Automatization streamlines repetitive tasks, significantly boosting efficiency and reducing human error in various industries. Implementing smart automation technologies can transform workflows, save valuable time, and enhance overall productivity. Explore the article to discover how automatization can revolutionize your operations and drive success.
Table of Comparison
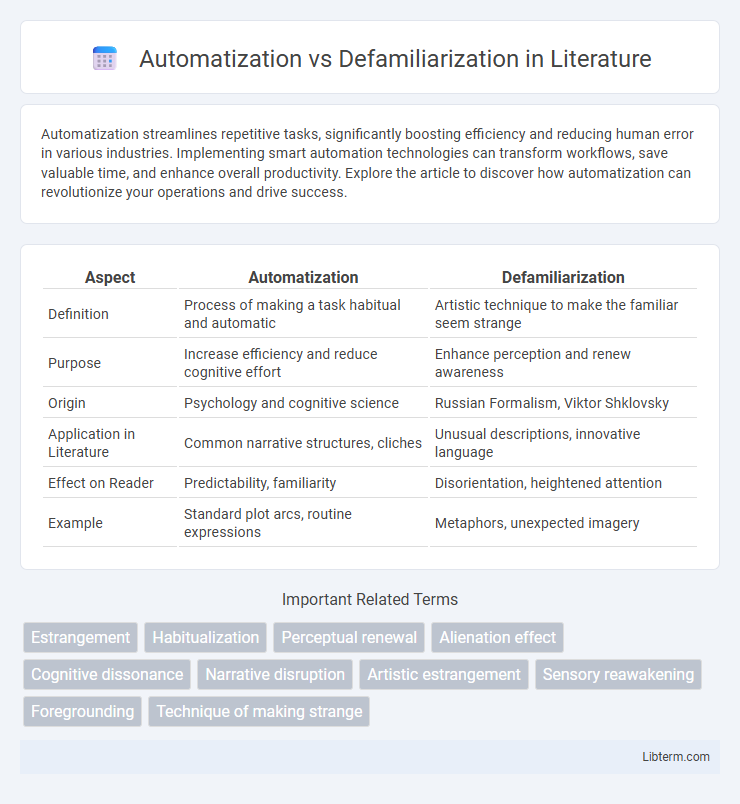
| Aspect | Automatization | Defamiliarization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of making a task habitual and automatic | Artistic technique to make the familiar seem strange |
| Purpose | Increase efficiency and reduce cognitive effort | Enhance perception and renew awareness |
| Origin | Psychology and cognitive science | Russian Formalism, Viktor Shklovsky |
| Application in Literature | Common narrative structures, cliches | Unusual descriptions, innovative language |
| Effect on Reader | Predictability, familiarity | Disorientation, heightened attention |
| Example | Standard plot arcs, routine expressions | Metaphors, unexpected imagery |
Introduction to Automatization and Defamiliarization
Automatization refers to the process by which tasks become automatic and require less conscious effort through repetition and practice, enhancing efficiency and reducing cognitive load. Defamiliarization, a concept originating from Russian Formalism, involves making familiar objects or concepts strange or new to disrupt routine perception and provoke deeper engagement. These contrasting processes highlight the balance between cognitive economy and artistic innovation in learning and perception.
The Origins and Concepts Explained
Automatization refers to the process by which actions become automatic through repeated practice, freeing cognitive resources and increasing efficiency in tasks such as reading or driving. Defamiliarization, a concept rooted in Russian Formalism introduced by Viktor Shklovsky, involves presenting common objects or experiences in an unfamiliar or strange way to disrupt habitual perception and enhance artistic effect. These contrasting concepts highlight how automatization optimizes cognitive processing while defamiliarization challenges perception to foster deeper engagement with text or art.
Automatization: How Routine Shapes Perception
Automatization significantly influences perception by enabling the brain to process routine tasks efficiently, freeing cognitive resources for complex problem-solving. This process leads to the formation of automatic patterns that shape how sensory information is interpreted, often resulting in a streamlined but less conscious engagement with the environment. In contrast to defamiliarization, which disrupts habitual perception to create awareness, automatization solidifies routine experiences, reinforcing familiar cognitive pathways.
Defamiliarization: Making the Ordinary Extraordinary
Defamiliarization transforms mundane experiences by altering perception, enabling individuals to see ordinary objects or situations in a novel and striking way. This literary and artistic technique disrupts automatic recognition, compelling deeper engagement and fresh understanding through unexpected perspectives. By breaking habitual patterns of thought, defamiliarization revitalizes meaning and encourages creative interpretation beyond rote automatization.
Key Differences Between Automatization and Defamiliarization
Automatization refers to the process by which tasks become automatic and require less conscious effort through repetition and practice, enhancing efficiency and speed in cognitive or physical activities. Defamiliarization, a literary and artistic technique, aims to make familiar objects or concepts appear strange or new, forcing the audience to perceive them more critically and thoughtfully. The key difference lies in automatization streamlining perception and action, while defamiliarization disrupts it to provoke deeper awareness and insight.
Psychological Impact on Readers and Viewers
Automatization in literature and media often leads to cognitive ease, promoting faster comprehension but potentially reducing emotional engagement and critical reflection. Defamiliarization disrupts habitual perception, compelling readers and viewers to reconsider familiar concepts, which enhances critical thinking and emotional resonance. The psychological impact hinges on balancing comfort with novelty to sustain attention while provoking deeper insight.
Literary and Artistic Techniques
Automatization in literary and artistic techniques refers to the process of creating works through habitual, repetitive patterns that blur the creator's conscious intervention, often resulting in a sense of predictability and fluidity. Defamiliarization disrupts these patterns by presenting familiar objects, language, or scenarios in unfamiliar ways, compelling audiences to perceive them with renewed attention and critical insight. Techniques such as collage, fragmented narrative, and unconventional syntax are employed to achieve defamiliarization, contrasting with the smooth, mechanical flow characteristic of automatized expression.
Practical Examples in Modern Media
Automatization in modern media is evident in algorithm-driven content recommendations on platforms like Netflix and Spotify, where user behavior triggers predictable, automated suggestions enhancing user engagement efficiently. Defamiliarization emerges in experimental films and interactive art installations that disrupt conventional narratives, such as Charlie Kaufman's "Synecdoche, New York," challenging viewers to reinterpret cinematic language and meaning. These contrasting approaches illustrate how automatization streamlines consumption while defamiliarization provokes critical thinking and deeper audience interaction.
The Importance in Contemporary Storytelling
Automatization in contemporary storytelling streamlines narrative techniques to enhance audience engagement through familiar patterns, ensuring accessibility and efficient communication. Defamiliarization disrupts conventional perspectives, provoking deeper reflection by presenting ordinary elements in novel, unexpected ways. Balancing automatization and defamiliarization is crucial for modern creators to maintain narrative impact while fostering innovation and critical thought.
Conclusion: Balancing Familiarity and Novelty
Effective communication balances automatization, which leverages familiarity for quick comprehension, with defamiliarization techniques that introduce novelty to capture attention and provoke thought. Incorporating defamiliarization strategically disrupts habitual cognition, enhancing engagement without overwhelming the audience. Optimal messaging integrates these forces, ensuring clarity while stimulating curiosity and deeper understanding.
Automatization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com