A metaphor transforms ordinary language by comparing one thing to another, revealing deeper meaning and evoking vivid imagery in your mind. This powerful literary device enriches communication and enhances both writing and speech by making abstract ideas tangible and relatable. Explore the article to discover how mastering metaphors can elevate your expression and captivate your audience.
Table of Comparison
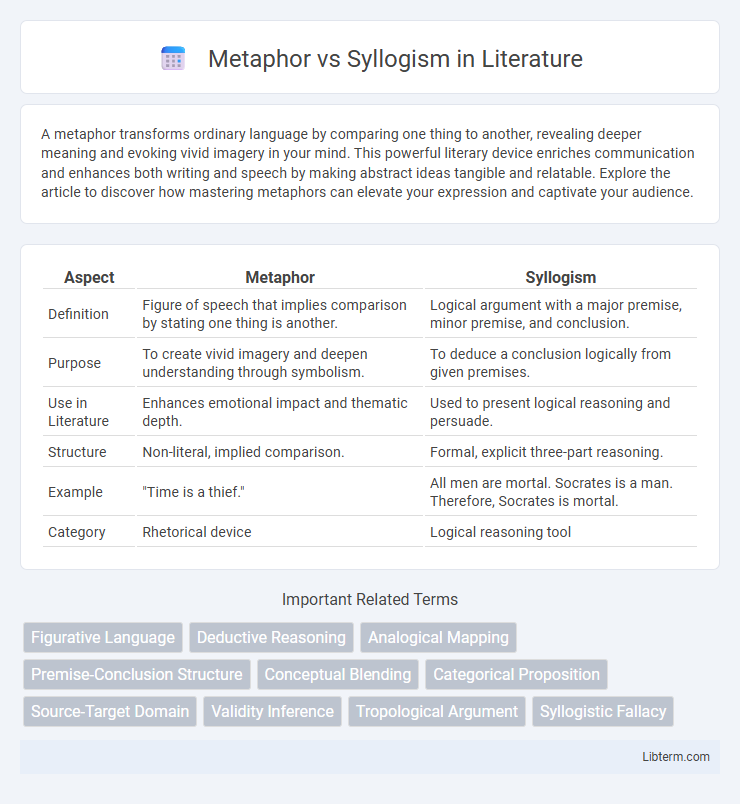
| Aspect | Metaphor | Syllogism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Figure of speech that implies comparison by stating one thing is another. | Logical argument with a major premise, minor premise, and conclusion. |
| Purpose | To create vivid imagery and deepen understanding through symbolism. | To deduce a conclusion logically from given premises. |
| Use in Literature | Enhances emotional impact and thematic depth. | Used to present logical reasoning and persuade. |
| Structure | Non-literal, implied comparison. | Formal, explicit three-part reasoning. |
| Example | "Time is a thief." | All men are mortal. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates is mortal. |
| Category | Rhetorical device | Logical reasoning tool |
Introduction to Metaphor and Syllogism
Metaphor is a figure of speech that conveys meaning by describing one thing as if it were another, creating vivid imagery and emotional resonance. Syllogism is a form of logical reasoning consisting of a major premise, a minor premise, and a conclusion, used to derive conclusions from given statements. Both play crucial roles in language and thought, with metaphor enhancing creativity and expression, while syllogism strengthens argumentation and critical analysis.
Defining Metaphor: Language and Meaning
Metaphor shapes meaning by linking concepts through imaginative language, enabling deeper understanding beyond literal expressions. Unlike syllogism, which relies on logical reasoning and structured premises, metaphor operates through symbolic comparison, enriching communication with nuance and emotional resonance. This linguistic tool transcends direct definitions, creating new insights by framing ideas in relatable, vivid imagery.
What is a Syllogism? Logical Structure Explained
A syllogism is a form of deductive reasoning consisting of two premises and a conclusion, structured to demonstrate a logical relationship between concepts. It typically follows a pattern where a major premise and a minor premise lead to a conclusion, such as "All humans are mortal; Socrates is a human; therefore, Socrates is mortal." Unlike metaphors that rely on figurative language and symbolic meaning, syllogisms provide a clear, formal method to validate arguments through logical inference.
Key Differences Between Metaphor and Syllogism
Metaphors convey abstract or complex ideas by comparing two unrelated concepts, creating vivid imagery that enhances understanding through symbolic representation. Syllogisms utilize formal logical structures, consisting of two premises and a conclusion, to derive valid inferences based on deductive reasoning. Unlike metaphors, which appeal to creativity and emotional resonance, syllogisms prioritize clarity, validity, and analytical precision in argumentation.
Functions of Metaphor in Communication
Metaphors function as powerful tools in communication by creating vivid imagery that facilitates understanding and emotional connection, transcending literal language constraints. They enhance cognitive processing by linking abstract concepts to familiar experiences, enabling deeper insight and memory retention. Unlike syllogisms, which rely on logical deduction for clarity and proof, metaphors enrich discourse through creativity and nuanced expression.
The Role of Syllogism in Argumentation
Syllogism plays a critical role in argumentation by providing a structured, logical framework that connects premises to reach a valid conclusion, ensuring clarity and rigor in reasoning. Unlike metaphors, which use figurative language to illustrate ideas, syllogisms rely on deductive logic with defined premises and conclusion to validate a point. This logical approach enhances persuasive communication by grounding arguments in universal truths and measurable evidence.
Metaphor vs Syllogism: Strengths and Weaknesses
Metaphors excel in evoking vivid imagery and emotional resonance, making complex concepts more accessible and memorable, yet they lack the rigorous logical structure needed for sound argumentation. Syllogisms provide clear, deductive reasoning that ensures validity and logical consistency, but they can be overly rigid and fail to capture nuanced or abstract ideas effectively. Balancing metaphor's creative power with syllogism's precision enhances persuasive communication by integrating emotional appeal and logical clarity.
Real-World Examples: Metaphor and Syllogism in Action
Metaphors appear in advertising, such as Nike's "Just Do It," symbolizing motivation beyond literal meaning, while syllogisms underpin legal reasoning, exemplified by "All humans are mortal; Socrates is a human; therefore, Socrates is mortal." In literature, metaphors enrich narratives by evoking emotions, whereas syllogisms clarify arguments, as seen in academic debates. These applications demonstrate how metaphors connect abstract ideas to experience, and syllogisms provide structured logic for decision-making.
Impact on Critical Thinking and Creativity
Metaphors enhance creativity by encouraging imaginative connections and abstract thinking, allowing individuals to explore complex ideas beyond literal boundaries. Syllogisms strengthen critical thinking through structured logic and deductive reasoning, fostering clear and precise analysis of arguments. Combining metaphorical insight with syllogistic rigor promotes both innovative problem-solving and disciplined evaluation.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Metaphor and Syllogism
Choosing between metaphor and syllogism depends on the communication goal: metaphors evoke imagery and emotional resonance, making complex ideas relatable through analogy, while syllogisms provide clear, logical conclusions based on structured premises. Metaphoric language enhances persuasive storytelling and conceptual understanding by linking abstract concepts to familiar experiences. In contrast, syllogistic reasoning ensures precision and validity in argumentation, ideal for analytical and critical thinking contexts.
Metaphor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com