Melos, a picturesque island in the Cyclades, captivates visitors with its stunning turquoise waters and unique volcanic landscapes. Known for its rich history rooted in ancient Greek culture and the famous Melian Dialogue, the island blends archaeological intrigue with natural beauty. Explore the rest of the article to uncover why Melos should be your next unforgettable destination.
Table of Comparison
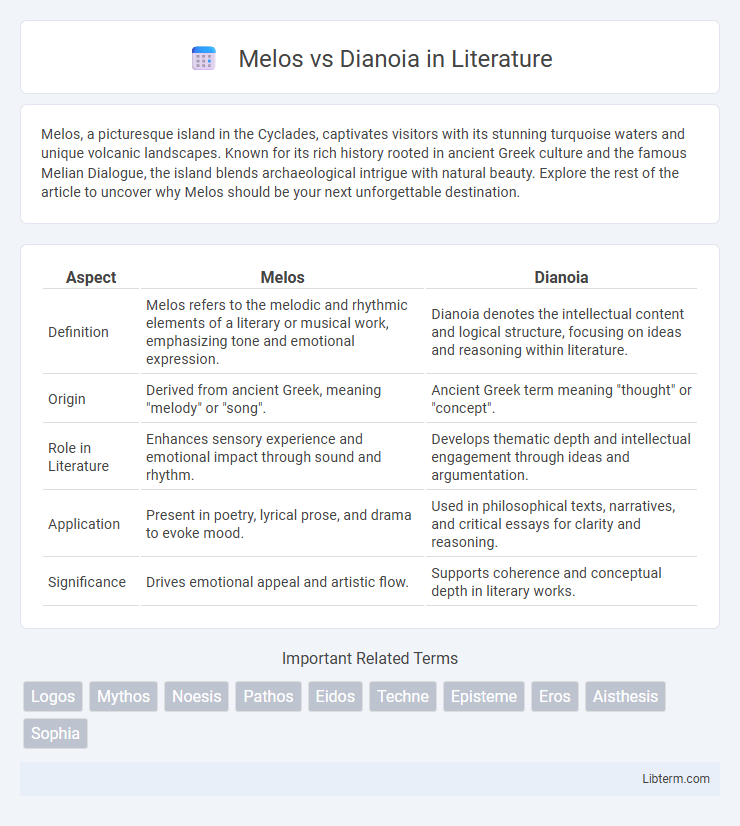
| Aspect | Melos | Dianoia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Melos refers to the melodic and rhythmic elements of a literary or musical work, emphasizing tone and emotional expression. | Dianoia denotes the intellectual content and logical structure, focusing on ideas and reasoning within literature. |
| Origin | Derived from ancient Greek, meaning "melody" or "song". | Ancient Greek term meaning "thought" or "concept". |
| Role in Literature | Enhances sensory experience and emotional impact through sound and rhythm. | Develops thematic depth and intellectual engagement through ideas and argumentation. |
| Application | Present in poetry, lyrical prose, and drama to evoke mood. | Used in philosophical texts, narratives, and critical essays for clarity and reasoning. |
| Significance | Drives emotional appeal and artistic flow. | Supports coherence and conceptual depth in literary works. |
Introduction to Melos and Dianoia
Melos and Dianoia represent distinct levels of cognition in classical philosophy, with Melos referring to immediate sensory perception and emotional experience, while Dianoia encompasses rational thought and conceptual analysis. Melos is associated with the intuitive grasp of phenomena, often linked to aesthetic or artistic insight, whereas Dianoia involves logical reasoning and systematic understanding. These cognitive modes highlight the interplay between feeling and intellect in human knowledge acquisition.
Defining Melos: Meaning and Origins
Melos originates from the ancient Greek word melos, referring to a melody or musical phrase that embodies emotional expression and rhythm. It signifies the structural and thematic element in music that carries the essence of a song's identity and mood. Understanding Melos involves recognizing its role in shaping the narrative and affective dimensions within musical compositions, distinguishing it from the more abstract, intellectual concept of Dianoia.
Understanding Dianoia: Concept and Significance
Dianoia refers to the process of discursive thinking or intellectual understanding, emphasizing logical reasoning and conceptual analysis in the acquisition of knowledge. It plays a crucial role in Platonic philosophy, contrasting with Melos, which represents intuitive or emotional insight. Understanding dianoia is essential for grasping structured, rational cognition that underpins scientific and philosophical inquiry.
Historical Context: Melos and Dianoia in Philosophy
Melos and Dianoia represent contrasting concepts in ancient Greek philosophy, where Melos signifies intuitive understanding and emotional insight, while Dianoia refers to rational thought and intellectual reasoning. Historically, philosophers like Plato distinguished Dianoia as a stage of cognitive development involving analytical processes, whereas Melos aligns with more immediate, sensory, or artistic forms of knowledge. This dichotomy influenced the evolution of epistemology, highlighting the balance between emotional experience and logical inference in human cognition.
Melos in Literature and Art
Melos, the concept of intuitive understanding and creative insight, features prominently in literature and art as a source of inspiration and originality. Artists and writers often portray Melos as the spark that transcends rational thought, fueling imaginative expression and emotional depth in their works. This juxtaposition against Dianoia, or logical reasoning, highlights Melos's essential role in fostering innovation and aesthetic experience.
Dianoia in Classical Thought
Dianoia, in classical thought, represents the rational, discursive thinking process that involves logical reasoning and intellectual understanding, contrasting with Melos, which symbolizes emotional or sensory experience. Rooted in Platonic philosophy, dianoia is the intermediary stage between sensory perception and higher abstract knowledge (noesis), emphasizing systematic analysis and the use of dialectic methods. This concept underscores the importance of structured thought in the pursuit of truth and the development of philosophical knowledge in ancient Greek epistemology.
Key Differences Between Melos and Dianoia
Melos primarily refers to musical melody in ancient Greek philosophy, emphasizing emotional expression through sound patterns, whereas dianoia pertains to intellectual thought or reasoning processes. Melos engages auditory perception and aesthetic experience, while dianoia involves cognitive functions such as analysis, reflection, and understanding concepts. The key difference lies in melos's connection to sensory, affective engagement and dianoia's role in abstract, rational contemplation.
Interplay and Relationship of Melos and Dianoia
Melos and Dianoia represent two fundamental elements in music and cognition, where Melos encapsulates the expressive, melodic aspect, and Dianoia embodies intellectual understanding and analytical thought. Their interplay forms a dynamic relationship crucial for artistic creation, allowing emotional resonance through Melos to be structured and refined by Dianoia's cognitive framework. This symbiotic connection enhances both the emotive power and conceptual depth of musical compositions, bridging affective experience with intellectual clarity.
Contemporary Relevance of Melos and Dianoia
Melos and Dianoia remain central to contemporary philosophy, with Melos representing emotive, artistic understanding and Dianoia embodying rational, analytical thinking. Modern discourse leverages Melos to explore human experience and creativity, while Dianoia underpins scientific inquiry and logical reasoning. The interplay between Melos and Dianoia informs interdisciplinary approaches, enhancing problem-solving in ethics, cognitive science, and education.
Conclusion: Insights from Melos vs Dianoia
Insights from Melos vs Dianoia reveal contrasting approaches to cognition and perception, with Melos emphasizing intuitive, sensory-based understanding, while Dianoia prioritizes logical and analytical reasoning. This distinction highlights the complementary roles of emotional intuition and intellectual analysis in human decision-making processes. Understanding these differences enhances the integration of emotional intelligence and rational thought in complex problem-solving scenarios.
Melos Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com