Clarification enhances understanding by resolving ambiguity and ensuring precise communication. This process is essential in both personal interactions and professional settings to prevent misunderstandings. Discover how effective clarification techniques can improve Your communication skills by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
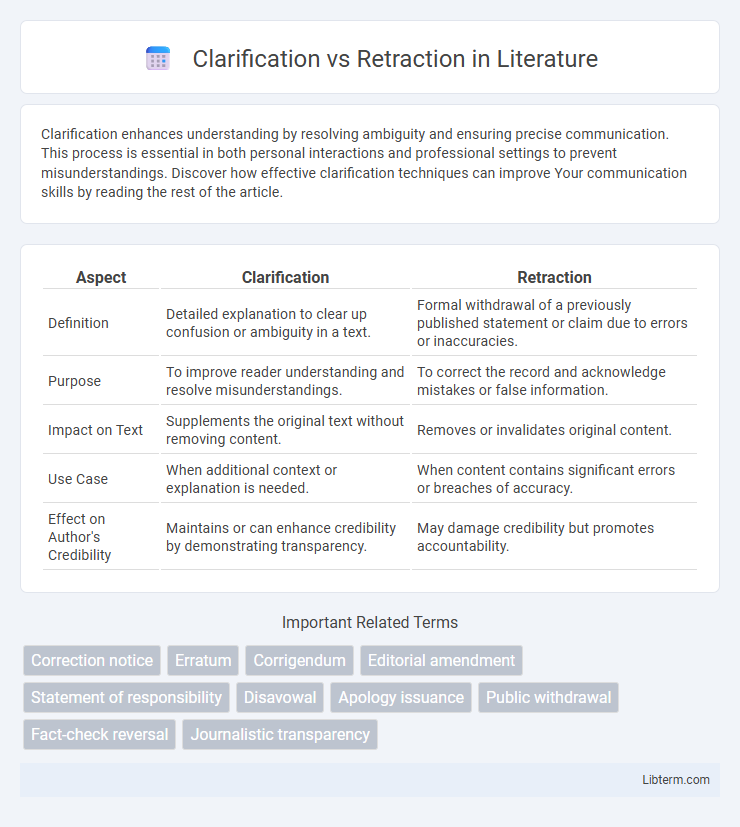
| Aspect | Clarification | Retraction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Detailed explanation to clear up confusion or ambiguity in a text. | Formal withdrawal of a previously published statement or claim due to errors or inaccuracies. |
| Purpose | To improve reader understanding and resolve misunderstandings. | To correct the record and acknowledge mistakes or false information. |
| Impact on Text | Supplements the original text without removing content. | Removes or invalidates original content. |
| Use Case | When additional context or explanation is needed. | When content contains significant errors or breaches of accuracy. |
| Effect on Author's Credibility | Maintains or can enhance credibility by demonstrating transparency. | May damage credibility but promotes accountability. |
Understanding Clarification: Definition and Purpose
Clarification involves providing additional information or explanations to resolve confusion and ensure accurate understanding of a statement or situation. Its primary purpose is to enhance communication by addressing ambiguities without negating the original message. Unlike retraction, which withdraws a previous statement, clarification aims to refine and expand meaning for clearer interpretation.
What is a Retraction? Key Characteristics
A retraction is a formal statement issued to withdraw or correct previously published information that is found to be erroneous, misleading, or invalid. Key characteristics of a retraction include the explicit acknowledgment of mistakes, removal or correction of inaccurate data, and clear communication to the audience to prevent the spread of false information. Retractions are commonly used in academic publishing, journalism, and legal contexts to maintain credibility and uphold ethical standards.
Clarification vs Retraction: Core Differences
Clarification provides additional information or explanation to make an original statement clearer without changing its intent, while retraction involves withdrawing a previously stated claim entirely due to errors or inaccuracies. Clarifications aim to resolve misunderstandings by expanding on the initial message, whereas retractions serve to correct false information and acknowledge mistakes. The key difference lies in preservation of the original position through clarification versus complete denial or correction in retraction.
When to Issue a Clarification
Issue a clarification when initial information contains inaccuracies or ambiguity that could mislead the audience but does not necessitate removing the entire statement. Clarifications help correct specific details while maintaining the overall message's integrity, ensuring transparency and trust with the audience. Use clarifications to address misunderstandings or partial errors promptly before reputational damage escalates.
When is a Retraction Necessary?
A retraction is necessary when a published statement contains significant errors or false information that could mislead readers or harm reputations, requiring the complete withdrawal of the original content. Clarifications are appropriate for minor inaccuracies or ambiguities that do not alter the main message, allowing the original information to remain accessible with additional context. Retractions are crucial in maintaining journalistic integrity and preserving public trust when factual accuracy is fundamentally compromised.
Impact of Clarifications on Public Perception
Clarifications serve to correct misinformation while maintaining the credibility of the original source, often preserving public trust by demonstrating transparency and accountability. Unlike retractions, which withdraw statements entirely and may significantly damage reputation, clarifications provide nuanced updates that help retain audience confidence. Research indicates that timely and clear clarifications reduce the spread of false narratives and mitigate negative public perception more effectively than retractions alone.
Consequences of Retractions for Credibility
Retractions significantly impact an author's credibility by signaling potential flaws in research methodology or ethical issues. Scientific communities often scrutinize retracted work, leading to diminished trust and reduced citation rates for the author. Institutions may impose professional consequences, including damage to reputation and limitations on future funding opportunities.
Best Practices: Deciding Between Clarification and Retraction
Choosing between clarification and retraction hinges on the severity and impact of the misinformation. Best practices recommend issuing a clarification when inaccuracies are minor or context-related, ensuring transparency while maintaining credibility. Retraction is reserved for fundamental errors or ethical concerns that undermine the original message's validity, preserving trust and accountability in communication.
Case Studies: Examples from Media and Academia
Case studies in media reveal that clarifications often address minor errors without altering the core message, such as news outlets correcting misquoted sources to maintain credibility. In academia, retractions are more severe, typically resulting from data fabrication or methodological flaws, exemplified by high-profile cases like the retraction of fraudulent studies in medical journals. These examples highlight the different impacts and corrective measures between clarifications, which preserve trust through transparency, and retractions, which protect scientific integrity by removing invalid findings.
Ethical Considerations in Corrections and Accuracy
Ethical considerations in corrections emphasize maintaining transparency and accountability when issuing clarifications or retractions to uphold public trust and journalistic integrity. Clarifications correct ambiguous or incomplete information without negating original reporting, ensuring accuracy while preserving credibility. Retractions, reserved for significant errors or falsehoods, require prompt and conspicuous disclosure to prevent misinformation and protect ethical standards in communication.
Clarification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com