Structuralism analyzes underlying structures that shape cultural phenomena, language, and society, emphasizing relationships between elements rather than individual components. This approach reveals deep patterns in myths, literature, and social practices, offering insights into how meaning is constructed. Explore the rest of the article to understand how structuralism can transform your perspective on human behavior and communication.
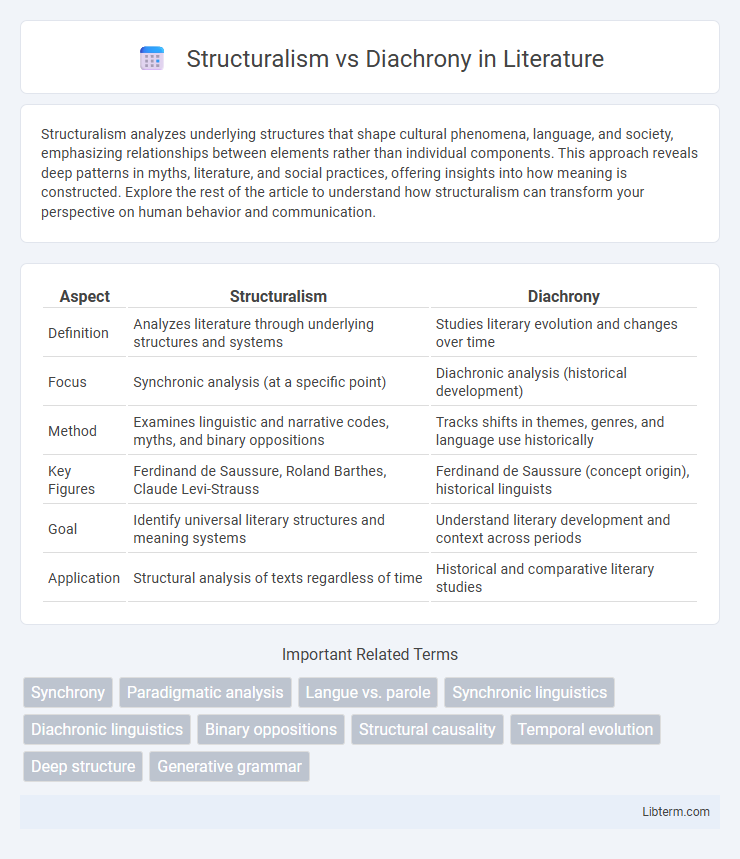
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Structuralism | Diachrony |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes literature through underlying structures and systems | Studies literary evolution and changes over time |
| Focus | Synchronic analysis (at a specific point) | Diachronic analysis (historical development) |
| Method | Examines linguistic and narrative codes, myths, and binary oppositions | Tracks shifts in themes, genres, and language use historically |
| Key Figures | Ferdinand de Saussure, Roland Barthes, Claude Levi-Strauss | Ferdinand de Saussure (concept origin), historical linguists |
| Goal | Identify universal literary structures and meaning systems | Understand literary development and context across periods |
| Application | Structural analysis of texts regardless of time | Historical and comparative literary studies |
Introduction to Structuralism and Diachrony
Structuralism analyzes language as a systematic network of interrelated elements, emphasizing synchronic study of linguistic structures at a specific point in time. Diachrony examines the historical development and evolution of language, tracing changes and transformations across different periods. Structuralism prioritizes the interdependence of units within a language system, while diachronic linguistics focuses on temporal shifts and historical progression.
Defining Structuralism: Concepts and Principles
Structuralism centers on analyzing systems by identifying relationships between elements within a structure, emphasizing synchronic study over time-based changes. Key principles include the idea that meaning arises from differences within a system rather than isolated entities, and that underlying structures govern observable phenomena. This approach contrasts with diachrony by focusing on the stability and organization of elements at a given moment rather than their historical evolution.
Understanding Diachrony: Historical Perspectives
Diachrony examines language development over time by analyzing historical changes in phonetics, syntax, and semantics, offering insights into linguistic evolution and cultural shifts. Structuralism, by contrast, focuses on understanding language as a system of interrelated elements within a specific time frame, emphasizing synchronic analysis. Understanding diachrony involves tracing language genealogy, etymology, and phonological transformations to reveal patterns that structuralism's synchronic approach often overlooks.
Key Figures: Saussure and Beyond
Ferdinand de Saussure pioneered structuralism by emphasizing the synchronic study of language as a system of interrelated signs, contrasting with diachronic analysis that investigates language change over time. Key figures expanding on his ideas include Claude Levi-Strauss, who applied structuralist principles to anthropology, and Roman Jakobson, who contributed to structural linguistics and phonology. These thinkers collectively shaped structuralism's focus on underlying systems and relationships rather than historical development.
Structuralism and Language Systems
Structuralism in linguistics analyzes language as a system of interrelated elements, emphasizing the synchronic study of linguistic structures at a specific point in time. It focuses on understanding language through underlying patterns and rules, such as phonemes, morphemes, and syntax, rather than historical changes. This approach contrasts with diachronic linguistics, which studies the evolution and historical development of language over time.
Diachronic Analysis in Linguistics
Diachronic analysis in linguistics examines the historical development and evolution of languages over time, revealing patterns of phonetic, morphological, and syntactic changes. It contrasts with structuralism by focusing on language change and historical context rather than the static system of language at a specific point. Essential for historical linguistics, diachronic studies enable reconstruction of proto-languages and understanding of language families through comparative methods.
Major Differences: Structuralism vs Diachrony
Structuralism emphasizes analyzing language or cultural phenomena as interconnected systems at a specific point in time, focusing on relationships between elements within that system. Diachrony studies the evolution and historical development of these systems across different time periods to understand changes and continuity. The major difference lies in Structuralism's synchronic approach versus Diachrony's diachronic perspective on language and culture.
Theoretical Implications in Modern Linguistics
Structuralism emphasizes the synchronic analysis of language as a system of interrelated elements, focusing on understanding linguistic structures at a specific point in time. Diachrony investigates language evolution and historical change, highlighting the dynamic and temporal aspects influencing linguistic development. Theoretical implications in modern linguistics involve integrating both perspectives to account for static structural relationships and dynamic historical processes, enriching the understanding of language complexity and change.
Applications in Literary and Cultural Studies
Structuralism analyzes literary texts by uncovering underlying systems of signs and relationships that shape meaning, emphasizing synchronic study of cultural phenomena at a specific point in time. Diachronic approaches trace the historical development and evolution of literary genres, themes, and cultural practices, revealing shifts in meaning across temporal contexts. Combining both methods enriches literary and cultural studies by integrating static structural patterns with dynamic historical transformations.
Conclusion: Relevance in Contemporary Research
Structuralism offers a framework for analyzing linguistic and cultural systems by emphasizing synchronic relationships and underlying structures, while diachrony focuses on historical development and language change over time. Contemporary research benefits from integrating both approaches, as structuralism provides clarity in understanding system-wide patterns, and diachronic analysis reveals evolutionary processes that shape these structures. Combining synchronic and diachronic perspectives enhances the depth and accuracy of linguistic, anthropological, and cultural studies in modern scholarship.
Structuralism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com