Narratology explores the structures and functions of narrative, analyzing how stories are constructed and understood across various media. It examines elements such as plot, character, and temporality to reveal the underlying mechanics that shape meaning. Dive deeper into this article to uncover how narratology can enhance Your comprehension of storytelling.
Table of Comparison
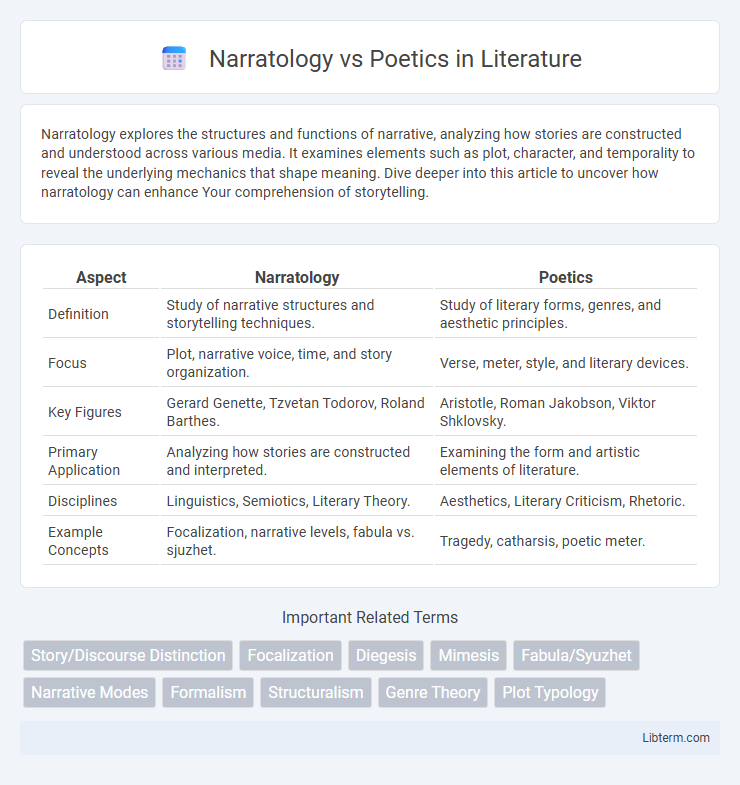
| Aspect | Narratology | Poetics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of narrative structures and storytelling techniques. | Study of literary forms, genres, and aesthetic principles. |
| Focus | Plot, narrative voice, time, and story organization. | Verse, meter, style, and literary devices. |
| Key Figures | Gerard Genette, Tzvetan Todorov, Roland Barthes. | Aristotle, Roman Jakobson, Viktor Shklovsky. |
| Primary Application | Analyzing how stories are constructed and interpreted. | Examining the form and artistic elements of literature. |
| Disciplines | Linguistics, Semiotics, Literary Theory. | Aesthetics, Literary Criticism, Rhetoric. |
| Example Concepts | Focalization, narrative levels, fabula vs. sjuzhet. | Tragedy, catharsis, poetic meter. |
Introduction to Narratology and Poetics
Narratology examines the structures and functions of narrative, analyzing how stories are constructed and understood through elements like plot, character, and temporal order. Poetics explores the principles and techniques of literary composition, focusing on the aesthetic and rhetorical devices that shape meaning and artistic effect in texts. Both fields intersect in their study of narrative but prioritize different aspects: narratology centers on story mechanics, while poetics emphasizes literary form and expression.
Defining Narratology: Core Concepts
Narratology explores the structure, elements, and functions of narrative, focusing on how stories are constructed and understood across various media. Core concepts include narrative time, plot, focalization, and narrative voice, which analyze the relationship between the story (fabula) and its presentation (sjuzhet). Unlike poetics, which examines literary forms and styles, narratology specifically investigates the mechanics of storytelling and the cognitive processes involved in narrative comprehension.
Understanding Poetics: Key Principles
Poetics centers on the study of literary forms, focusing on the rules and conventions that govern the creation and interpretation of texts. Key principles include the analysis of plot structure, character development, and the use of language and imagery to evoke emotion and meaning. Understanding poetics involves exploring how these elements combine to produce aesthetic effects and convey thematic depth in literary works.
Historical Development of Narratology
Narratology emerged as a distinct field in the 1960s through the work of scholars like Gerard Genette and Roland Barthes, emphasizing the structures and functions of narrative. Its historical development traces back to early formalist theories in the 1920s and 1930s, which laid the groundwork for systematic analysis of storytelling elements such as plot, time, and perspective. Unlike poetics, which traditionally focuses on the aesthetic and rhetorical conventions of poetry and literature, narratology seeks to uncover universal narrative principles applicable across genres and media.
Evolution of Poetics in Literary Studies
The evolution of poetics in literary studies has shifted from prescriptive rules of classical rhetoric to dynamic frameworks incorporating cultural and psychological dimensions. Narratology emphasizes the structures and functions of narrative, while poetics increasingly explores the aesthetics and effects of literary form and style. This transformation reflects broader interdisciplinary influences, integrating semiotics, cognitive theory, and digital media analysis to redefine poetic interpretation.
Comparative Analysis: Narratology vs Poetics
Narratology examines the structures and functions of narrative across various media, focusing on the overarching framework of storytelling elements such as plot, time, and perspective. Poetics analyzes the principles and techniques specific to literary forms, emphasizing style, rhetoric, and genre conventions in poetry and prose. Comparative analysis reveals narratology's broader application to narrative theory, while poetics offers a detailed study of artistic expression, highlighting their complementary roles in literary criticism.
Methodologies in Narratology and Poetics
Methodologies in narratology emphasize the structural analysis of narrative elements such as plot, characters, and temporality, often utilizing frameworks like Todorov's narrative equilibrium or Propp's morphology. Poetics centers on the study of literary devices, style, and aesthetic principles, analyzing meter, rhyme, and figurative language to interpret meaning and emotional impact. While narratology dissects the mechanics of storytelling, poetics explores the artistic expression and formal qualities that shape a literary work's effect.
Major Theorists and Influential Works
Narratology, pioneered by Gerard Genette and Mikhail Bakhtin, centers on the structure and function of narrative, with Genette's "Narrative Discourse" and Bakhtin's concepts of dialogism and heteroglossia serving as foundational texts. Poetics, grounded in Aristotle's "Poetics," expanded by Northrop Frye and Roman Jakobson, examines the principles and aesthetics of literary forms, emphasizing genre theory and the poetics of language. These major theorists and their influential works delineate narratology's focus on narrative mechanics from poetics' emphasis on literary form and artistic expression.
Applications in Literary Criticism and Analysis
Narratology focuses on the structure and function of narrative elements such as plot, time, and perspective, enabling literary critics to dissect how stories are constructed and how meaning is generated through narrative techniques. Poetics examines the formal and aesthetic principles of literary texts, emphasizing devices like metaphor, rhythm, and genre conventions to analyze the artistry and thematic depth in literature. Both frameworks complement each other in literary criticism by providing distinct, yet interconnected tools for interpreting texts through narrative mechanics and poetic expression.
Future Directions and Interdisciplinary Perspectives
Emerging trends in narratology emphasize integrating digital humanities, cognitive science, and artificial intelligence to analyze narrative structures through computational methods, enhancing our understanding of story dynamics. Poetics increasingly intersects with media studies and cultural theory, exploring how evolving forms of storytelling in virtual reality and transmedia redefine aesthetic principles. The future of both fields lies in interdisciplinary collaboration that combines linguistic, psychological, and technological approaches to deepen insights into narrative creation and reception.
Narratology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com