Hyperbole is a powerful literary device that uses deliberate exaggeration to emphasize a point or evoke strong emotions. It enhances storytelling by creating vivid imagery and making descriptions more memorable. Explore the rest of the article to discover how hyperbole can transform your writing and communication skills.
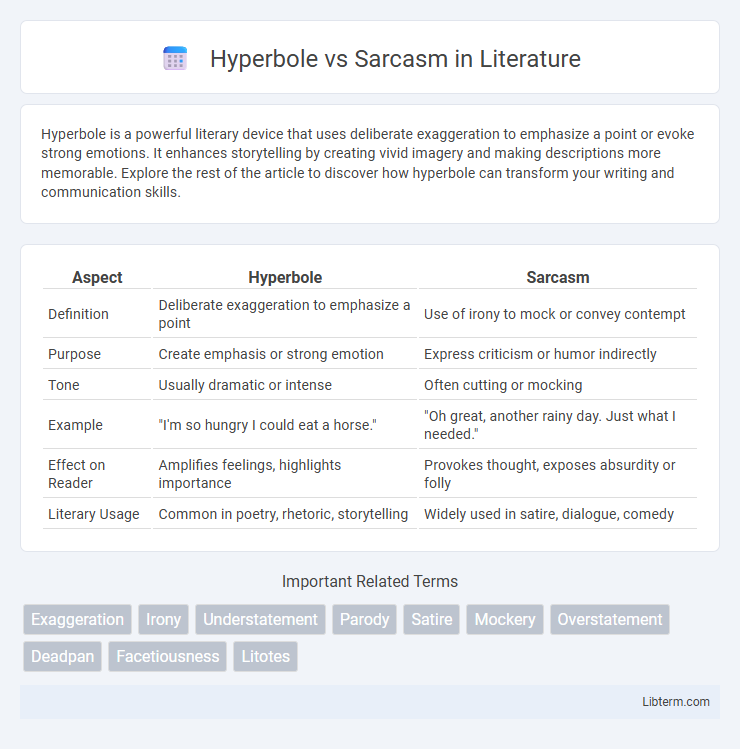
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hyperbole | Sarcasm |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate exaggeration to emphasize a point | Use of irony to mock or convey contempt |
| Purpose | Create emphasis or strong emotion | Express criticism or humor indirectly |
| Tone | Usually dramatic or intense | Often cutting or mocking |
| Example | "I'm so hungry I could eat a horse." | "Oh great, another rainy day. Just what I needed." |
| Effect on Reader | Amplifies feelings, highlights importance | Provokes thought, exposes absurdity or folly |
| Literary Usage | Common in poetry, rhetoric, storytelling | Widely used in satire, dialogue, comedy |
Understanding Hyperbole: Definition and Purpose
Hyperbole is a deliberate exaggeration used to emphasize a point or evoke strong feelings, often found in literature, everyday speech, and advertising. It aims to create a vivid impression or highlight the intensity of an emotion rather than convey literal truth. Understanding hyperbole involves recognizing its role in enhancing expression by stretching reality for dramatic or humorous effect.
What Is Sarcasm? A Clear Explanation
Sarcasm is a form of verbal irony where the speaker says the opposite of what they truly mean, often to mock or convey contempt. It relies on tone of voice and context to signal the intended meaning, making it distinct from hyperbole, which is deliberate exaggeration for emphasis. Understanding sarcasm requires recognizing the speaker's intent behind the contrast between literal words and actual meaning.
Key Differences Between Hyperbole and Sarcasm
Hyperbole is an intentional exaggeration used to emphasize a point, while sarcasm involves using irony to mock or convey contempt. Hyperbole often serves to create strong impressions or evoke emotions, whereas sarcasm relies on tone and context to deliver a biting or humorous critique. Understanding these distinctions helps in interpreting communication styles and recognizing the underlying intent behind statements.
The Role of Context in Hyperbole and Sarcasm
Hyperbole and sarcasm rely heavily on context to convey their intended meanings, as hyperbole exaggerates facts for emphasis while sarcasm uses irony often to mock or criticize. The surrounding verbal tone, situational cues, and shared knowledge between speaker and listener help distinguish whether a statement is a harmless exaggeration or a cutting sarcastic remark. Without context, hyperboles may be misinterpreted as literal, and sarcasm can easily be missed or taken at face value, underscoring the importance of pragmatic awareness in effective communication.
Common Examples of Hyperbole in Everyday Language
Common examples of hyperbole in everyday language include phrases like "I'm so hungry I could eat a horse," used to exaggerate extreme hunger, and "This bag weighs a ton," emphasizing heaviness beyond literal truth. Hyperbole often appears in expressions such as "I'm dying of laughter" to amplify emotional experiences or "I've told you a million times" to stress repetition. These exaggerated statements enhance communication by conveying intensity and strong feelings in a vivid, memorable way.
Recognizing Sarcasm: Verbal and Nonverbal Cues
Recognizing sarcasm involves identifying verbal cues like tone of voice, exaggerated intonation, and contradictory statements where the literal meaning diverges from the speaker's intent. Nonverbal signals such as facial expressions, including smirks or raised eyebrows, and body language like eye-rolling or gestures, often accompany sarcastic remarks and help clarify the speaker's true meaning. Understanding these combined verbal and nonverbal cues is essential for differentiating sarcasm from hyperbole, which primarily relies on deliberate exaggeration without the layered intent of ridicule or irony.
Impact of Hyperbole vs Sarcasm in Communication
Hyperbole intensifies messages by exaggerating for emphasis, creating strong emotional responses that highlight the importance of a point. Sarcasm relies on irony and tone to convey contempt or humor, often leading to mixed interpretations depending on the listener's perception. The impact of hyperbole tends to clarify intent through amplification, while sarcasm can introduce ambiguity, affecting clarity and engagement in communication.
Hyperbole in Literature and Popular Culture
Hyperbole, a deliberate exaggeration used for emphasis or effect, is a cornerstone of literature and popular culture, enhancing emotional impact and humor. In classic literature, authors like Shakespeare and Dickens frequently employ hyperbole to deepen characterizations and dramatize situations, while contemporary media uses it in advertising and social commentary to create memorable and relatable content. This rhetorical device magnifies realities beyond literal meaning, enriching narratives and engaging audiences across genres and mediums.
The Psychological Effects of Sarcasm and Hyperbole
Sarcasm often triggers cognitive processing that can enhance creativity and social bonding but may also evoke feelings of distrust or hurt if perceived as insincerity. Hyperbole, by exaggerating reality, tends to amplify emotional responses and memory retention, making messages more impactful yet sometimes leading to misunderstandings. Both forms influence psychological states by engaging emotional and analytical brain regions differently, shaping communication effectiveness and interpersonal dynamics.
Tips for Using Hyperbole and Sarcasm Effectively
Use hyperbole sparingly to emphasize emotions or highlight key points without confusing your audience, ensuring the exaggeration is clearly intentional. Employ sarcasm carefully by tailoring your tone and context to the listeners' familiarity and cultural background, as it can easily be misunderstood or perceived as offensive. Combining clear vocal cues or written indicators helps distinguish sarcasm from genuine statements, enhancing communication effectiveness.
Hyperbole Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com