Poetics explores the art and theory of poetry, analyzing elements such as rhythm, meter, imagery, and symbolism that create profound emotional and intellectual effects. Understanding poetics enhances your ability to appreciate, interpret, and craft poetic works with greater skill and insight. Dive into the rest of this article to unravel the fascinating components that make poetry a timeless form of expression.
Table of Comparison
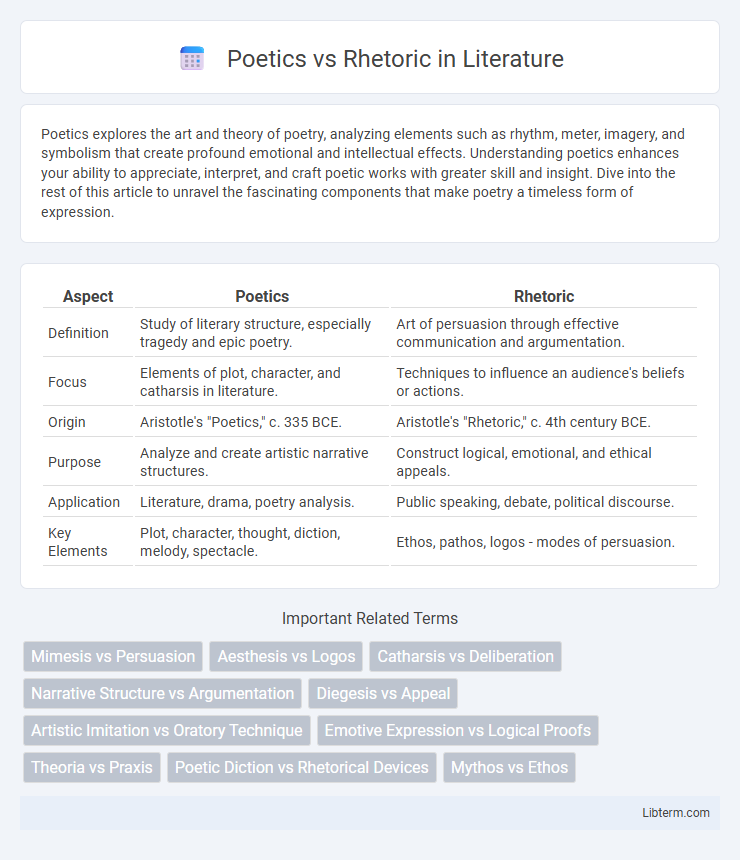
| Aspect | Poetics | Rhetoric |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of literary structure, especially tragedy and epic poetry. | Art of persuasion through effective communication and argumentation. |
| Focus | Elements of plot, character, and catharsis in literature. | Techniques to influence an audience's beliefs or actions. |
| Origin | Aristotle's "Poetics," c. 335 BCE. | Aristotle's "Rhetoric," c. 4th century BCE. |
| Purpose | Analyze and create artistic narrative structures. | Construct logical, emotional, and ethical appeals. |
| Application | Literature, drama, poetry analysis. | Public speaking, debate, political discourse. |
| Key Elements | Plot, character, thought, diction, melody, spectacle. | Ethos, pathos, logos - modes of persuasion. |
Defining Poetics and Rhetoric
Poetics focuses on the study and principles of literary art, emphasizing creativity, narrative structure, and aesthetic expression in poetry and drama. Rhetoric centers on the art of persuasion, using language strategically to influence, convince, and engage an audience through ethos, pathos, and logos. Both disciplines analyze language but differ as poetics prioritizes artistic form while rhetoric targets effective communication and argumentation.
Historical Origins and Key Thinkers
Poetics originated in ancient Greece with Aristotle's seminal work, emphasizing the principles of literary art, especially tragedy and epic poetry. Rhetoric, founded by figures like Aristotle and further developed by Cicero and Quintilian, focused on persuasive communication and effective speech. These disciplines laid foundational theories in literature and public speaking, influencing Western intellectual tradition.
Core Objectives: Expression vs. Persuasion
Poetics centers on the art of expression, aiming to evoke emotions and create aesthetic experiences through structured language and imagery. Rhetoric prioritizes persuasion, employing strategies and appeals to convince or influence an audience's beliefs and actions. While poetics emphasizes creative communication and emotional resonance, rhetoric focuses on argumentative techniques and effective delivery to achieve specific outcomes.
Structural Principles in Poetics vs. Rhetoric
Structural principles in Poetics emphasize the organization of narrative elements such as plot, character, and theme to evoke emotional responses and convey universal truths. In contrast, Rhetoric prioritizes the arrangement of persuasive elements including ethos, pathos, and logos to influence audiences and achieve specific communicative goals. While Poetics seeks an aesthetic coherence rooted in artistic expression, Rhetoric centers on strategic structure to maximize argument effectiveness and audience engagement.
Language Techniques and Stylistic Devices
Poetics employs metaphors, similes, and imagery to evoke emotions and create vivid mental pictures, focusing on aesthetic and imaginative language techniques. Rhetoric utilizes repetition, parallelism, and rhetorical questions to persuade and influence audiences, relying on strategic stylistic devices for argument construction. Both disciplines use figures of speech but diverge in their purposes: poetics emphasizes artistic expression while rhetoric prioritizes effective communication and persuasion.
Audience Engagement: Aesthetic vs. Practical
Poetics engages the audience through aesthetic appeal by employing metaphor, rhythm, and vivid imagery to evoke emotional and imaginative responses. Rhetoric focuses on practical engagement by using logical arguments, ethos, and pathos to persuade and influence the audience's decisions or beliefs. The distinct methods highlight poetics' emphasis on artistic experience versus rhetoric's goal of effective communication and persuasion.
Poetics in Literary Genres
Poetics explores the principles and structures of literary genres such as tragedy, epic, and lyric poetry, emphasizing the elements that evoke emotions and convey universal truths. Aristotle's Poetics serves as a foundational text, analyzing plot, character, and catharsis to define effective storytelling within dramatic and narrative forms. Literary genres are shaped by poetics to create meaning and aesthetic experience through language, rhythm, and thematic coherence.
Rhetoric in Public Discourse
Rhetoric in public discourse serves as a powerful tool for persuasion, leveraging ethos, pathos, and logos to influence audience beliefs and actions. It shapes political debates, legal arguments, and media communication by crafting messages that resonate with diverse publics through strategic language and emotional appeal. Mastery of rhetorical techniques enhances the effectiveness of public speaking, policy advocacy, and social movements, making rhetoric essential in shaping public opinion and decision-making.
Overlapping Boundaries and Intersections
Poetics and rhetoric share overlapping boundaries in the use of language to persuade and evoke emotional responses, blending artistic expression with strategic communication. Both disciplines employ devices like metaphor, imagery, and rhythm to influence audiences, demonstrating intersections in their goals of shaping perception and meaning. The study of poetics informs rhetorical techniques by highlighting narrative structures and aesthetic elements that enhance persuasive impact.
Contemporary Relevance and Applications
Poetics and rhetoric remain vital in contemporary communication, with poetics shaping creative and literary expression through metaphor, narrative structure, and emotional resonance, while rhetoric influences persuasive discourse in politics, marketing, and media. Poetics enhances the aesthetic experience and deepens audience engagement by evoking imagery and symbolic meaning. Rhetoric applies principles of argumentation, ethos, pathos, and logos to effectively shape public opinion, brand messaging, and social campaigns.
Poetics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com