between genetic and synchronic approaches is essential for comprehensive linguistic research and effective application in philology and language studies.
Defining Genetic Analysis in Linguistics
Genetic analysis in linguistics examines the historical development and evolutionary relationships among languages by tracing their common ancestry and changes over time. This approach focuses on identifying language families and reconstructing proto-languages to understand how contemporary languages diverged from shared origins. Synchronic analysis, in contrast, studies languages at a specific point in time without considering their historical development.
Understanding Synchronic Analysis
Synchronic analysis examines linguistic elements at a specific point in time, emphasizing the structure and use of language without considering historical development. It focuses on the relationships between words, syntax, and semantics within a given language state, providing insights into how language functions in context. Understanding synchronic analysis allows linguists to analyze language patterns, rule systems, and social linguistics phenomena from a contemporary perspective, distinct from genetic analysis, which traces language evolution over time.
Key Differences: Genetic vs Synchronic Approaches
Genetic analysis studies the historical development and evolutionary processes that shape language over time, emphasizing diachronic changes and the origin of linguistic forms. Synchronic analysis examines language structures and usage at a specific point in time, focusing on contemporary linguistic patterns without considering historical evolution. The key difference lies in genetic analysis being diachronic and evolutionary, while synchronic analysis is static and descriptive.
Historical Development of Genetic Analysis
Genetic analysis, originating in the early 20th century, studies the evolution and historical development of languages by tracing their roots and changes over time, revealing patterns of linguistic ancestry and divergence. Pioneers like Ferdinand de Saussure distinguished genetic analysis from synchronic analysis, emphasizing diachronic methods that investigate language transformation through historical stages. Advances in comparative linguistics and the integration of computational models have refined genetic analysis, enabling more precise reconstruction of proto-languages and the mapping of language families.
Applications of Synchronic Analysis in Modern Linguistics
Synchronic analysis in modern linguistics focuses on studying language at a specific point in time, enabling precise examination of phonetics, syntax, and semantics as they exist in current or documented stages. This method is widely applied in language education, computational linguistics, and sociolinguistics to develop language models, natural language processing algorithms, and dialect mapping. Synchronic analysis provides essential data for designing effective communication tools and understanding language use within contemporary social contexts.
Pros and Cons: Genetic Analysis
Genetic analysis excels in tracing the historical development and evolution of languages by uncovering relationships between linguistic forms over time, providing deep insight into language change and origin. However, it can be limited by its reliance on historical data and may struggle to account for contemporary language variation or the influence of external factors. This method is less effective for understanding current linguistic systems or social language use, making it less suitable for synchronic studies.
Pros and Cons: Synchronic Analysis
Synchronic analysis offers a snapshot view of a language at a specific point in time, facilitating the study of contemporary linguistic structures and usage patterns without the complexity of historical changes. This method provides clarity and simplicity, making it ideal for analyzing current language phenomena and communication in real-world contexts. However, it may overlook the evolution and development of language, limiting insights into the origins and transformations of linguistic features over time.
Case Studies Comparing the Two Methods
Case studies comparing genetic analysis and synchronic analysis reveal distinct advantages depending on the research goals. Genetic analysis excels in tracing the historical development and evolution of languages across time, providing insights into language change and origin through diachronic data. Synchronic analysis focuses on the structure and usage of language at a specific point in time, offering detailed examination of linguistic phenomena without historical context.
Conclusion: Integrating Genetic and Synchronic Insights
Integrating genetic analysis and synchronic analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of linguistic evolution and structure by combining historical development with present-day language function. Genetic analysis uncovers diachronic relationships and language change over time, while synchronic analysis examines language at a specific moment, revealing functional and systemic patterns. This integrated approach enables deeper insights into language dynamics, enhancing both theoretical frameworks and practical applications in linguistics.
Genetic Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com