Asyndeton is a rhetorical device that omits conjunctions between words, phrases, or clauses to create a concise and impactful effect. This technique accelerates the rhythm of the text, making each element stand out with greater emphasis and urgency. Explore the rest of the article to learn how you can effectively use asyndeton to enhance your writing style.
Table of Comparison
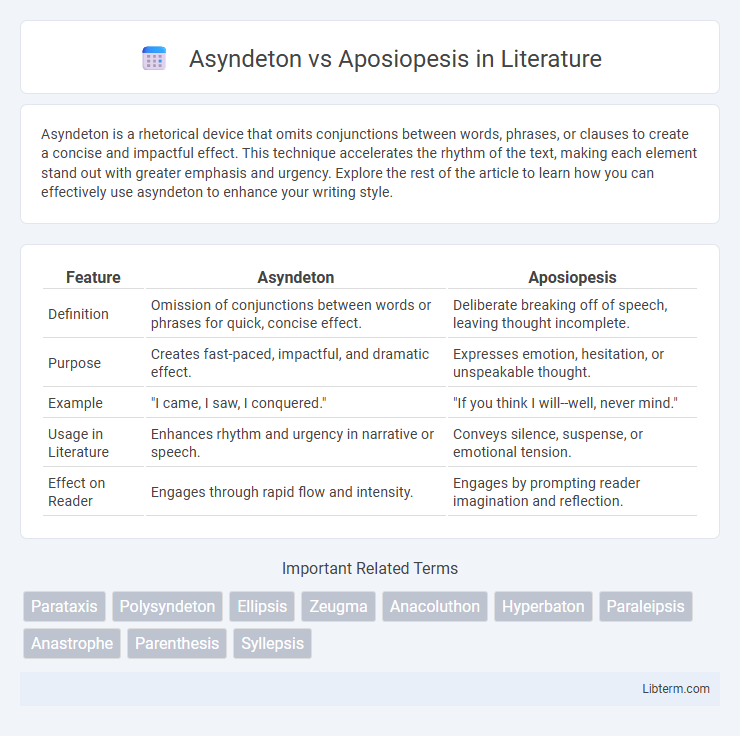
| Feature | Asyndeton | Aposiopesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Omission of conjunctions between words or phrases for quick, concise effect. | Deliberate breaking off of speech, leaving thought incomplete. |
| Purpose | Creates fast-paced, impactful, and dramatic effect. | Expresses emotion, hesitation, or unspeakable thought. |
| Example | "I came, I saw, I conquered." | "If you think I will--well, never mind." |
| Usage in Literature | Enhances rhythm and urgency in narrative or speech. | Conveys silence, suspense, or emotional tension. |
| Effect on Reader | Engages through rapid flow and intensity. | Engages by prompting reader imagination and reflection. |
Understanding Asyndeton: Definition and Usage
Asyndeton is a rhetorical device characterized by the deliberate omission of conjunctions between a series of words, phrases, or clauses to create a concise, impactful effect. It enhances the rhythm and pace of speech or writing, often generating a sense of urgency or intensity, commonly found in persuasive texts and speeches. This technique differs from aposiopesis, which involves the sudden breaking off of a sentence to imply emotion or unfinished thought.
What is Aposiopesis? Key Characteristics
Aposiopesis is a rhetorical device where a sentence is deliberately broken off and left unfinished, creating a pause that suggests strong emotion or hesitation. Key characteristics include an abrupt silence, implied continuation that readers must infer, and its use to convey anger, fear, or awe. Unlike asyndeton, which omits conjunctions for speed and emphasis, aposiopesis relies on intentional omission to generate suspense or emotional impact.
Grammatical Functions of Asyndeton
Asyndeton functions grammatically by omitting conjunctions between words, phrases, or clauses to create a concise and impactful rhythm. It enhances coordination in sentences, allowing multiple elements to be presented in a rapid sequence without conjunctions, thereby emphasizing each item equally. This syntactic structure facilitates a sense of urgency, intensity, or simplicity in expression.
The Rhetorical Power of Aposiopesis
Aposiopesis, a rhetorical device characterized by deliberate sentence breaks, enhances emotional intensity and invites audience imagination through unfinished thoughts. Unlike asyndeton, which uses omission of conjunctions to create rhythm and urgency, aposiopesis conveys hesitation or overwhelming emotion, highlighting the speaker's psychological state. This intentional silence provokes engagement and emphasizes unspeakable feelings, amplifying persuasive and dramatic effect in discourse.
Asyndeton vs Aposiopesis: Core Differences
Asyndeton involves the deliberate omission of conjunctions between words, phrases, or clauses to create a concise, impactful rhythm, while aposiopesis occurs when a sentence is deliberately broken off and left incomplete, signaling an emotional or rhetorical interruption. Asyndeton emphasizes speed and urgency by linking elements without conjunctions, whereas aposiopesis conveys hesitation, suspense, or unspoken thoughts by trailing off mid-sentence. The core difference lies in asyndeton's structural omission to enhance flow versus aposiopesis's intentional silence to evoke emotional or dramatic effect.
Effects on Tone and Style
Asyndeton creates a rapid, concise tone by omitting conjunctions, which intensifies the rhythm and urgency of the text, often evoking a sense of excitement or intensity. Aposiopesis interrupts a sentence intentionally, conveying hesitation, emotion, or unfinished thought, producing a dramatic, suspenseful, or emotional style. Both rhetorical devices influence the reader's engagement by shaping tone--asyndeton with briskness and immediacy, aposiopesis with a pause that invites interpretation or emphasis.
Famous Literary Examples of Asyndeton
Famous literary examples of asyndeton include Julius Caesar's "I came, I saw, I conquered," which emphasizes rapid action through the deliberate omission of conjunctions, creating a powerful and concise rhythm. Ernest Hemingway's writing often employs asyndeton to produce a terse, impactful style, evident in phrases like "He was a man of action, determination, courage," that heighten emotional intensity. Shakespeare's plays also utilize asyndeton for dramatic effect, such as in Macbeth's line "I'll go no more: I am afraid to think what I have done; Look on't again I dare not," where the omission generates a sense of urgency and momentum.
Memorable Uses of Aposiopesis in Literature
Aposiopesis creates a striking effect by deliberately breaking off a sentence, leaving the thought unfinished and evoking strong emotions or tension, as exemplified by Shakespeare's use in "King Lear" where Lear's abrupt halt ("How sharper than a serpent's tooth it is to have a thankless child!") highlights intense grief. Unlike asyndeton, which omits conjunctions to speed up the rhythm and create a concise impact, aposiopesis relies on the power of silence and the reader's imagination to complete the meaning. Classic literature often uses aposiopesis to convey characters' ineffable feelings or hesitation, making these moments profoundly memorable and emotionally charged.
Asyndeton and Aposiopesis in Modern Writing
Asyndeton in modern writing often enhances rhythm and pace by deliberately omitting conjunctions, creating a sense of urgency or emphasis, as seen in genres like advertising and political speeches. Aposiopesis, characterized by abrupt halting of a sentence, evokes dramatic tension or emotional intensity, frequently utilized in contemporary fiction and dialogue to mimic natural speech or internal conflict. Both techniques serve distinct functions in crafting impactful prose, with asyndeton driving momentum and aposiopesis inviting reader interpretation.
Tips for Using Asyndeton or Aposiopesis Effectively
Utilize asyndeton to create a rhythmic, fast-paced flow by omitting conjunctions between short phrases or words, enhancing urgency or intensity. Employ aposiopesis to convey emotions or suspense by deliberately breaking off a sentence, prompting readers to infer the unstated conclusion and heightening dramatic effect. Balance these devices carefully to avoid confusion, ensuring asyndeton accelerates the narrative while aposiopesis effectively captures hesitation or strong feelings.
Asyndeton Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com